Difference between revisions of "Asbestos"
m (Text replace - "== Authority ==" to "== Sources Checked for Data in Record ==") |
|||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
[[File:Asbestosemr3.jpg|thumb|Asbestos]] | [[File:Asbestosemr3.jpg|thumb|Asbestos]] | ||
| − | + | [[File:pa30221asbestos.jpg|thumb|Asbestos]] | |
== Synonyms and Related Terms == | == Synonyms and Related Terms == | ||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
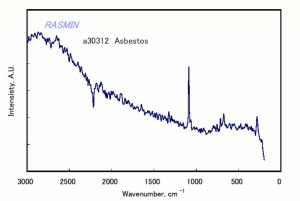
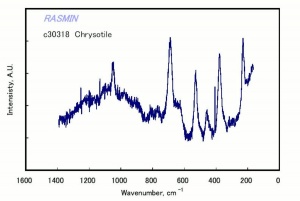
[[[SliderGallery rightalign|asbestosRSFTR.jpg~Raman|chrysotileRS.jpg~Raman]]] | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|asbestosRSFTR.jpg~Raman|chrysotileRS.jpg~Raman]]] | ||
| + | == Risks == | ||
| − | == | + | Noncombustible. Carcinogenic. Highly toxic by inhalation of dust. Skin contact causes irritation. TLV (chrysotile ) = 2.0 fibers/cc TLV (amosite) = 0.5 fibers/cc TLV (crocidolite) = 0.2 fibers/cc |
| + | |||
| + | LINK (white asbestos): [http://www.cdc.gov/niosh/ipcsneng/neng0014.html International Chemical Safety Card] | ||
| + | == Physical and Chemical Properties == | ||
Unaffected by acids alkalis or organic solvents (except hydrofluoric acid). Fiber length = 12-300 mm (0.5 - 12 inches) Diameter = 300-350 angstroms. Cross section is polygonal or circular | Unaffected by acids alkalis or organic solvents (except hydrofluoric acid). Fiber length = 12-300 mm (0.5 - 12 inches) Diameter = 300-350 angstroms. Cross section is polygonal or circular | ||
| Line 24: | Line 28: | ||
| 2.5 | | 2.5 | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
== Additional Images == | == Additional Images == | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
| − | + | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
Revision as of 12:14, 15 October 2020
Description
A common name given to any of several fibrous magnesium silicate minerals. The most widely used asbestos mineral is a type of serpentine called Chrysotile (white asbestos). Other asbestos minerals are: riebeckite, Crocidolite (blue asbestos), amianthus, anthophyllite, amphibole, Amosite (brown asbestos), tremolite, or actinolite. Asbestos is noncombustible and heat resistant. It was used by the ancient Greeks, Egyptians, and Chinese as a fireproof material. In the 19th and early 20th centuries, asbestos was used for fireproofing and insulating new houses. Small asbestos fibers were mixed with binders and compressed into boards, paper, pipe covering, ironing board covers, shingles, tiles, and sprayed onto ceilings. Long asbestos fibers were woven into fabrics for used in brake linings, heat-resistant shields, gloves, and fireproof garments and blankets. Health concerns have limited the use of asbestos since the early 1960s. In the U.S., it was declared a hazardous material in 1986.
Synonyms and Related Terms
amphibole; asbestus; serpentine; earth flax; chrysotile; cork fossil; mountain leather; mountain cork; mountain flax; mineral fiber; amosite; crocidolite; silicate fiber; amianthus; riebeckite; anthophyllite; tremolite; actinolite; salamander wool; asbest (Dan., Ned., Sven.); Asbest (Deut.); asbesto (Esp.); amiante (Fr.); asbestos (Port.)
Risks
Noncombustible. Carcinogenic. Highly toxic by inhalation of dust. Skin contact causes irritation. TLV (chrysotile ) = 2.0 fibers/cc TLV (amosite) = 0.5 fibers/cc TLV (crocidolite) = 0.2 fibers/cc
LINK (white asbestos): International Chemical Safety Card
Physical and Chemical Properties
Unaffected by acids alkalis or organic solvents (except hydrofluoric acid). Fiber length = 12-300 mm (0.5 - 12 inches) Diameter = 300-350 angstroms. Cross section is polygonal or circular
| CAS | 12001-29-5 |
|---|---|
| Density | 2.5 |
Additional Images
Sources Checked for Data in Record
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 70
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- ASTM, "Standard Terminology Relating to Paint, Varnish, Lacquer and Related Products", Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Section 6, Paints, Related Coatings and Aromatics, ASTM, D16, 7-Jan, Jul-96
- Hoechst Celanese Corporation, Dictionary of Fiber & Textile Technology (older version called Man-made Fiber and Textile Dictionary, 1965), Hoechst Celanese Corporation, Charlotte NC, 1990
- Rosalie Rosso King, Textile Identification, Conservation, and Preservation, Noyes Publications, Park Ridge, NJ, 1985
- Michael McCann, Artist Beware, Watson-Guptill Publications, New York City, 1979
- Dictionary of Building Preservation, Ward Bucher, ed., John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York City, 1996
- The Dictionary of Paper, American Paper Institute, New York, Fourth Edition, 1980
- Thomas C. Jester (ed.), Twentieth-Century Building Materials, McGraw-Hill Companies, Washington DC, 1995
- J.Gordon Cook, Handbook of Textile Fibres:I Natural Fibres, Merrow Publishing Co. , Durham, England, 1984
- Identification of Textile Materials, The Textile Institute, Manchester, England, 1985
- Encyclopedia Britannica, http://www.britannica.com Comment: "asbestos." Encyclopædia Britannica. 2005. Encyclopædia Britannica Premium Service 7 Apr. 2005 .
- Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia, at http://www.wikipedia.com Comment: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Asbestos (accessed Aug 30 2005)
- CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, Robert Weast (ed.), CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, v. 61, 1980 Comment: density=2.0-2.8
- Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia, Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976
- Random House, Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language, Grammercy Book, New York, 1997