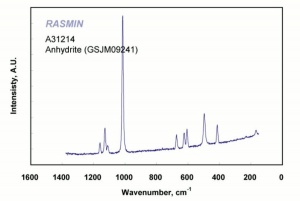
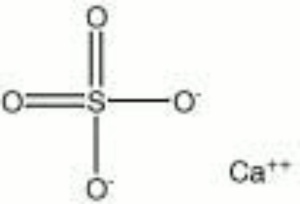
Calcium sulfate, anhydrous
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Description
White, odorless crystals whose mineral form is called Anhydrite. Anhydrous calcium sulfate is ground to form a colorless, inert pigment which is often used as a paper filler. It is strongly hygroscopic and is also used as a drying agent for solids, organic liquids, and gases. Anhydrous calcium sulfate is commercially sold under the name of Drierite. Its drying capacity can be regenerated an unlimited number of times.
Synonyms and Related Terms
anhydrite; karstenite; muriacite; anhydrous sulfate of lime; anhydrous gypsum;
Brand names: Drierite (contains cobalt chloride as an indicator)
Risks
- IntegraChem: SDS
Physical and Chemical Properties
Slightly soluble in water.
| Composition | CaSO4 |
|---|---|
| CAS | 7778-18-9 |
| Mohs Hardness | 3.0 - 3.5 |
| Melting Point | 1450 C |
| Density | 2.93-2.964 g/ml |
| Molecular Weight | mol. wt. = 136.14 |
| Refractive Index | 1.570; 1.614; 1.575 |
Resources and Citations
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- The Merck Index, Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983
- Encyclopedia Britannica, http://www.britannica.com Comment: 'anhydrite' [Accessed December 4, 2001]
- R. J. Gettens, G.L. Stout, Painting Materials, A Short Encyclopaedia, Dover Publications, New York, 1966 Comment: density=2.93 ref. index=1.570; 1.614; 1.575
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971
- C.W.Chesterman, K.E.Lowe, Audubon Society Field Guide to North American Rocks and Minerals, Alfred A. Knopf, New York, 1979