Difference between revisions of "Chemical wood pulp"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
JMcGlinchey (talk | contribs) |
m (Text replace - "== Authority ==" to "== Sources Checked for Data in Record ==") |
||
| (11 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
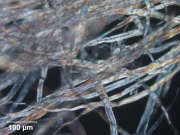
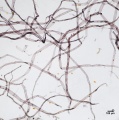
| − | Paper pulp made from chemically treated wood fibers. Chemical pulp is produced by treating debarked, ground wood with strong solutions to dissolve the lignin. The undissolved cellulose fibers are washed, rinsed, sometimes bleached, then used to produce paper. The three main types of solutions used to make chemical pulp are: | + | Paper pulp made from chemically treated wood fibers. Chemical pulp is produced by treating debarked, ground wood or chips with strong solutions to dissolve the lignin and hemicellulose. The undissolved cellulose fibers are washed, rinsed, sometimes bleached, then used to produce paper. The three main types of solutions used to make chemical pulp are: |
- alkaline: [[sodium sulfide]] followed by [[sodium hydroxide|caustic soda]] solution ([[kraft process]]), | - alkaline: [[sodium sulfide]] followed by [[sodium hydroxide|caustic soda]] solution ([[kraft process]]), | ||
| − | - alkaline: caustic soda (soda process), | + | - alkaline: caustic soda ([[soda process]]), |
| − | - acid: [[calcium bisulfite|acid bisulfite]] (sulfite process). | + | - acid: [[calcium bisulfite|acid bisulfite]] ([[sulfite process]]). |
[[File:100_Chem. softwood_conif_pol adj.jpg|thumb|Chemical hardwood (non-coniferous)]] | [[File:100_Chem. softwood_conif_pol adj.jpg|thumb|Chemical hardwood (non-coniferous)]] | ||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
== Other Properties == | == Other Properties == | ||
| − | Produces a pale blue-violet to red violet response to iodine-zinc chloride solution. | + | Produces a pale blue-violet to red violet response to iodine-zinc chloride solution. [[Graff "C" stain]] can be used to distinguish types of chemical pulping and bleaching. |
== Additional Images == | == Additional Images == | ||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
File:99_Chem. softwood_conif adj.jpg|Chemical softwood (coniferous) | File:99_Chem. softwood_conif adj.jpg|Chemical softwood (coniferous) | ||
File:99_Chem. softwood_conif_pol adj.jpg|Chemical softwood (coniferous) | File:99_Chem. softwood_conif_pol adj.jpg|Chemical softwood (coniferous) | ||
| + | File:SWBS puget 10x label.jpg|Chemical softwood stained with Graff "C" Stain | ||
| + | File:SUBK 10x2 label.jpg|Chemical softwood stained with Graff "C" Stain | ||
| + | File:SBA 40x pinoidpitslabel.jpg|Chemical softwood stained with Graff "C" Stain | ||
| + | File:Redoak vessels 10x.jpg|Chemical hardwood stained with Graff "C" stain | ||
| + | File:Elm 40x.jpg|Chemical hardwood stained with Graff "C" stain | ||
| + | Sycamore 40x.jpg|Chemical hardwood stained with Graff "C" stain | ||
| + | Redgum 10x.jpg|Chemical hardwood stained with Graff "C" stain | ||
| + | Yellowpoplar 40x.jpg|Chemical hardwood stained with Graff "C" stain | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
| − | + | == Sources Checked for Data in Record == | |
| − | == | ||
* ''Encyclopedia Britannica'', http://www.britannica.com Comment: "Paper Pulp." Encyclopædia Britannica. 2003. 11 Sep, 2003 . | * ''Encyclopedia Britannica'', http://www.britannica.com Comment: "Paper Pulp." Encyclopædia Britannica. 2003. 11 Sep, 2003 . | ||
| Line 41: | Line 48: | ||
* Boise Cascade Paper Group, ''The Paper Handbook'', Boise Cascade, Portland OR, 1989 | * Boise Cascade Paper Group, ''The Paper Handbook'', Boise Cascade, Portland OR, 1989 | ||
| + | |||
| + | * J. H. Graff "Color Atlas for Fiber Identification" The Institute of Paper Chemistry, Appleton, WI, 1940. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Walter Rantanen. "Fiber ID Course." Integrated Paper Services. June 2013. Lecture. | ||
* Matt Roberts, Don Etherington, ''Bookbinding and the Conservation of Books: a Dictionary of Descriptive Terminology'', U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington DC, 1982 | * Matt Roberts, Don Etherington, ''Bookbinding and the Conservation of Books: a Dictionary of Descriptive Terminology'', U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington DC, 1982 | ||
| + | |||
| + | * TAPPI Official Standard T401 om-08. ''Fiber analysis of paper and paperboard''. 2008. http://www.tappi.org/Downloads/Test-Methods/UNTITLED-0104T401pdf.aspx | ||
* Silvie Turner, ''Which Paper?'', Design Press, New York, 1991 | * Silvie Turner, ''Which Paper?'', Design Press, New York, 1991 | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
[[Category:Materials database]] | [[Category:Materials database]] | ||
Latest revision as of 14:50, 29 April 2016
Description
Paper pulp made from chemically treated wood fibers. Chemical pulp is produced by treating debarked, ground wood or chips with strong solutions to dissolve the lignin and hemicellulose. The undissolved cellulose fibers are washed, rinsed, sometimes bleached, then used to produce paper. The three main types of solutions used to make chemical pulp are:
- alkaline: Sodium sulfide followed by caustic soda solution (Kraft process),
- alkaline: caustic soda (Soda process),
- acid: acid bisulfite (Sulfite process).
Synonyms and Related Terms
chemical pulp; woodfree pulp
Other Properties
Produces a pale blue-violet to red violet response to iodine-zinc chloride solution. Graff "C" stain can be used to distinguish types of chemical pulping and bleaching.
Additional Images
Sources Checked for Data in Record
- Encyclopedia Britannica, http://www.britannica.com Comment: "Paper Pulp." Encyclopædia Britannica. 2003. 11 Sep, 2003 .
- Random House, Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language, Grammercy Book, New York, 1997
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 574
- The Dictionary of Paper, American Paper Institute, New York, Fourth Edition, 1980
- E.J.LaBarre, Dictionary and Encyclopedia of Paper and Paper-making, Swets & Zeitlinger, Amsterdam, 1969
- Boise Cascade Paper Group, The Paper Handbook, Boise Cascade, Portland OR, 1989
- J. H. Graff "Color Atlas for Fiber Identification" The Institute of Paper Chemistry, Appleton, WI, 1940.
- Walter Rantanen. "Fiber ID Course." Integrated Paper Services. June 2013. Lecture.
- Matt Roberts, Don Etherington, Bookbinding and the Conservation of Books: a Dictionary of Descriptive Terminology, U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington DC, 1982
- TAPPI Official Standard T401 om-08. Fiber analysis of paper and paperboard. 2008. http://www.tappi.org/Downloads/Test-Methods/UNTITLED-0104T401pdf.aspx
- Silvie Turner, Which Paper?, Design Press, New York, 1991