Difference between revisions of "Indigo"
| (99 intermediate revisions by 8 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | [[File:Indigotextile931108.jpg|thumb|Japanese textile<br>MFA# 93.1108]] | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
| + | [[File:49.414-SC2674.jpg|thumb|Pieced quilt<br>MFA# 49.414]] | ||
| + | A natural dark blue dye obtained from ''Indigofera tinctoria'' plants native to India, ''Java'', Peru, and other tropical areas. The use of indigo was first mentioned in Indian manuscripts in the 4th century BCE. It was exported to Europe in Roman times but did not become plentiful until sea routes opened up in the 17th century. The natural material is collected as a precipitate from a fermented solution of the plant. The coloring component, indigotin, is extracted as a colorless glycoside, but turns blue with oxidation. Synthetic indigo was first produced in 1880 by Adolf von Baeyer. Made from anthranilic acid, the synthetic colorant is chemically identical to natural indigo and has almost entirely replaced the natural dyestuff. Indigo is a fine, intense powder which may be used directly as a [[pigment]] in oil, tempera, or watercolor media. The exposed pigment can fade rapidly in strong sunlight. Indigo is still used to dye jeans, where its fading and uneven coloring have become favorable characteristics. | ||
| + | * See also [[https://cameo.mfa.org/wiki/Category:Uemura_dye_archive (Sukumo-Ai)]] in Uemera Dye Archive | ||
| + | [[File:indigo tinctoria t.jpg|thumb|Indigo plant (''Indigofera tinctoria'')]] | ||
| − | + | == Synonyms and Related Terms == | |
| − | + | 2,2'-biindolinyliden-3,3'-dion; '' Indigofera tinctoria''; Natural Blue 1; CI 75780 (natural); Vat Blue 1; CI 73000 (synthetic); Pigment Blue 66; indigotin; indicum (Pliny); indigo (Esp. Fr., Dan., Ned., Port., Sven.); Indigo (Deut.); anil (Esp.); Indiko (Gr.); indaco (It.); aneel; anile; ai (Jap.); rams (Tibetan); blue ynde; blue inde; anneil; India blue; intense blue; rock indigo; stone blue; indigo carmine; intense blue; indico; indicoe; indego; nil | |
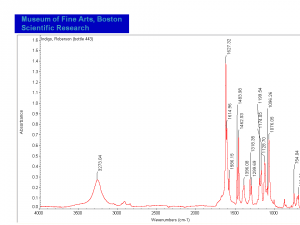
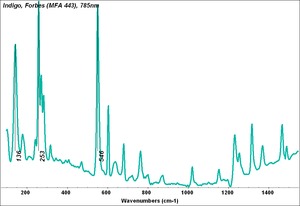
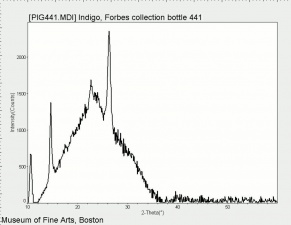
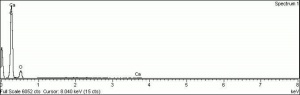
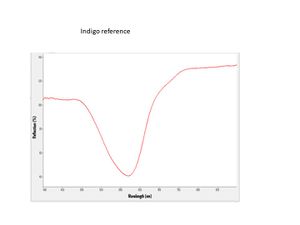
| − | + | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|Indigo(443).PNG~FTIR (MFA)|Indigo, Forbes (MFA 443), 785nm.TIF~Raman (MFA)|PIG441.jpg~XRD|f441sem.jpg~SEM|f441edsbw.jpg~EDS|Indigo_FORS.JPG~FORS|indigo.jpg~Chemical structure]]] | |
| + | == Risks == | ||
| − | == | + | * Discolored by reducing agents and bleaches. |
| + | * Fisher Scientific: [https://fscimage.fishersci.com/msds/62055.htm MSDS] | ||
| + | == Physical and Chemical Properties == | ||
| − | Soluble in nitrobenzene, phenol, chloroform, glacial acetic acid. Insoluble in water, ethanol, acetone, ethyl acetate, pinene. | + | * Soluble in nitrobenzene, phenol, chloroform, glacial acetic acid. Insoluble in water, ethanol, acetone, ethyl acetate, pinene. |
| − | + | * Absorption max = 599 (in xylene). | |
| − | Absorption max = 599 (in xylene). | + | * ISO R105 Lightfastness Classification = 3-4 |
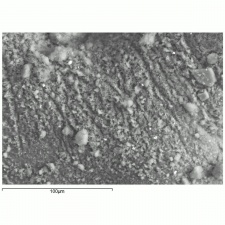
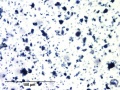
| − | + | * Microscopically, indigo has fine, translucent dark blue, rounded particles that are weakly birefringent and appear red under Chelsea filter. | |
| − | ISO R105 Lightfastness Classification = 3-4 | ||
| − | |||
| − | Microscopically, indigo has fine, translucent dark blue, rounded particles that are weakly birefringent and appear red under Chelsea filter. | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| Line 26: | Line 31: | ||
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Melting Point | ! scope="row"| Melting Point | ||
| − | | 390-392 | + | | 390-392 C |
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Molecular Weight | ! scope="row"| Molecular Weight | ||
| Line 35: | Line 40: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | == | + | == Comparisons == |
| + | |||
| + | [[media:download_file_488.pdf|Characteristics of Common Blue Pigments]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Additional Images == | ||
| + | |||
| + | <gallery> | ||
| + | File:indigo_piece_1.jpg|thumb|Indigo piece (''Indigofera tinctoria'') | ||
| + | File:indigo_powder.jpg|thumb|Indigo powder (''Indigofera tinctoria'') | ||
| + | File:dyed indigo.jpg|Paper dyed with indigo | ||
| + | File:indigo_50X2.jpg|Paper dyed with indigo at 50x | ||
| + | File:Indigo C100x.jpg|Indigo at 100x (visible light left; UV light right) | ||
| + | File:46_Indigo_blue_500X.jpg|Indigo blue at 500x | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Resources and Citations == | ||
| + | * H.Schweppe, "Indigo and Woad", ''Artists Pigments'', Volume 3, E. West FitzHugh (ed.), Oxford University Press: Oxford, 1997. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Pigments Through the Ages: [http://webexhibits.org/pigments/indiv/overview/indigo.html Indigo] | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Analytical strategies for natural dyestuffs in cultural heritage objects - EU-ARTECH European research project - http://www.organic-colorants.org | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Nicholas Eastaugh, Valentine Walsh, Tracey Chaplin, Ruth Siddall, ''Pigment Compendium'', Elsevier Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford, 2004 | ||
| + | |||
| + | * ''The Dictionary of '', Grove's Dictionaries Inc., New York, 1996 Comment: 'Pigment' | ||
| + | |||
| + | * , ''A Dictionary of Terms and Techniques'', Harper and Row Publishers, New York, 1969 (also 1945 printing) | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Palmy Weigle, ''Ancient Dyes for Modern Weavers'', Watson-Guptill Publications, New York, 1974 | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Matt Roberts, Don Etherington, ''Bookbinding and the Conservation of Books: a Dictionary of Descriptive Terminology'', U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington DC, 1982 | ||
| + | |||
| + | * ''Dictionary of Building Preservation'', Ward Bucher, ed., John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York City, 1996 | ||
| + | |||
| + | * ''The Merck Index'', Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: entry 4977 | ||
| + | |||
| + | * A.Scharff, 'Synthetic dyestuffs for textiles and their fastness to washing', ''ICOM-CC Preprints'' Lyon, Getty Conservation Institute, Los Angeles, 1999 | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Hermann Kuhn, ''Conservation and Restoration of Works of and Antiquities'', Butterworths, London, 1986 | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Thomas B. Brill, ''Light Its Interaction with and Antiquities'', Plenum Press, New York City, 1980 | ||
| + | |||
| + | * R., M.Curran, C.Bailie, 'Identification of Traditional Organic Colorants Employed in Prints and Determination of their Rates of Fading', '' Woodblock Prints'', Allen Memorial Museum, Oberlin College, Oberlin, 1984 | ||
| + | |||
| + | * F. Crace-Calvert, ''Dyeing and Calico Printing'', Palmer & Howe, London, 1876 | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Random House, ''Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language'', Grammercy Book, New York, 1997 | ||
| + | |||
| + | * ''Encyclopedia Britannica'', http://www.britannica.com Comment: "indigo" [Accessed May 6, 2004]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Website: at www.colour-index.org | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Book and Paper Group, ''Paper Conservation Catalog'', AIC, 1984, 1989 | ||
| + | |||
| + | * ''The American Heritage Dictionary'' or ''Encarta'', via 98, ., 1998 | ||
| + | |||
| + | * AAT: http://www.getty.edu/research/tools/vocabulary/aat/, J. Paul Getty Trust, Los Angeles, 2000 | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
[[Category:Materials database]] | [[Category:Materials database]] | ||
Latest revision as of 11:12, 29 November 2022
Description
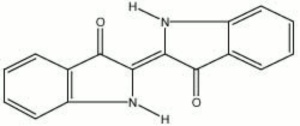
A natural dark blue dye obtained from Indigofera tinctoria plants native to India, Java, Peru, and other tropical areas. The use of indigo was first mentioned in Indian manuscripts in the 4th century BCE. It was exported to Europe in Roman times but did not become plentiful until sea routes opened up in the 17th century. The natural material is collected as a precipitate from a fermented solution of the plant. The coloring component, indigotin, is extracted as a colorless glycoside, but turns blue with oxidation. Synthetic indigo was first produced in 1880 by Adolf von Baeyer. Made from anthranilic acid, the synthetic colorant is chemically identical to natural indigo and has almost entirely replaced the natural dyestuff. Indigo is a fine, intense powder which may be used directly as a Pigment in oil, tempera, or watercolor media. The exposed pigment can fade rapidly in strong sunlight. Indigo is still used to dye jeans, where its fading and uneven coloring have become favorable characteristics.
- See also [(Sukumo-Ai)] in Uemera Dye Archive
Synonyms and Related Terms
2,2'-biindolinyliden-3,3'-dion; Indigofera tinctoria; Natural Blue 1; CI 75780 (natural); Vat Blue 1; CI 73000 (synthetic); Pigment Blue 66; indigotin; indicum (Pliny); indigo (Esp. Fr., Dan., Ned., Port., Sven.); Indigo (Deut.); anil (Esp.); Indiko (Gr.); indaco (It.); aneel; anile; ai (Jap.); rams (Tibetan); blue ynde; blue inde; anneil; India blue; intense blue; rock indigo; stone blue; indigo carmine; intense blue; indico; indicoe; indego; nil
Risks
- Discolored by reducing agents and bleaches.
- Fisher Scientific: MSDS
Physical and Chemical Properties
- Soluble in nitrobenzene, phenol, chloroform, glacial acetic acid. Insoluble in water, ethanol, acetone, ethyl acetate, pinene.
- Absorption max = 599 (in xylene).
- ISO R105 Lightfastness Classification = 3-4
- Microscopically, indigo has fine, translucent dark blue, rounded particles that are weakly birefringent and appear red under Chelsea filter.
| Composition | C16H10N2O2 |
|---|---|
| CAS | 482-89-3 |
| Melting Point | 390-392 C |
| Molecular Weight | mol. wt. = 262.26 |
| Refractive Index | >1.662 |
Comparisons
Characteristics of Common Blue Pigments
Additional Images
Resources and Citations
- H.Schweppe, "Indigo and Woad", Artists Pigments, Volume 3, E. West FitzHugh (ed.), Oxford University Press: Oxford, 1997.
- Pigments Through the Ages: Indigo
- Analytical strategies for natural dyestuffs in cultural heritage objects - EU-ARTECH European research project - http://www.organic-colorants.org
- Nicholas Eastaugh, Valentine Walsh, Tracey Chaplin, Ruth Siddall, Pigment Compendium, Elsevier Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford, 2004
- The Dictionary of , Grove's Dictionaries Inc., New York, 1996 Comment: 'Pigment'
- , A Dictionary of Terms and Techniques, Harper and Row Publishers, New York, 1969 (also 1945 printing)
- Palmy Weigle, Ancient Dyes for Modern Weavers, Watson-Guptill Publications, New York, 1974
- Matt Roberts, Don Etherington, Bookbinding and the Conservation of Books: a Dictionary of Descriptive Terminology, U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington DC, 1982
- Dictionary of Building Preservation, Ward Bucher, ed., John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York City, 1996
- The Merck Index, Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: entry 4977
- A.Scharff, 'Synthetic dyestuffs for textiles and their fastness to washing', ICOM-CC Preprints Lyon, Getty Conservation Institute, Los Angeles, 1999
- Hermann Kuhn, Conservation and Restoration of Works of and Antiquities, Butterworths, London, 1986
- Thomas B. Brill, Light Its Interaction with and Antiquities, Plenum Press, New York City, 1980
- R., M.Curran, C.Bailie, 'Identification of Traditional Organic Colorants Employed in Prints and Determination of their Rates of Fading', Woodblock Prints, Allen Memorial Museum, Oberlin College, Oberlin, 1984
- F. Crace-Calvert, Dyeing and Calico Printing, Palmer & Howe, London, 1876
- Random House, Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language, Grammercy Book, New York, 1997
- Encyclopedia Britannica, http://www.britannica.com Comment: "indigo" [Accessed May 6, 2004].
- Website: at www.colour-index.org
- Book and Paper Group, Paper Conservation Catalog, AIC, 1984, 1989
- The American Heritage Dictionary or Encarta, via 98, ., 1998
- AAT: http://www.getty.edu/research/tools/vocabulary/aat/, J. Paul Getty Trust, Los Angeles, 2000