Anthracene
Revision as of 13:49, 27 April 2022 by MDerrick (talk | contribs) (→Physical and Chemical Properties)
Description
A colorless, crystalline compound composed of three attached aromatic rings. Anthracene is derived from the fractional distillation of Coal tar. Anthracene is used to make synthetic alizarin. It is also used to manufacture other organic dyes, resins, plasticizers, and tanning agents.
Synonyms and Related Terms
anthracin; paranaphthalene; antracen (Ces., Pol.); Anthracen (Deut.); antraceno(Esp.); anthracène (Fr.); anthraceen (Ned.);
Hazards and Safety
Combustible. Carcinogenic.
ThermoFisher: SDS
Physical and Chemical Properties
Slightly soluble in ethanol, ether and benzene. Insoluble in water.
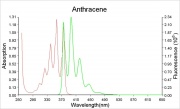
Violet fluorescence when pure, yellow-green when impure.
| Composition | C14H10 |
|---|---|
| CAS | 120-12-7 |
| Melting Point | 218 C |
| Density | 1.1-1.2 g/ml |
| Molecular Weight | mol. wt. = 178.2 |
| Boiling Point | 342 C |
Resources and Citations
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 801
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- John and Margaret Cannon, Dye Plants and Dyeing, Herbert Press, London, 1994
- Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia, Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976
- The Merck Index, Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: entry 721
- Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Anthracene (Accessed Mar. 20, 2006) -for non-English terms
- Random House, Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language, Grammercy Book, New York, 1997
- The American Heritage Dictionary or Encarta, via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998