Difference between revisions of "Mechanical wood pulp"
m (→Description) |
m (Text replace - "== Authority ==" to "== Sources Checked for Data in Record ==") |
||
| (8 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
| − | A mass of wood fibers produced by physically grinding rather than chemically treatment. To produce mechanical wood pulp, bark-free, cut wood is sent to a sandstone abrasion-type grinding machine. It is then screened and filtered to remove large pieces and foreign material. The resultant pulp contains [[lignin]], [[hemicellulose]], [[resin]], and colouring materials which yellow and deteriorate the paper over time. Thus, the pulp is often bleached with [[peroxide]] or | + | A mass of wood fibers produced by physically grinding rather than chemically treatment. To produce mechanical wood pulp, bark-free, cut wood is sent to a sandstone abrasion-type grinding machine. It is then screened and filtered to remove large pieces and foreign material. The resultant pulp contains [[lignin]], [[hemicellulose]], [[resin]], and colouring materials which yellow and deteriorate the paper over time. Thus, the pulp is often bleached with [[peroxide]] or hydrosulfite to improve whiteness. [[Groundwood paper]] is produced from coniferous trees. It is inexpensive and has low strength but high opacity and bulk. It is used for newsprint and other low cost printing papers. Groundwood paper is chemically unstable. |
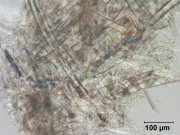
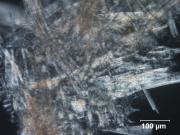
[[File:98_Mechanical softwood_200X_pol adj.jpg|thumb|Mechanical softwood]] | [[File:98_Mechanical softwood_200X_pol adj.jpg|thumb|Mechanical softwood]] | ||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
== Other Properties == | == Other Properties == | ||
| − | Tests used to determine the presence of mechanical wood pulp in a paper are: 1) [ | + | Tests used to determine the presence of mechanical wood pulp in a paper are: 1) [[iodine]]-[[zinc chloride]] test gives a positive yellow, 2) [[aniline sulfate]] turns yellow for positive, 3) [[paranitroaniline]] turns orange, 4) [[phloroglucinol]] turns red (Roberts and Etherington 1982), 5) and [[Graff "C" stain]] will turn yellow due the presence of lignin. |
== Additional Information == | == Additional Information == | ||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
Matt Roberts, Don Etherington, ''Bookbinding and the Conservation of Books: a Dictionary of Descriptive Terminology'', U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington DC, 1982 | Matt Roberts, Don Etherington, ''Bookbinding and the Conservation of Books: a Dictionary of Descriptive Terminology'', U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington DC, 1982 | ||
| − | == | + | == Additional Images == |
| + | |||
| + | <gallery> | ||
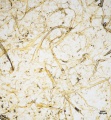
| + | File:SWGW 10x label.jpg|Softwood groundwood pulp stained with Graff "C" Stain | ||
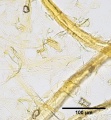
| + | File:SWGW 40x label.jpg|Softwood groundwood pulp stained with Graff "C" Stain | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Sources Checked for Data in Record == | ||
* R. J. Gettens, G.L. Stout, ''Painting Materials, A Short Encyclopaedia'', Dover Publications, New York, 1966 | * R. J. Gettens, G.L. Stout, ''Painting Materials, A Short Encyclopaedia'', Dover Publications, New York, 1966 | ||
| Line 26: | Line 33: | ||
* ''Encyclopedia Britannica'', http://www.britannica.com Comment: "Papermaking." Encyclopædia Britannica. 15 July 2004 . | * ''Encyclopedia Britannica'', http://www.britannica.com Comment: "Papermaking." Encyclopædia Britannica. 15 July 2004 . | ||
| − | + | * Walter Rantanen. "Fiber ID Course." Integrated Paper Services. June 2013. Lecture. | |
[[Category:Materials database]] | [[Category:Materials database]] | ||
Revision as of 13:34, 1 May 2016
Description
A mass of wood fibers produced by physically grinding rather than chemically treatment. To produce mechanical wood pulp, bark-free, cut wood is sent to a sandstone abrasion-type grinding machine. It is then screened and filtered to remove large pieces and foreign material. The resultant pulp contains Lignin, Hemicellulose, Resin, and colouring materials which yellow and deteriorate the paper over time. Thus, the pulp is often bleached with Peroxide or hydrosulfite to improve whiteness. Groundwood paper is produced from coniferous trees. It is inexpensive and has low strength but high opacity and bulk. It is used for newsprint and other low cost printing papers. Groundwood paper is chemically unstable.
Synonyms and Related Terms
mechanical wood-pulp; groundwood pulp
Other Properties
Tests used to determine the presence of mechanical wood pulp in a paper are: 1) Iodine-Zinc chloride test gives a positive yellow, 2) Aniline sulfate turns yellow for positive, 3) Paranitroaniline turns orange, 4) Phloroglucinol turns red (Roberts and Etherington 1982), 5) and Graff "C" stain will turn yellow due the presence of lignin.
Additional Information
Matt Roberts, Don Etherington, Bookbinding and the Conservation of Books: a Dictionary of Descriptive Terminology, U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington DC, 1982
Additional Images
Sources Checked for Data in Record
- R. J. Gettens, G.L. Stout, Painting Materials, A Short Encyclopaedia, Dover Publications, New York, 1966
- Matt Roberts, Don Etherington, Bookbinding and the Conservation of Books: a Dictionary of Descriptive Terminology, U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington DC, 1982
- Encyclopedia Britannica, http://www.britannica.com Comment: "Papermaking." Encyclopædia Britannica. 15 July 2004 .
- Walter Rantanen. "Fiber ID Course." Integrated Paper Services. June 2013. Lecture.