Difference between revisions of "Muscovite"
(username removed) |
(username removed) |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
| − | A light colored mica mineral composed of potassium aluminum silicate hydroxide fluoride. Muscovite is the most common type of [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=mica mica]. The transparent to translucent mineral can be colorless, pale yellow, green, gray, or light brown. It cleaves easily to form thin, flexible mineral sheets. The name [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=Muscovy | + | A light colored mica mineral composed of potassium aluminum silicate hydroxide fluoride. Muscovite is the most common type of [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=mica mica]. The transparent to translucent mineral can be colorless, pale yellow, green, gray, or light brown. It cleaves easily to form thin, flexible mineral sheets. The name [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=Muscovy%20glass Muscovy glass] was formerly used for this mineral because of its use by Russians for windows. Significant muscovite deposits occur in India (Nellore), Pakistan, Brazil and the U.S. (New England, Pennsylvania, Maryland, Virginia, North Carolina, Georgia, South Dakota, New Mexico). A rare variety found in Brazil has twinned crystals that form yellow five-pointed stars (star muscovite). Muscovite is a good electrical and thermal insulator. For many years, it was used for kitchen oven windows. Muscovite is still used as an electrical insulator and as a fireproofing material. |
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:muscovitelarge.jpg|thumb|Muscovite]] |
== Synonyms and Related Terms == | == Synonyms and Related Terms == | ||
white mica; potash mica; potash silicate; potassium mica; common mica; isinglass; Muscovy glass; star muscovite; Muscovit (Deut.); Moskauer Glas (Deut.); muscovita (Esp.); muscovite (Fr., Port.); muscoviet (Ned.); muscowit (Pol.) | white mica; potash mica; potash silicate; potassium mica; common mica; isinglass; Muscovy glass; star muscovite; Muscovit (Deut.); Moskauer Glas (Deut.); muscovita (Esp.); muscovite (Fr., Port.); muscoviet (Ned.); muscowit (Pol.) | ||
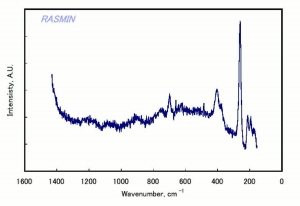
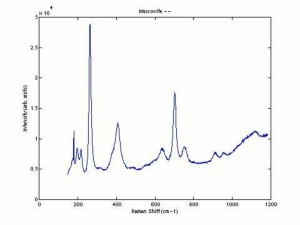
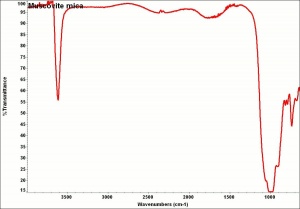
| − | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|muscoviteRS.jpg~Raman|Muscoviteitaly2.jpg~Raman]]] | + | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|muscoviteRS.jpg~Raman|Muscoviteitaly2.jpg~Raman|Muscovite micaj1.jpg~FTIR|Muscovite micaj1.jpg~FTIR]]] |
== Other Properties == | == Other Properties == | ||
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
Mineralogy Database: [http://www.webmineral.com/data/Muscovite.shtml Muscovite] | Mineralogy Database: [http://www.webmineral.com/data/Muscovite.shtml Muscovite] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
== Authority == | == Authority == | ||
| − | * | + | * R. J. Gettens, G.L. Stout, ''Painting Materials, A Short Encyclopaedia'', Dover Publications, New York, 1966 Comment: density=2.89; ref. index=1.563; 1.604; 1.599 |
| − | * | + | * Robert Fournier, ''Illustrated Dictionary of Practical Pottery'', Chilton Book Company, Radnor, PA, 1992 |
| − | * | + | * Frank A. Lent, ''Trade names and Descriptions of Marbles, Limestones, Sandstones, Granites and Other Building Stones Quarried in the United States Canada and other Countries.'', Stone Publishing Co, New York, 1925 |
| − | * ''Encyclopedia Britannica'', http://www.britannica.com Comment: "muscovite" | + | * ''Encyclopedia Britannica'', http://www.britannica.com Comment: "muscovite" Encyclopædia Britannica [Accessed December 4, 2001]. |
| − | * | + | * C.W.Chesterman, K.E.Lowe, ''Audubon Society Field Guide to North American Rocks and Minerals'', Alfred A. Knopf, New York, 1979 |
* Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia, at http://www.wikipedia.com Comment: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Muscovite (Accessed Sept. 10, 2005) | * Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia, at http://www.wikipedia.com Comment: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Muscovite (Accessed Sept. 10, 2005) | ||
| − | * | + | * G.S.Brady, ''Materials Handbook'', McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 505 |
| − | * | + | * Richard S. Lewis, ''Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary'', Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993 |
* ''Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia'', Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976 | * ''Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia'', Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976 | ||
| − | * | + | * Random House, ''Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language'', Grammercy Book, New York, 1997 |
* ''The American Heritage Dictionary'' or ''Encarta'', via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998 | * ''The American Heritage Dictionary'' or ''Encarta'', via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998 | ||
Revision as of 07:41, 24 July 2013
Description
A light colored mica mineral composed of potassium aluminum silicate hydroxide fluoride. Muscovite is the most common type of mica. The transparent to translucent mineral can be colorless, pale yellow, green, gray, or light brown. It cleaves easily to form thin, flexible mineral sheets. The name Muscovy glass was formerly used for this mineral because of its use by Russians for windows. Significant muscovite deposits occur in India (Nellore), Pakistan, Brazil and the U.S. (New England, Pennsylvania, Maryland, Virginia, North Carolina, Georgia, South Dakota, New Mexico). A rare variety found in Brazil has twinned crystals that form yellow five-pointed stars (star muscovite). Muscovite is a good electrical and thermal insulator. For many years, it was used for kitchen oven windows. Muscovite is still used as an electrical insulator and as a fireproofing material.
Synonyms and Related Terms
white mica; potash mica; potash silicate; potassium mica; common mica; isinglass; Muscovy glass; star muscovite; Muscovit (Deut.); Moskauer Glas (Deut.); muscovita (Esp.); muscovite (Fr., Port.); muscoviet (Ned.); muscowit (Pol.)
Other Properties
Monoclinic crystal system with pseudo-hexagonal forms. High birefringence.
Cleavage = laminar forming thin, elastic plates.
Luster = vitreous to pearly. Streak = colorless. Fracture = uneven.
| Composition | KAl2(AlSi3O10)(F,OH)2 |
|---|---|
| Mohs Hardness | 2.0 - 2.5 |
| Density | 2.7-3.0 |
| Refractive Index | 1.563; 1.604; 1.599 |
Additional Information
Mineralogy Database: Muscovite
Authority
- R. J. Gettens, G.L. Stout, Painting Materials, A Short Encyclopaedia, Dover Publications, New York, 1966 Comment: density=2.89; ref. index=1.563; 1.604; 1.599
- Robert Fournier, Illustrated Dictionary of Practical Pottery, Chilton Book Company, Radnor, PA, 1992
- Frank A. Lent, Trade names and Descriptions of Marbles, Limestones, Sandstones, Granites and Other Building Stones Quarried in the United States Canada and other Countries., Stone Publishing Co, New York, 1925
- Encyclopedia Britannica, http://www.britannica.com Comment: "muscovite" Encyclopædia Britannica [Accessed December 4, 2001].
- C.W.Chesterman, K.E.Lowe, Audubon Society Field Guide to North American Rocks and Minerals, Alfred A. Knopf, New York, 1979
- Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia, at http://www.wikipedia.com Comment: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Muscovite (Accessed Sept. 10, 2005)
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 505
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia, Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976
- Random House, Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language, Grammercy Book, New York, 1997
- The American Heritage Dictionary or Encarta, via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998
- CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, Robert Weast (ed.), CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, v. 61, 1980 Comment: density=2.76-3.00