Difference between revisions of "Neoprene"
| (9 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
| − | A family of synthetic rubbers made by polymerizing chlorinated butadiene. | + | A family of synthetic rubbers made by polymerizing chlorinated butadiene. Chloroprene was first developed by DuPont in 1931 by Ira Williams and sold under the name of DuPrene in 1932. In 1936, DuPont changed its brand name to Neoprene; now neoprene is a generic term used for this class of synthetic rubbers. Neoprene is vulcanized with metal oxides rather than sulfur which makes it less elastic than rubber, but more resistant to chemicals, heat, and light. It is also resistant to water and biodegradation. Neoprene has a service temperature range of -50 to 95 C and has good compressibility. Neoprene is used for gaskets, roof coatings, shoe soles, wet suits, gloves, contact adhesives, and as a coating for fabrics. |
| + | |||
| + | Neoprene adhesives and coatings are typically anionic colloidial dispersions in aqueous solutions. The adhesives can be repared as pressure sensitive or heat activated forms. The coatings and sealants have additives to vary viscosites and surface penetration levels. | ||
== Synonyms and Related Terms == | == Synonyms and Related Terms == | ||
| Line 9: | Line 11: | ||
Examples: Butaclor® [PolimeriEuropa]; Baypren® [Lanxess]; Sovprene (Russian); Mustone (Japan); DuPrene [DuPont]; GR-M, Evostik [Evode]; Pattex [Henkel]; Butyl [Standard Oil Co.] | Examples: Butaclor® [PolimeriEuropa]; Baypren® [Lanxess]; Sovprene (Russian); Mustone (Japan); DuPrene [DuPont]; GR-M, Evostik [Evode]; Pattex [Henkel]; Butyl [Standard Oil Co.] | ||
| + | == Applications == | ||
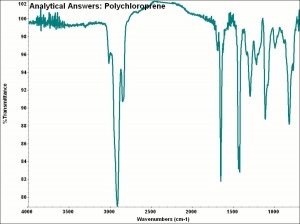
[[[SliderGallery rightalign|aaiNEOPRENE.jpg~FTIR]]] | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|aaiNEOPRENE.jpg~FTIR]]] | ||
| − | == | + | == Personal Risks == |
| + | |||
| + | Federal Mogul: [[http://pt-pcs.federalmogul.com/MSDSSheets/Chloroprene_Neoprene_Rubber56b55ae8-3301-46d5-8636-1db909f99a16.pdf| Safety Data Sheet]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Collection Risks == | ||
| + | |||
| + | Fire-retardant. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Physical and Chemical Properties == | ||
Soluble in chlorinated and aromatic hydrocarbons. | Soluble in chlorinated and aromatic hydrocarbons. | ||
| Line 27: | Line 38: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | + | Examples characteristics and compositions for the Denka series are: | |
| − | + | {| class="wikitable" | |
| + | !Product Grade ||Solids Content %||Characteritics||Data sheets | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Neoprene 571|| 50||high tensile strength ||[[http://13.58.24.27/wp-content/uploads/2017/04/LD571-Tech-Data-Sheet.pdf website]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Neoprene 671A|| 59||general purpose ||[[http://13.58.24.27/wp-content/uploads/2017/04/LD671A-Tech-Data-Sheet.pdf website]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Neoprene 750|| 50||excellent flexibility ||[[http://13.58.24.27/wp-content/uploads/2017/04/LD750-Tech-Data-Sheet.pdf website]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Neoprene 842A|| 50||fast curing, low modulus ||[[http://13.58.24.27/wp-content/uploads/2017/04/LD842A-Tech-Data-Sheet.pdf website]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |} | ||
== Additional Information == | == Additional Information == | ||
| − | ° DuPont | + | ° Denka Neoprene (formerly DuPont) [https://www.denka.us.com/services/elastomers-dept/denka-neoprene/ Website] |
° M.Steinfink, "Neoprene Adhesives: Solvent and Latex" in ''Handbook of Adhesives'', I.Skeist (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1977, p.343-367. | ° M.Steinfink, "Neoprene Adhesives: Solvent and Latex" in ''Handbook of Adhesives'', I.Skeist (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1977, p.343-367. | ||
| Line 41: | Line 63: | ||
* ''Fairchild's Dictionary of Textiles'', Phyllis G.Tortora, Robert S. Merkel (eds.), Fairchild Publications, New York City, 7th edition, 1996 | * ''Fairchild's Dictionary of Textiles'', Phyllis G.Tortora, Robert S. Merkel (eds.), Fairchild Publications, New York City, 7th edition, 1996 | ||
| − | * Website address 1 | + | * Website address 1: www.nswpmith.com.au/historyofplastics.html |
| − | |||
| − | |||
* Irving Skeist, ''Handbook of Adhesives'', Van Nostrand Reinhold Company, New York, 1977 Comment: ..The first public announcement of this polymer was made in 1931, commercialization began in April 1932. At first known as DuPrene, the polymer was designated neoprene by DuPont in 1936 | * Irving Skeist, ''Handbook of Adhesives'', Van Nostrand Reinhold Company, New York, 1977 Comment: ..The first public announcement of this polymer was made in 1931, commercialization began in April 1932. At first known as DuPrene, the polymer was designated neoprene by DuPont in 1936 | ||
Revision as of 11:13, 18 May 2020
Description
A family of synthetic rubbers made by polymerizing chlorinated butadiene. Chloroprene was first developed by DuPont in 1931 by Ira Williams and sold under the name of DuPrene in 1932. In 1936, DuPont changed its brand name to Neoprene; now neoprene is a generic term used for this class of synthetic rubbers. Neoprene is vulcanized with metal oxides rather than sulfur which makes it less elastic than rubber, but more resistant to chemicals, heat, and light. It is also resistant to water and biodegradation. Neoprene has a service temperature range of -50 to 95 C and has good compressibility. Neoprene is used for gaskets, roof coatings, shoe soles, wet suits, gloves, contact adhesives, and as a coating for fabrics.
Neoprene adhesives and coatings are typically anionic colloidial dispersions in aqueous solutions. The adhesives can be repared as pressure sensitive or heat activated forms. The coatings and sealants have additives to vary viscosites and surface penetration levels.
Synonyms and Related Terms
chloroprene; polychloroprene; poly(2-chloro-1,3-butadiene); neopreno (Esp.); néoprène (Fr.); neoprene (It.); neopreno (Port.);
Examples: Butaclor® [PolimeriEuropa]; Baypren® [Lanxess]; Sovprene (Russian); Mustone (Japan); DuPrene [DuPont]; GR-M, Evostik [Evode]; Pattex [Henkel]; Butyl [Standard Oil Co.]
Applications
Personal Risks
Federal Mogul: [Safety Data Sheet]
Collection Risks
Fire-retardant.
Physical and Chemical Properties
Soluble in chlorinated and aromatic hydrocarbons.
| Composition | (CH3ClC:CHCH3)n |
|---|---|
| CAS | 126-99-8 |
| Density | 1.23 |
Examples characteristics and compositions for the Denka series are:
| Product Grade | Solids Content % | Characteritics | Data sheets |
|---|---|---|---|
| Neoprene 571 | 50 | high tensile strength | [website] |
| Neoprene 671A | 59 | general purpose | [website] |
| Neoprene 750 | 50 | excellent flexibility | [website] |
| Neoprene 842A | 50 | fast curing, low modulus | [website] |
Additional Information
° Denka Neoprene (formerly DuPont) Website
° M.Steinfink, "Neoprene Adhesives: Solvent and Latex" in Handbook of Adhesives, I.Skeist (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1977, p.343-367.
Sources Checked for Data in Record
- Fairchild's Dictionary of Textiles, Phyllis G.Tortora, Robert S. Merkel (eds.), Fairchild Publications, New York City, 7th edition, 1996
- Website address 1: www.nswpmith.com.au/historyofplastics.html
- Irving Skeist, Handbook of Adhesives, Van Nostrand Reinhold Company, New York, 1977 Comment: ..The first public announcement of this polymer was made in 1931, commercialization began in April 1932. At first known as DuPrene, the polymer was designated neoprene by DuPont in 1936
- M. Baker, E. McManus, 'History, Care and Handling of America's Spacesuits', JAIC, 31, 77-85, 1992
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 680
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- Dictionary of Building Preservation, Ward Bucher, ed., John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York City, 1996
- Pam Hatchfield, Pollutants in the Museum Environment, Archetype Press, London, 2002
- Thomas C. Jester (ed.), Twentieth-Century Building Materials, McGraw-Hill Companies, Washington DC, 1995
- Edward Reich, Carlton J. Siegler, Consumer Goods: How to Know and Use Them, American Book Company, New York City, 1937 Comment: p. 285
- Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia, Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976
- Random House, Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language, Grammercy Book, New York, 1997
- The American Heritage Dictionary or Encarta, via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998
- Art and Architecture Thesaurus Online, http://www.getty.edu/research/tools/vocabulary/aat/, J. Paul Getty Trust, Los Angeles, 2000