Oak
Description
Common hardwood trees of the family Fagaceae and genus Quercus that are widespread throughout the northern temperate zones. Oaks, with over 600 species, can range in size from shrubs to 20 m with girths maeasure up to 12 m for a tree that is 1000 years old. Oaks have spirally arrange leaves with multiple lobes and smooth margins. The fruit is called an acorn, a small nut, that is polular with squirrels. Oaks trees produce a durable wood that is resistant to insect damage due to its high tannin content. The timber has a distinctive coarse grain and has been used for centuries in construction, cabinetry, flooring, paneling, musical instruments, ship interiors, and moldings. It was used for panel paintings in the Netherlands, England, Germany and northern France until the 18th century (Kuhn 1986). During the gothic period, oak was also used for sculptures in the northern parts of Germany, France and western Belgium (Kuhn, 1986), The thick bark from the cork oak tree (Quercus suber) is used for its buoyancy. Tannins and dyes can be extracted from the bark of oak trees. Oak galls were used to produce iron gall ink.
See also Black oak, Blue oak, Bog oak, Cork oak, Dyer's oak, English oak, Live oak, Northern red oak, Pin oak, Red oak, Scarlet oak, Shingle oak, Spanish oak, White oak.
Synonyms and Related Terms
Quercus; oake; eg (Dan.); Eichen (Deut.); roble (Esp.); chêne (Fr.); quercia (It.); eik (Ned., Nor.); carvalho roble (Port.); Ekar (Sven.)
Other Properties
| Density | 37-56 ppcf |
|---|
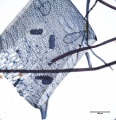
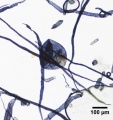
Paper fiber type: hardwood, ring porous. Using transmitted light microscopy, pulp is identified by two sizes of vessels with profuse pitting. The smaller late wood vessels of Red oak will stain darker than the early wood vessels, which can help distinguish pulp from White oak. Vasocentric tracheids are worm-like and heavily pitted. Perforations are simple. Tyloses are present in White oak. Appearance with Graff "C" stain: dark blue, but varies with bleaching. Average dimensions of fibers: length 1.47mm, 14-22μm wide. Common pulping method: kraft.
Hazards and Safety
Oak emits organic acids as it ages.
Additional Information
H.Kuhn, Conservation and Restoration of Works of Art and Antiquities, Butterworths, London, 1986.
Schoch, W., Heller, I., Schweingruber, F.H., Kienast, F., 2004:Wood anatomy of central European Species: Pedunculate Oak,Quercus robur L.
Additional Images
Authority (List of sources checked for information on this subject)
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 555
- Hermann Kuhn, Conservation and Restoration of Works of Art and Antiquities, Butterworths, London, 1986
- F. H. Titmuss, Commercial Timbers of the World, The Technical Press Ltd., London, 1965 Comment: 40-50 ppcf
- Encyclopedia Britannica, http://www.britannica.com Comment: "oak" Encyclopædia Britannica [Accessed October 24, 2001]
- Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia, at http://www.wikipedia.com Comment: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Oak (Accessed Oct. 8, 2005)
- R. J. Gettens, G.L. Stout, Painting Materials, A Short Encyclopaedia, Dover Publications, New York, 1966
- Caring for your Collections, Arthur W Schulz (ed.), Harry N. Abrams, Inc. , New York, 1992
- Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia, Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976
- The American Heritage Dictionary or Encarta, via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998
- CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, Robert Weast (ed.), CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, v. 61, 1980 Comment: density=37-56 ppcf (0.60-0.90 g/cm3)
- Marja-Sisko Ilvessalo-Pfäffli. Fiber Atlas: Identification of Papermaking Fibers (Springer Series in Wood Science). Springer, 1995.
- Walter Rantanen. "Fiber ID Course." Integrated Paper Services. June 2013. Lecture.