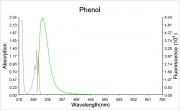
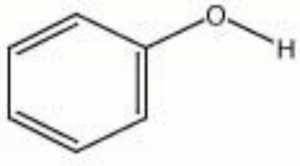
Phenol
Revision as of 07:32, 24 July 2013 by (username removed)
Description
Colorless or white acicular crystals with a characteristic odor. Phenol was discovered in coal-tar by Runge. It is used in the production of dyes and resins. Phenol is also used as an disinfectant and fungicide; it has been added to paints and glues as a preservative and odorant.
Synonyms and Related Terms
carbolic acid; phenylic acid; phenic acid; benzophenol; hydroxybenzene; oxybenzene; monohydroxybenzene
Other Properties
Soluble in water, ethanol, chloroform, ether, glycerol, carbon disulfide, oils, dilute alkalis.
| Composition | C6H5OH |
|---|---|
| CAS | 108-95-2 |
| Melting Point | 43 |
| Density | 1.071 |
| Molecular Weight | mol. wt.=94.11 |
| Refractive Index | 1.5425 |
| Boiling Point | 182 |
Hazards and Safety
Highly toxic by ingestion, inhalation and skin absorption. LD50 = 530 mg/kg
It is readily absorbed through the skin and causes severe burns.
Combustible. Flash point = 79 (174 F)
Mallinckrodt Baker: MSDS
Authority
- Ralph Mayer, A Dictionary of Art Terms and Techniques, Harper and Row Publishers, New York, 1969 (also 1945 printing)
- Susan E. Schur, Conservation Terminology: A review of Past & Current Nomenclature of Materials, Technology and Conservation, Spring (p.34-39); Summer (p.35-38); Fall (p.25-36), 1985
- Michael McCann, Artist Beware, Watson-Guptill Publications, New York City, 1979