Difference between revisions of "Polyethylene"
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
PE; polietileno (Esp.); polythylne (Fr.); polietilene (It.); polietileno (Port.); polyolefin; polythene; alkathene | PE; polietileno (Esp.); polythylne (Fr.); polietilene (It.); polietileno (Port.); polyolefin; polythene; alkathene | ||
| − | Examples: [[Volara]]; [[Ethafoam]]; [[Tyvek]] [DuPont]; [[Hi-Core]] [Matra Plast]; [[Tupperware]]; Lennite; Corrulite; Cellu-Cushion; Trirod; Ethalux; [[Plastazote]]; Colara; [[Correx]]; [[Polythene]]; Fortiflex; Poly-T | + | Examples: [[Volara]]; [[Ethafoam]]; [[Tyvek]] [DuPont]; [[Hi-Core]] [Matra Plast]; [[Tupperware]]; Lennite; Corrulite; Cellu-Cushion; Trirod; Ethalux; [[Plastazote]]; Colara; [[Correx]]; [[Polythene]]; Fortiflex; Poly-T; Sentinel; Cell=Aire, Microfoam |
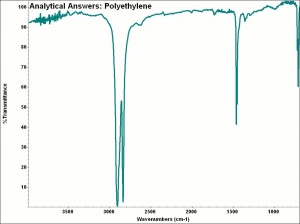
[[[SliderGallery rightalign|aaiP-ETHYLN.jpg~FTIR]]] | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|aaiP-ETHYLN.jpg~FTIR]]] | ||
Revision as of 15:52, 5 December 2020
Description
A thermoplastic polymerin the polyolefin familywith a base formula of [-CH2-]n. Ethylene was first polymerized in 1933 by ICI in England and was commercially released as Alkathene in 1939. In 1954, Karl Ziegler developed a process for high molecular weight polyethylene that allowed it to be spun into fibers, molded into durable but flexible forms and cast as tough thin sheets. Polyethylene made by the original process is now called Low density polyethylene (LDPE; density = 0.92, melting pt=110-120 C) because if has extensive branching resulting in a softer, more flexible product with low tensile strength. Polymers made by the later Ziegler or Phillips processes are called High density polyethylene or (HDPE; density=0.95-0.96, melting pt=130-138C) because they lave a low degree of branching resulting in high tensile strength. LDPE is softer, more flexible and has of lower tensile strength than HDPE [1], [2]. HDPE tends to have a longer lifespan than LDPE [1]. In general, polyethylenes are translucent waxy polymers with good impact strength that are widely used for packaging, coatings, liners, plastic sheets, wire coatings, underwater cables, containers, waste bags, toys, and squeeze bottles. Small amounts of additives (antioxidants, light stabilizers, slip agents, antistatic agents, flame retardants, pigments, etc.) are typically added to the final products. Polyethylene is recyclable and many products, such as Tyvek, contain the recycled polymer.
Examples include:
| Polyethylene Types | Forms | Products |
|---|---|---|
| High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) | Closed cell foam
(non-crosslinked) |
Sealed Air Corp. formerly Dow; Ethafoam 180, 220, 400, 600, 900, 180 AS, 220 AS Pregis Corp; PolyPlank |
| High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) | Closed-cell foam (cross-linked) | Sekisui Voltek; Volara
Zotefoams Ltd.; Plastazote MicroCell |
| High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) | Spun bonded fiber | DuPont; Tyvek-10(stiff), Tyvek-14(soft), Tyvek-16(perforated) |
| Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) |
Closed cell foam (non-crosslinked) | Sealed Air Corp.(Cellu-Cushion; Celluplank; Cell-Aire; Stratocell |
| Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) | Plastic film with sealed bubbles | Sealed Air Corp (Bubble Wrap, Polycap, Aircap) Pregis (Astro-Cell; Astro-Bubble; Astro-Suprabubble) |
Some brands available in Antistatic (Pink), Flame-retardant (Blue), and Recycled (Green).
Synonyms and Related Terms
PE; polietileno (Esp.); polythylne (Fr.); polietilene (It.); polietileno (Port.); polyolefin; polythene; alkathene
Examples: Volara; Ethafoam; Tyvek [DuPont]; Hi-Core [Matra Plast]; Tupperware; Lennite; Corrulite; Cellu-Cushion; Trirod; Ethalux; Plastazote; Colara; Correx; Polythene; Fortiflex; Poly-T; Sentinel; Cell=Aire, Microfoam
Applications
- Storage containers
- Transparent sheets and films
- Foams
- Hot-melt adhesives
- Spun-bonded fibers products
Personal Risks
Dow Corning: SDS
Collection Risks
- Degraded by ultraviolet light with discoloration, mechanical damage, and potential sulfur containing pollutants. Discoloration and mechanical damage will also occur in the dark at 50 degrees Celsius [2].
- May contain additives (such as antioxidant BHT) that can migrate to adjacent materials that may be absorbed by adjacent objects and cause staining [1].
- Slip agents such as alkyl amides may be transferred to objects
- Not as chemically stable as polyester films and not as clear.
- Polyethylene can be damaged by contact with objects that contain oils, fats, waxes or solvents., [1], [3]
- Slip agents, suck as alkyl amides may be transferred to objects
- Not susceptible to hydrolysis. “Highly hydrophobic polymers such as polyethylene and polypropylene are unlikely to have hydrolysable chemical groups, so are not subject to hydrolytic breakdown” [2].
Environmental Risks
Physical and Chemical Properties
- Soluble in xylene, trichlorobenzene, decane at room temperature and most chlorinated and aromatic solvents when gently heated.
- Insoluble in acetone, diethyl ether.
- Burns with yellow flame and blue center that smells like paraffin.
- Floats on water.
- CAS = 9002-88-4
- Melting Point = 110-138
- Density = 0.92-0.96
- Refractive Index = 1.52
Working Properties
Less transparent than polypropylene. Polyethylene has good chemical resistance.
Comparisons
Physical Properties for Selected Thermoplastic Resins
General Characteristics of Polymers
Resources and Citations
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Tetreault, Jean. Products Used in Preventative Conservation- Technical Bulletin 32. https://www.canada.ca/en/conservation-institute/services/conservation-preservation-publications/technical-bulletins/products-used-preventive-conservation.html#a3b1e
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Shashoua, Yvonne. Conservation of Plastics: Materials Science, Degradation and Preservation. Amsterdam etc.: Elsevier, 2008.
- ↑ Scott R. Williams. Plastic Storage Products. In ‘Preventive Conservation: Collection Storage’ Lisa Elkin and Christopher A. Norris (eds.), Society for the Preservation of Natural History Collections, New York. 2019. 773,774.
- Contributions: Gina Watkinson, AIC Plastics Panel, 2020.
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 304
- Marjorie Shelley, The Care and Handling of Art Objects, The Metropolitan Museum, New York, 1987
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- Rosalie Rosso King, Textile Identification, Conservation, and Preservation, Noyes Publications, Park Ridge, NJ, 1985
- Matt Roberts, Don Etherington, Matt Roberts, Don Etherington, Bookbinding and the Conservation of Books: a Dictionary of Descriptive Terminology, U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington DC, 1982
- Pam Hatchfield, Pollutants in the Museum Environment, Archetype Press, London, 2002
- Thomas C. Jester (ed.), Twentieth-Century Building Materials, McGraw-Hill Companies, Washington DC, 1995
- Random House, Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language, Grammercy Book, New York, 1997
- M.Kaufman, The First Century of Plastics, The Plastics and Rubber Institute, London, 1963
- Art and Architecture Thesaurus Online, http://www.getty.edu/research/tools/vocabulary/aat/, J. Paul Getty Trust, Los Angeles, 2000
- Website address 1 Comment: www.nswpmith.com.au/historyofplastics.html
- The Dictionary of Art, Grove's Dictionaries Inc., New York, 1996 Comment: "Plastics"
- Sharon Blank, An introduction to plastics and rubbers in collections, Studies in Conservation, 35, 53-63, 1990