Difference between revisions of "Polyvinylidene fluoride"
m (Text replace - "== Authority ==" to "== Sources Checked for Data in Record ==") |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
| − | A thermoplastic fluorocarbon polymer made from vinylidene fluoride. Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) can be molded, extruded, or cast. It is used for protective coatings and linings because of its excellent chemical resistance. PVDF is also resistant to weathering and UV light. | + | A thermoplastic fluorocarbon polymer made from vinylidene fluoride. Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) was invented and patented by the DuPont Corporation in 1948. Developed as a coating, its first widespread commercial use was as a pigmented liquid coating called Kynar 500®. It is often made into a copolymer with other fluorinated monomers in order to improve or modify its properties. PVDF can be molded, extruded, or cast. It is used for protective coatings and linings (often for metals) because of its excellent chemical resistance. PVDF is also resistant to weathering and UV light. |
== Synonyms and Related Terms == | == Synonyms and Related Terms == | ||
| − | PVDF; poli(fluoruro de vinilideno) (Esp.); fluorure de polyvinylidène (Fr.); polivinilidene fluoruro (It.); fluoreto de polivinilideno (Port.) | + | PVDF; Polyvinylidene difluoride; poly(vinylene fluoride); poli(fluoruro de vinilideno) (Esp.); fluorure de polyvinylidène (Fr.); polivinilidene fluoruro (It.); fluoreto de polivinilideno (Port.) |
| − | Examples: Kynar [Pennwalt Corp.] | + | Examples: Kynar [Pennwalt Corp.]; Kynar 500 (Arkema); Hylar 5000 (Solvay Solexis) ; Solef (Solvay); Sygef; poly(1,1-difluoroethane) |
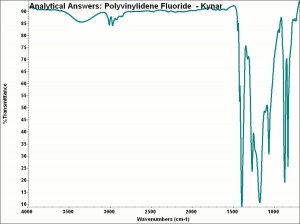
[[[SliderGallery rightalign|aaiKYNAR.jpg~FTIR]]] | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|aaiKYNAR.jpg~FTIR]]] | ||
| − | == | + | == Applications == |
| − | + | == Personal Risks == | |
| + | At room temperature and during normal use, this material is considered to be safe for handling. | ||
| − | + | Fluoropolymers will degrade upon prolonged heating or in a fire, liberating Hydrogen Fluoride (HF) and Carbonyl Fluoride (COF2). HF is toxic to skin and can damage bones if allowed to seep into the skin. COF2 is toxic if inhaled or it comes into contact with moist skin. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | == | + | == Collection Risks == |
| + | Unclear how this material would be introduced into a collection unless an artist had used industrial materials to make an object. This is an unusual polymer, ie, very specialized and hence very expensive. | ||
| − | + | == Environmental Risks == | |
| − | == | + | == Physical and Chemical Properties == |
| + | * Slightly soluble in n-butylamine, dimethylacetamide. | ||
| + | * Resistant to acids, alkalis, oxidizers, halogens. | ||
| + | * Composition = [-HC2=CF2-]n | ||
| + | * Melting Point = 171 | ||
| + | * Density = 1.7-1.8 | ||
| + | * Refractive Index = 1.42 | ||
| + | * Elongation = 300% | ||
| + | * Moisture regain = 0.4%. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Resources and Citations == | ||
| + | * Contributions: Catherine Stephens, AIC Plastics Panel, 2020 | ||
* Theodore J. Reinhart, 'Glossary of Terms', ''Engineered Plastics'', ASM International, 1988 | * Theodore J. Reinhart, 'Glossary of Terms', ''Engineered Plastics'', ASM International, 1988 | ||
Revision as of 10:30, 4 July 2020
Description
A thermoplastic fluorocarbon polymer made from vinylidene fluoride. Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) was invented and patented by the DuPont Corporation in 1948. Developed as a coating, its first widespread commercial use was as a pigmented liquid coating called Kynar 500®. It is often made into a copolymer with other fluorinated monomers in order to improve or modify its properties. PVDF can be molded, extruded, or cast. It is used for protective coatings and linings (often for metals) because of its excellent chemical resistance. PVDF is also resistant to weathering and UV light.
Synonyms and Related Terms
PVDF; Polyvinylidene difluoride; poly(vinylene fluoride); poli(fluoruro de vinilideno) (Esp.); fluorure de polyvinylidène (Fr.); polivinilidene fluoruro (It.); fluoreto de polivinilideno (Port.)
Examples: Kynar [Pennwalt Corp.]; Kynar 500 (Arkema); Hylar 5000 (Solvay Solexis) ; Solef (Solvay); Sygef; poly(1,1-difluoroethane)
Applications
Personal Risks
At room temperature and during normal use, this material is considered to be safe for handling.
Fluoropolymers will degrade upon prolonged heating or in a fire, liberating Hydrogen Fluoride (HF) and Carbonyl Fluoride (COF2). HF is toxic to skin and can damage bones if allowed to seep into the skin. COF2 is toxic if inhaled or it comes into contact with moist skin.
Collection Risks
Unclear how this material would be introduced into a collection unless an artist had used industrial materials to make an object. This is an unusual polymer, ie, very specialized and hence very expensive.
Environmental Risks
Physical and Chemical Properties
- Slightly soluble in n-butylamine, dimethylacetamide.
- Resistant to acids, alkalis, oxidizers, halogens.
- Composition = [-HC2=CF2-]n
- Melting Point = 171
- Density = 1.7-1.8
- Refractive Index = 1.42
- Elongation = 300%
- Moisture regain = 0.4%.
Resources and Citations
- Contributions: Catherine Stephens, AIC Plastics Panel, 2020
- Theodore J. Reinhart, 'Glossary of Terms', Engineered Plastics, ASM International, 1988
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- Pam Hatchfield, Pollutants in the Museum Environment, Archetype Press, London, 2002