Difference between revisions of "Pyrite"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
See also [[pyrrhotite|pyrrhotite]]. | See also [[pyrrhotite|pyrrhotite]]. | ||
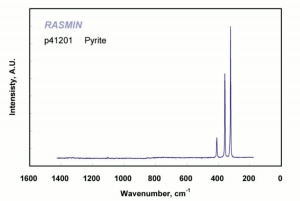
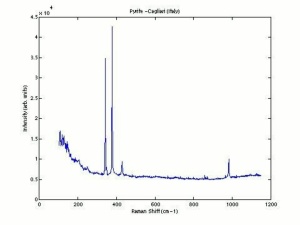
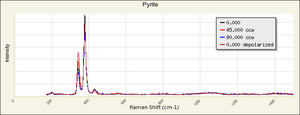
| − | [[ | + | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|pyriteRS.jpg~Raman (RASMIN)|Pyriteitaly2.jpg~Raman (U of Parma)|Pyrite Raman RRUFF R050190.png~Raman (RRUFF)]]] |
== Synonyms and Related Terms == | == Synonyms and Related Terms == | ||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
== Physical and Chemical Properties == | == Physical and Chemical Properties == | ||
| − | * Insoluble in water | + | * Insoluble in water |
| − | * Magnetic after heating | + | * Magnetic after heating (iron pyrite) |
* Crystal system = isometric | * Crystal system = isometric | ||
* Cleavage = poor | * Cleavage = poor | ||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
! scope="row"| Mohs Hardness | ! scope="row"| Mohs Hardness | ||
| 6.0 - 6.5 | | 6.0 - 6.5 | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Density | ! scope="row"| Density | ||
| Line 48: | Line 45: | ||
* Wikipedia: [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pyrite Pyrite] (Accessed Sept. 14, 2005 and Dec 2022) | * Wikipedia: [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pyrite Pyrite] (Accessed Sept. 14, 2005 and Dec 2022) | ||
* WebMinerals: [http://webmineral.com/data/Pyrite.shtml Pyrite] | * WebMinerals: [http://webmineral.com/data/Pyrite.shtml Pyrite] | ||
| − | |||
[[Category:Materials database]] | [[Category:Materials database]] | ||
Revision as of 13:17, 28 December 2022
Description
General name for any metal sulfide mineral. The name pyrite is also commonly used for one mineral form of Iron disulfide. Other types of pyrite include the sulfide salts of arsenic (Mispickel), copper (Chalcopyrite), cobalt (Smaltite) and tin. Ethanolamine thioglycollate treatments have been used to minimize the decomposition of pyritic specimens (Cornish 1984).
See also Pyrrhotite.
Synonyms and Related Terms
Fool's gold; iron disulfide; mundic; andodamus (Pliny); Pyrit (Deut.); pirita (Esp.); pyrite (Fr.); pyriet (Ned.); piryt (Pol.); pirite (Port.)
Risks
- Can evolve low levels of sulfur dioxide.
- Degrades in high humidity environments.
Physical and Chemical Properties
- Insoluble in water
- Magnetic after heating (iron pyrite)
- Crystal system = isometric
- Cleavage = poor
- Fracture = uneven
- Luster = metallic
- Streak = greenish black to brown
| Composition | FeS2 |
|---|---|
| Mohs Hardness | 6.0 - 6.5 |
| Density | 4.9-5.1 g/ml |
Resources and Citations
- L. Cornish, A.M. Doyle. "Use of Ethanolamine Thioglycollate in the Conservation of Pyritised Fossils" Palaeontology 27(2), 1984, 421-424.
- Gem Identification Lab Manual, Gemological Institute of America, 2016.
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 422
- Susan E. Schur, Conservation Terminology: A review of Past & Current Nomenclature of Materials, Technology and Conservation, Spring (p.34-39); Summer (p.35-38); Fall (p.25-36), 1985
- Jack Odgen, Jewellery of the Ancient World, Rizzoli International Publications Inc., New York City, 1982
- Pam Hatchfield, Pollutants in the Museum Environment, Archetype Press, London, 2002
- Wikipedia: Pyrite (Accessed Sept. 14, 2005 and Dec 2022)
- WebMinerals: Pyrite