Difference between revisions of "Red oak"
JMcGlinchey (talk | contribs) |
JMcGlinchey (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
==Other Properties== | ==Other Properties== | ||
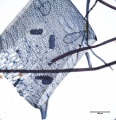
| − | Paper fiber type: hardwood, ring porous. Using transmitted light microscopy, pulp is identified by two sizes of vessels with profuse pitting. The smaller late wood vessels of red oak will stain darker than white oak. Vasocentric trachieds are worm-like and heavily pitted. Perforations are simple. Appearance with [[Graff "C" stain]]: dark blue, but varies with bleaching. Average dimensions of fibers: length 1.47mm, 14-22μm wide. Common pulping method: [[kraft process|kraft]]. | + | Paper fiber type: hardwood, ring porous. Using transmitted light microscopy, pulp is identified by two sizes of vessels with profuse pitting. The smaller late wood vessels of red oak will stain darker than white oak. Vasocentric trachieds are worm-like and heavily pitted. Perforations are simple. Tyloses are not present. Appearance with [[Graff "C" stain]]: dark blue, but varies with bleaching. Average dimensions of fibers: length 1.47mm, 14-22μm wide. Common pulping method: [[kraft process|kraft]]. |
== Additional Images == | == Additional Images == | ||
Revision as of 09:44, 15 July 2015
Description
Any of several oak trees, such as Quercus rubra, Quercus borealis, or Quercus falcata, native to eastern North America. Red oak trees have a hard, coarse-grain wood that is widely used commercially for flooring, furniture, cabinets, paneling, and millwork.
Synonyms and Related Terms
northern red oak (Quercus rubra, Quercus borealis); southern red oak (Quercus falcata); willow oak (Quercus phellos); scarlet oak (Quercus coccinea); pink oak; chêne pourpre (Fr.); carvalho vermelho (Port.); quercia rossa (It.)
Other Properties
Paper fiber type: hardwood, ring porous. Using transmitted light microscopy, pulp is identified by two sizes of vessels with profuse pitting. The smaller late wood vessels of red oak will stain darker than white oak. Vasocentric trachieds are worm-like and heavily pitted. Perforations are simple. Tyloses are not present. Appearance with Graff "C" stain: dark blue, but varies with bleaching. Average dimensions of fibers: length 1.47mm, 14-22μm wide. Common pulping method: kraft.
Additional Images
Authority
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 555
- Dictionary of Building Preservation, Ward Bucher, ed., John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York City, 1996
- Random House, Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language, Grammercy Book, New York, 1997
- The American Heritage Dictionary or Encarta, via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998
- Website address 1 Comment: Virginia Tech Dendrology website at www.fw.vt.edu/dendro/dendrology/main.htm (accessed Oct. 8, 2005)
- Marja-Sisko Ilvessalo-Pfäffli. Fiber Atlas: Identification of Papermaking Fibers (Springer Series in Wood Science). Springer, 1995.
- Walter Rantanen. "Fiber ID Course." Integrated Paper Services. June 2013. Lecture.