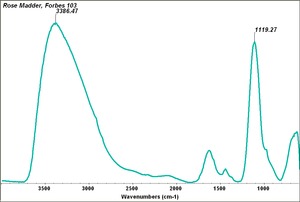
Rose madder
Revision as of 13:21, 4 August 2020 by MDerrick (talk | contribs) (→Sources Checked for Data in Record)
Description
A natural dark pink Madder colorant. Rose madder became popular as an artist pigment after the madder plant was imported to Holland in the 16th century. The colorant was extracted from madder roots with an acid, then the precipitate, primarily Pseudopurpurin, was redissolved in alum then reprecipitated with Calcium carbonate (chalk) to produce a pink lake (Schweppe and Winter 1997).
Synonyms and Related Terms
Natural red 9; rosa de garança (Port.); rose de garance (Fr.);
Other Properties
ASTM (1999) lightfastness = IV (poor)
Additional Information
H.Schweppe, J.Winter, "Madder and Alizarin", Artists Pigments, Volume 3, E. West FitzHugh (ed.), Oxford University Press: Oxford, 1997.
Additional Images
Resources and Citations
- Ralph Mayer, A Dictionary of Art Terms and Techniques, Harper and Row Publishers, New York, 1969 (also 1945 printing)
- Artists' Pigments: A Handbook of their History and Characteristics, Elisabeth West FitzHugh, Oxford University Press, Oxford, Vol. 3, 1997 Comment: H.Schweppe, J.Winter, "Madder and Alizarin",
- Comment: www.handprint.com - ASTM lightfastness = IV