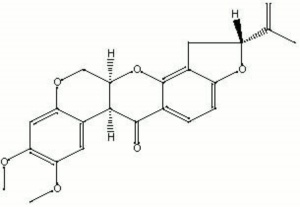
Rotenone
Description
Odorless, colorless, crystals that are highly toxic to insects and fish but only midly toxic to mammals. Rotenone naturally occurs in derris root and cubé. It was first isolated in 1895 by E. Geoffroy from the plant now called Lonchocarpus nicou. This powdered plant was used to catch fish by poisoning them. The pesticide is still used to eradicate exotic fish from non-native habitats. Rotenone is also used as an Insecticide, particularly in home gardens, due to its low toxicity to mammals. USDA allowed rotenone to be used on organic produce until 2005.
Synonyms and Related Terms
Tubatoxin; Prentox; Rotocide; Barbasco; Chem Fish; Cube; Deril
Other Properties
Soluble in alcohol, benzene, acetone, carbon tetrachloride, chloroform, ether. Insoluble in water.
| Composition | C23H22O6 |
|---|---|
| CAS | 83-79-4 |
| Melting Point | 165-166 |
| Density | 1.27 |
| Molecular Weight | mol. wt. = 394.4 |
| Boiling Point | 210-220 |
Hazards and Safety
Combustibe. Decomposes on exposure to light and air.
Ingestion, inhalation, and skin absorption causes irritation. Generally considered nontoxic to mammals but can cause death in large doses.
LINK: International Chemical Safety Card
Sources Checked for Data in Record
- The Merck Index, Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: entry 8138
- Random House, Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language, Grammercy Book, New York, 1997
- Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia, at http://www.wikipedia.com Comment: Rotenone (accessed Jan. 9 2009)