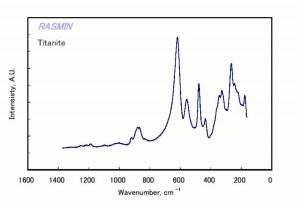
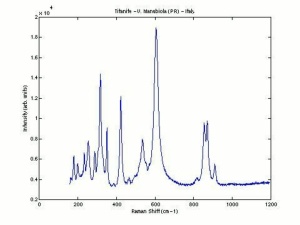
Difference between revisions of "Sphene"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
* Distinct cleavage in parallel planes | * Distinct cleavage in parallel planes | ||
* Luster = adamantine to resinous | * Luster = adamantine to resinous | ||
| − | * Fracture = conchoidal | + | * Fracture = conchoidal to splintery |
* Streak = white | * Streak = white | ||
* Fluorescence = none | * Fluorescence = none | ||
| + | * Pleochroism = moderate to strong | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| Line 30: | Line 31: | ||
! scope="row"| Refractive Index | ! scope="row"| Refractive Index | ||
| 1.84 - 2.11 | | 1.84 - 2.11 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row"| Birefringence | ||
| + | | 0.100 - 0.135 (visible doubling) | ||
|} | |} | ||
==Resources and Citations== | ==Resources and Citations== | ||
| + | * Gem Identification Lab Manual, Gemological Institute of America, 2016. | ||
| + | * Mineralogy Database: [http://www.webmineral.com/data/Titanite.shtml Titanite] | ||
| + | * ''Encyclopedia Britannica'', http://www.britannica.com Comment: "sphene" [Accessed December 4, 2001] | ||
| + | * C.W.Chesterman, K.E.Lowe, ''Audubon Society Field Guide to North American Rocks and Minerals'', Alfred A. Knopf, New York, 1979 | ||
| + | * Wikipedia: [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Titanite Titanite] (Accessed Sept. 17, 2005 and Dec 2022) | ||
| + | * ''Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia'', Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976 | ||
| + | * Random House, ''Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language'', Grammercy Book, New York, 1997 | ||
| + | * ''The American Heritage Dictionary'' or ''Encarta'', via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998 | ||
| − | |||
[[Category:Materials database]] | [[Category:Materials database]] | ||
Revision as of 15:23, 19 December 2022
Description
Small yellow, green or brown crystals (also called titanite) occasionally used as gemstones. Sphene is composed of calcium titanium silicate and is often found associated with granite. Sphene has good luster and fire but is too soft for general wear. Gem quality sphene crystals come from the Austrian and Swiss Alps, Myanmar, Canada (Ontario) and the U.S. (California, New York, Montana).
Synonyms and Related Terms
titanite; esfena, titanita (Esp.); esfena (Port.); Sphen, Titanit (Deut.); sfeen (Ned.)
Physical and Chemical Properties
- Monoclinic system, often forming wedge-shaped, twinned crystals; sometimes compact, massive
- Distinct cleavage in parallel planes
- Luster = adamantine to resinous
- Fracture = conchoidal to splintery
- Streak = white
- Fluorescence = none
- Pleochroism = moderate to strong
| Composition | CaTiSiO5 |
|---|---|
| Mohs Hardness | 5.0 - 5.5 |
| Density | 3.4-3.6 g/ml |
| Refractive Index | 1.84 - 2.11 |
| Birefringence | 0.100 - 0.135 (visible doubling) |
Resources and Citations
- Gem Identification Lab Manual, Gemological Institute of America, 2016.
- Mineralogy Database: Titanite
- Encyclopedia Britannica, http://www.britannica.com Comment: "sphene" [Accessed December 4, 2001]
- C.W.Chesterman, K.E.Lowe, Audubon Society Field Guide to North American Rocks and Minerals, Alfred A. Knopf, New York, 1979
- Wikipedia: Titanite (Accessed Sept. 17, 2005 and Dec 2022)
- Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia, Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976
- Random House, Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language, Grammercy Book, New York, 1997
- The American Heritage Dictionary or Encarta, via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998