Difference between revisions of "Sudan Black B"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m (Text replace - "\[http:\/\/cameo\.mfa\.org\/materials\/fullrecord\.asp\?name=([^\s]+)\s(.*)\]" to "$2") |
|||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
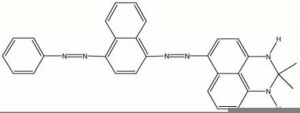
[[[SliderGallery rightalign|Sudan Black B.jpg~Chemical structure]]] | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|Sudan Black B.jpg~Chemical structure]]] | ||
| − | == | + | == Physical and Chemical Properties == |
Soluble in nonpolar solvents. Maximum absorption wavelength = 598 nm. | Soluble in nonpolar solvents. Maximum absorption wavelength = 598 nm. | ||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Melting Point | ! scope="row"| Melting Point | ||
| − | | 120-124 | + | | 120-124 C |
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Molecular Weight | ! scope="row"| Molecular Weight | ||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | == | + | == Risks == |
| − | Contact may cause irritation. | + | * Contact may cause irritation. |
| + | * Fisher Scientific: [https://fscimage.fishersci.com/msds/01919.htm MSDS] | ||
| − | + | == Additional Information == | |
| − | + | * J.Messinger, "Ultraviolet-Fluorescence Microscopy of Paint Cross Sections", 31(3):267-274, 1992. [http://aic.stanford.edu/jaic/articles/jaic31-03-001_indx.html Link] | |
| − | + | * R.Wolbers, G.Landry, "The Use of Direct Reactive Fluorescent Dyes for the Characterization of Binding Media in Cross Sectional Examinations" in Preprints of the AIC Meeting in Vancouver, 1987. | |
| − | + | * M.Johnson, E.Packard, "Methods Used for Identification of Binding Media in Italian paintings of the 15th and 16th Centuries" ''Studies in Conservation'', 16:145-164, 1971. | |
* Aldrich Chemical Catalog | * Aldrich Chemical Catalog | ||
Revision as of 13:39, 6 June 2022
Description
A nonfluorescent black biological stain. Sudan Black B is a diazo type dye that has been used as a general stain for oils and fats. It also stains acrylic emulsions (Messinger 1992).
Synonyms and Related Terms
SB; CI 26150; Fat Black HB; Solvent Black 3; negro sudán B (Esp.)
Physical and Chemical Properties
Soluble in nonpolar solvents. Maximum absorption wavelength = 598 nm.
| Composition | C29H24N6 |
|---|---|
| CAS | 4197-25-5 |
| Melting Point | 120-124 C |
| Molecular Weight | mol. wt. = 456.2082 |
Risks
- Contact may cause irritation.
- Fisher Scientific: MSDS
Additional Information
- J.Messinger, "Ultraviolet-Fluorescence Microscopy of Paint Cross Sections", 31(3):267-274, 1992. Link
- R.Wolbers, G.Landry, "The Use of Direct Reactive Fluorescent Dyes for the Characterization of Binding Media in Cross Sectional Examinations" in Preprints of the AIC Meeting in Vancouver, 1987.
- M.Johnson, E.Packard, "Methods Used for Identification of Binding Media in Italian paintings of the 15th and 16th Centuries" Studies in Conservation, 16:145-164, 1971.
- Aldrich Chemical Catalog