Difference between revisions of "Triacetate fiber"
(username removed) |
(username removed) |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
| − | A manufactured fiber produced from [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=cellulose | + | A manufactured fiber produced from [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=cellulose%20triacetate cellulose triacetate]. Cellulose triacetate was first developed by Schutzenberger in 1865. However, this early acetate was a tough hard [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=plastic plastic] that contained high amounts of [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=acid acids] and was only soluble in expensive chlorinated [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=solvent solvents]. Thus, cellulose triacetate was not commercially viable until the mid-1950s when economical solvents became available. Triacetate is a durable fiber that is resistant to wrinkles, stains, chemicals, sunlight, insects, and moisture. It should not be dry-cleaned but is not degraded by normal laundering. It dries quickly in air or cool driers and maintains its shape without ironing. Triacetate is a crisp, firm fabric that is often used in [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=taffeta taffetas] and [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=suiting suitings]. It is used in drip-dry clothing, tablecloths, skirts, and slacks. It is often used in wool blends to increase washability and crease retention. A surface saponification finishing process, called S-Finishing, is often applied to triacetate fabrics to minimize static. |
| − | See also [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=acetate | + | See also [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=acetate%20fiber acetate fiber]. |
| − | |||
== Synonyms and Related Terms == | == Synonyms and Related Terms == | ||
| − | triacetate fibre; | + | triacetate fibre; Arnel® [Celanese, America]; Tricel [British Celanese]; Trilan; primary acetate; JPS [Courtaulds]; Courpleta [Courtaulds];fibra de triacetato(Esp.) |
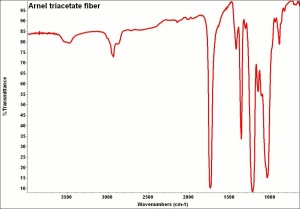
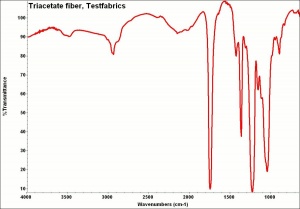
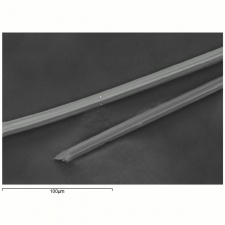
| − | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|arnel500m.jpg~SEM]]] | + | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|Arnelfiberkj1.jpg~FTIR|TriacetateTestfabrics.jpg~FTIR|arnel500m.jpg~SEM]]] |
== Other Properties == | == Other Properties == | ||
| Line 35: | Line 34: | ||
== Additional Information == | == Additional Information == | ||
| − | G.Cook, ''Handbook of Textile Fibres:II. Man-made Fibres'', 5th edition, Merrow Publishing Co., Durham, England, 1984. p.99. | + | ° G.Cook, ''Handbook of Textile Fibres:II. Man-made Fibres'', 5th edition, Merrow Publishing Co., Durham, England, 1984. p.99. |
== Comparisons == | == Comparisons == | ||
| Line 41: | Line 40: | ||
[[media:download_file_44.pdf|Properties of Synthetic Fibers]] | [[media:download_file_44.pdf|Properties of Synthetic Fibers]] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
== Authority == | == Authority == | ||
| − | * | + | * Hoechst Celanese Corporation, ''Dictionary of Fiber & Textile Technology'' (older version called Man-made Fiber and Textile Dictionary, 1965), Hoechst Celanese Corporation, Charlotte NC, 1990 |
| − | * | + | * Rosalie Rosso King, ''Textile Identification, Conservation, and Preservation'', Noyes Publications, Park Ridge, NJ, 1985 |
| − | * | + | * Marjory L. Joseph, ''Introductory Textile Science'', Holt, Rinehart and Winston, Fort Worth, TX, 1986 |
* ''Identification of Textile Materials'', The Textile Institute, Manchester, England, 1985 | * ''Identification of Textile Materials'', The Textile Institute, Manchester, England, 1985 | ||
| − | * | + | * J.Gordon Cook, ''Handbook of Textile Fibres:II Man-made Fibres'', Merrow Publishing Co. , Durham, England |
* Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia, at http://www.wikipedia.com Comment: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Triacetate (Accessed Nov. 9, 2005) | * Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia, at http://www.wikipedia.com Comment: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Triacetate (Accessed Nov. 9, 2005) | ||
Revision as of 07:34, 24 July 2013
Description
A manufactured fiber produced from cellulose triacetate. Cellulose triacetate was first developed by Schutzenberger in 1865. However, this early acetate was a tough hard plastic that contained high amounts of acids and was only soluble in expensive chlorinated solvents. Thus, cellulose triacetate was not commercially viable until the mid-1950s when economical solvents became available. Triacetate is a durable fiber that is resistant to wrinkles, stains, chemicals, sunlight, insects, and moisture. It should not be dry-cleaned but is not degraded by normal laundering. It dries quickly in air or cool driers and maintains its shape without ironing. Triacetate is a crisp, firm fabric that is often used in taffetas and suitings. It is used in drip-dry clothing, tablecloths, skirts, and slacks. It is often used in wool blends to increase washability and crease retention. A surface saponification finishing process, called S-Finishing, is often applied to triacetate fabrics to minimize static.
See also acetate fiber.
Synonyms and Related Terms
triacetate fibre; Arnel® [Celanese, America]; Tricel [British Celanese]; Trilan; primary acetate; JPS [Courtaulds]; Courpleta [Courtaulds];fibra de triacetato(Esp.)
Other Properties
Soluble in chloroform, methylene chloride, m-cresol, 90% phenol. Insoluble in acetone. Unaffected by dilute acids, alkalis and bleaches. Cross section is bulbous; fiber has longitudinal striations Tenacity = 1.1-1.4 g/denier (dry) ; 0.7-0.8 g/denier (wet); Elongation 25-35% (dry); 30-40% (wet) Moisture regain = 2.5-3.5%
| CAS | 9012-09-3 |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | 300 |
| Density | 1.32 |
Hazards and Safety
Subject to static cling
Additional Information
° G.Cook, Handbook of Textile Fibres:II. Man-made Fibres, 5th edition, Merrow Publishing Co., Durham, England, 1984. p.99.
Comparisons
Properties of Synthetic Fibers
Authority
- Hoechst Celanese Corporation, Dictionary of Fiber & Textile Technology (older version called Man-made Fiber and Textile Dictionary, 1965), Hoechst Celanese Corporation, Charlotte NC, 1990
- Rosalie Rosso King, Textile Identification, Conservation, and Preservation, Noyes Publications, Park Ridge, NJ, 1985
- Marjory L. Joseph, Introductory Textile Science, Holt, Rinehart and Winston, Fort Worth, TX, 1986
- Identification of Textile Materials, The Textile Institute, Manchester, England, 1985
- J.Gordon Cook, Handbook of Textile Fibres:II Man-made Fibres, Merrow Publishing Co. , Durham, England
- Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia, at http://www.wikipedia.com Comment: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Triacetate (Accessed Nov. 9, 2005)
- Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia, Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976