Siderite
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Description
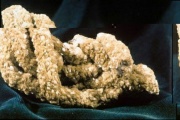
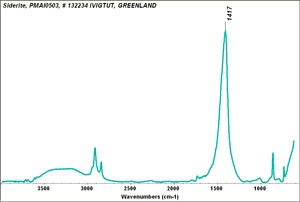
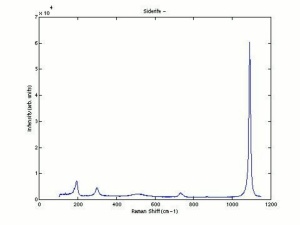
1) A yellowish-brown iron ore composed of iron carbonate. Siderite, also called chalybite, is mined in England, Austria, Czech Republic, France, Italy, Greenland, Australia, Brazil, Bolivia, and the U.S. It has a specific gravity of 3.83-3.88 along with an uneven fracture, pearly luster, and pale yellow streak.
2) A metallic Meteorite composed primarily of Iron and Nickel.
Synonyms and Related Terms
chalybite; spathic iron ore; siderita (Esp.); sidérite (Fr.); siderite (Port.); Siderit (Deut.); sideriet (Ned.)
Physical and Chemical Properties
- Hexagonal crystal system.
- Perfect cleavage in three directions forming a rhobohedron.
- Fracture = uneven.
- Streak = pale yellow.
- Luster = vitreous to dull.
| Composition | FeCO3 |
|---|---|
| Mohs Hardness | (1) 3.5 - 4.0 |
| Density | 3.8-3.9 g/ml |
Resources and Citations
- Mineralogy Database: Siderite
- Encyclopedia Britannica, http://www.britannica.com Comment: "siderite." Accessed 9 Dec. 2004.
- C.W.Chesterman, K.E.Lowe, Audubon Society Field Guide to North American Rocks and Minerals, Alfred A. Knopf, New York, 1979
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 421
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia, Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976
- Random House, Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language, Grammercy Book, New York, 1997
- The American Heritage Dictionary or Encarta, via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998