Difference between revisions of "Tupelo"
JMcGlinchey (talk | contribs) |
|||
| (8 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | [[File:45_Tupleo.jpg|thumb|Tupelo | + | [[File:Wellesley College Tupelo point.jpg|thumb|Tupelo Point Wellesley College]][[File:45_Tupleo.jpg|thumb|Tupelo (''Nyssa aquatica'')]] |
| − | |||
| − | (''Nyssa aquatica'')]] | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
| − | A medium sized deciduous tree, such as Nyssa sylvatica and Nyssa aquatica, native to the eastern United States. Tupelo trees produce a stiff, tough wood that is hard to split. It is used for pallets, baskets, boxes, veneer, barrels and firewood. Tupelo bark dye has good washfastness and fair lightfastness. | + | A medium sized deciduous tree, such as ''Nyssa sylvatica'' and ''Nyssa aquatica'', native to the eastern United States. Tupelo trees produce a stiff, tough wood that is hard to split. It is used for pallets, baskets, boxes, veneer, barrels and firewood. [[Tupelo bark]] dye has good washfastness and fair lightfastness. |
== Synonyms and Related Terms == | == Synonyms and Related Terms == | ||
| − | black gum (Nyssa sylvatica); sour gum; pepperidge; beetlebung; water tupelo (Nyssa aquatica) | + | black gum (''Nyssa sylvatica''); sour gum; pepperidge; beetlebung; water tupelo (''Nyssa aquatica'') |
| − | == | + | == Physical and Chemical Properties == |
| − | Medium sized tree growing to 25 m. Bark=grayish brown with shallow, irregular furrows. Leaf=simple alternate, pinnately veined oval (3-5 inches long) with coarse teeth, turning an intense red/purple color in fall. | + | * Medium sized tree growing to 25 m. |
| − | + | * Bark=grayish brown with shallow, irregular furrows. | |
| − | + | * Leaf=simple alternate, pinnately veined oval (3-5 inches long) with coarse teeth, turning an intense red/purple color in fall. | |
| − | + | * Fruit = purple drupe (1 cm) ripening in late summer. | |
| − | + | * Density = 35 ppcf. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
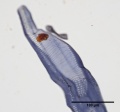
Paper fiber type: hardwood, diffuse porous. Using transmitted light microscopy, pulp is identified by long vessels with profuse opposite pitting. Spirals may be present on tips. Perforations are scalariform with >15 bars. Appearance with [[Graff "C" stain]]: dark blue, but varies with bleaching. Average dimensions of fibers: length, 1.8mm. 20-32μm wide. Common pulping method: [[kraft process|kraft]]. | Paper fiber type: hardwood, diffuse porous. Using transmitted light microscopy, pulp is identified by long vessels with profuse opposite pitting. Spirals may be present on tips. Perforations are scalariform with >15 bars. Appearance with [[Graff "C" stain]]: dark blue, but varies with bleaching. Average dimensions of fibers: length, 1.8mm. 20-32μm wide. Common pulping method: [[kraft process|kraft]]. | ||
| − | == | + | ==Additional Images== |
| + | <gallery> | ||
| + | Blackgum opp pitting 40x.jpg|Black gum paper pulp stained with Graff "C" stain | ||
| + | Blackgum 40x.jpg|Black gum paper pulp stained with Graff "C" stain | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | ==Resources and Citations== | ||
* R.J. Adrosko, ''Natural Dyes in the United States'', Smithsonian Institution Press, Washington, DC, 1968 | * R.J. Adrosko, ''Natural Dyes in the United States'', Smithsonian Institution Press, Washington, DC, 1968 | ||
| − | |||
* G.S.Brady, ''Materials Handbook'', McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 380 | * G.S.Brady, ''Materials Handbook'', McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 380 | ||
| − | |||
* John and Margaret Cannon, ''Dye Plants and Dyeing'', Herbert Press, London, 1994 | * John and Margaret Cannon, ''Dye Plants and Dyeing'', Herbert Press, London, 1994 | ||
| − | + | * Hardwood Manufacturers Institute, Memphis, Tenn.: air-dry weight = 35 ppcf | |
| − | * | ||
| − | |||
* Edward Reich, Carlton J. Siegler, ''Consumer Goods: How to Know and Use Them'', American Book Company, New York City, 1937 | * Edward Reich, Carlton J. Siegler, ''Consumer Goods: How to Know and Use Them'', American Book Company, New York City, 1937 | ||
| − | + | * Wikipedia: [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tupelo_(tree) Tupelo] (Accessed Dec. 9, 2005 and October 2024) | |
| − | * Wikipedia | ||
| − | |||
* ''Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia'', Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976 | * ''Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia'', Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976 | ||
| − | |||
* Marja-Sisko Ilvessalo-Pfäffli. ''Fiber Atlas: Identification of Papermaking Fibers'' (Springer Series in Wood Science). Springer, 1995. | * Marja-Sisko Ilvessalo-Pfäffli. ''Fiber Atlas: Identification of Papermaking Fibers'' (Springer Series in Wood Science). Springer, 1995. | ||
| + | * Walter Rantanen. "Fiber ID Course." Integrated Paper Services. June 2013. Lecture. | ||
| − | |||
[[Category:Materials database]] | [[Category:Materials database]] | ||
Latest revision as of 11:59, 18 November 2024
Description
A medium sized deciduous tree, such as Nyssa sylvatica and Nyssa aquatica, native to the eastern United States. Tupelo trees produce a stiff, tough wood that is hard to split. It is used for pallets, baskets, boxes, veneer, barrels and firewood. Tupelo bark dye has good washfastness and fair lightfastness.
Synonyms and Related Terms
black gum (Nyssa sylvatica); sour gum; pepperidge; beetlebung; water tupelo (Nyssa aquatica)
Physical and Chemical Properties
- Medium sized tree growing to 25 m.
- Bark=grayish brown with shallow, irregular furrows.
- Leaf=simple alternate, pinnately veined oval (3-5 inches long) with coarse teeth, turning an intense red/purple color in fall.
- Fruit = purple drupe (1 cm) ripening in late summer.
- Density = 35 ppcf.
Paper fiber type: hardwood, diffuse porous. Using transmitted light microscopy, pulp is identified by long vessels with profuse opposite pitting. Spirals may be present on tips. Perforations are scalariform with >15 bars. Appearance with Graff "C" stain: dark blue, but varies with bleaching. Average dimensions of fibers: length, 1.8mm. 20-32μm wide. Common pulping method: kraft.
Additional Images
Resources and Citations
- R.J. Adrosko, Natural Dyes in the United States, Smithsonian Institution Press, Washington, DC, 1968
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 380
- John and Margaret Cannon, Dye Plants and Dyeing, Herbert Press, London, 1994
- Hardwood Manufacturers Institute, Memphis, Tenn.: air-dry weight = 35 ppcf
- Edward Reich, Carlton J. Siegler, Consumer Goods: How to Know and Use Them, American Book Company, New York City, 1937
- Wikipedia: Tupelo (Accessed Dec. 9, 2005 and October 2024)
- Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia, Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976
- Marja-Sisko Ilvessalo-Pfäffli. Fiber Atlas: Identification of Papermaking Fibers (Springer Series in Wood Science). Springer, 1995.
- Walter Rantanen. "Fiber ID Course." Integrated Paper Services. June 2013. Lecture.