Difference between revisions of "Acetic anhydride"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(username removed) |
(→Risks) |
||
| (6 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
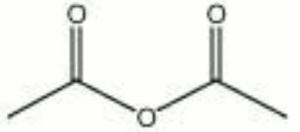
| − | A colorless liquid with a strong [ | + | A colorless liquid with a strong [[acetic acid]] odor. Acetic anhydride is a strong acetylating agent and is used primarily for the production of [[cellulose%20acetate|cellulose acetate]] fibers and plastics. It is also used in the production of pharmaceuticals, dyes, perfumes, and explosives. |
| − | + | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|acetic anhydride.jpg~Chemical structure]]] | |
== Synonyms and Related Terms == | == Synonyms and Related Terms == | ||
acetic acid anhydride; acetyl oxide; acetic oxide; ethanoic anhydride | acetic acid anhydride; acetyl oxide; acetic oxide; ethanoic anhydride | ||
| − | [ | + | == Risks == |
| + | |||
| + | * Readily combustible, fire hazard. | ||
| + | * Overexposure may result in edema, eye irritation, cough, skin burns and dermatitis. | ||
| + | * ThermoFisher: [https://www.fishersci.com/store/msds?partNumber=S25119A&productDescription=ACETIC+ANHYDRIDE+500ML&vendorId=VN00115888&countryCode=US&language=en SDS] | ||
| − | == | + | == Physical and Chemical Properties == |
Reacts with water slowly to form acetic acid. Reacts with alcohols to form the corresponding acetate. Soluble in chloroform and ether. | Reacts with water slowly to form acetic acid. Reacts with alcohols to form the corresponding acetate. Soluble in chloroform and ether. | ||
| Line 22: | Line 26: | ||
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Melting Point | ! scope="row"| Melting Point | ||
| − | | -73 | + | | -73 C |
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Density | ! scope="row"| Density | ||
| − | | 1.080 | + | | 1.080 g/ml |
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Molecular Weight | ! scope="row"| Molecular Weight | ||
| Line 34: | Line 38: | ||
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Boiling Point | ! scope="row"| Boiling Point | ||
| − | | 139 | + | | 139 C |
|} | |} | ||
| − | == | + | == Resources and Citations == |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | * | + | * Richard S. Lewis, ''Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary'', Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993 |
* ''The Merck Index'', Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: ref. index=1.3904 | * ''The Merck Index'', Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: ref. index=1.3904 | ||
| − | * | + | * G.S.Brady, ''Materials Handbook'', McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p.8 |
| − | * | + | * Hoechst Celanese Corporation, ''Dictionary of Fiber & Textile Technology'' (older version called Man-made Fiber and Textile Dictionary, 1965), Hoechst Celanese Corporation, Charlotte NC, 1990 |
* ''CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics'', Robert Weast (ed.), CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, v. 61, 1980 Comment: ref. index=1.389 | * ''CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics'', Robert Weast (ed.), CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, v. 61, 1980 Comment: ref. index=1.389 | ||
Latest revision as of 14:29, 9 September 2022
Description
A colorless liquid with a strong Acetic acid odor. Acetic anhydride is a strong acetylating agent and is used primarily for the production of Cellulose acetate fibers and plastics. It is also used in the production of pharmaceuticals, dyes, perfumes, and explosives.
Synonyms and Related Terms
acetic acid anhydride; acetyl oxide; acetic oxide; ethanoic anhydride
Risks
- Readily combustible, fire hazard.
- Overexposure may result in edema, eye irritation, cough, skin burns and dermatitis.
- ThermoFisher: SDS
Physical and Chemical Properties
Reacts with water slowly to form acetic acid. Reacts with alcohols to form the corresponding acetate. Soluble in chloroform and ether.
| Composition | (CH3CO)2O |
|---|---|
| CAS | 108-24-7 |
| Melting Point | -73 C |
| Density | 1.080 g/ml |
| Molecular Weight | mol. wt. = 102.2 |
| Refractive Index | 1.3904 |
| Boiling Point | 139 C |
Resources and Citations
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- The Merck Index, Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: ref. index=1.3904
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p.8
- Hoechst Celanese Corporation, Dictionary of Fiber & Textile Technology (older version called Man-made Fiber and Textile Dictionary, 1965), Hoechst Celanese Corporation, Charlotte NC, 1990
- CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, Robert Weast (ed.), CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, v. 61, 1980 Comment: ref. index=1.389