Difference between revisions of "Agate"
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
May contain silica dust; chronic inhalation can cause silicosis. | May contain silica dust; chronic inhalation can cause silicosis. | ||
| − | == | + | == Physical and Chemical Properties == |
| − | Fracture = conchoidal. Luster = vitreous to waxy. Streak = white to none | + | * Fracture = conchoidal. |
| − | + | * Luster = vitreous to waxy. | |
| − | Colors may include white, grey, light blue, orange, red, and black. | + | * Streak = white to none |
| − | + | * Colors may include white, grey, light blue, orange, red, and black. | |
| − | Crystal system=hexagonal | + | * Crystal system=hexagonal |
| − | + | * Mohs Hardness = 7.0 | |
| − | + | * Density = 2.65 g/ml | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
== Comparisons == | == Comparisons == | ||
Revision as of 15:30, 24 April 2022
Description
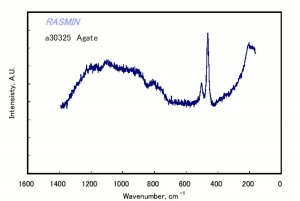
A cryptocrystalline variety of Silica, showing a variegated banded structure and waxy luster. Agate bands are due to the deposition of successive mineral layers from solution and may be either straight, wavy, or concentric. Agate is slightly harder than Quartz. It has been gathered or mined since Neolithic times. Sources for agate include western Asia, India, Brazil, Uruguay, and Germany. Onyx is a type of agate in which the bands are parallel. Sardonyx is a variety of onyx that has alternating red and cream layers. Moss agates contain brown dendritic or fernlike patterns. Agates are used for gemstones, beads, amulets, mortars and pestles, burnishers for gilding, textile rollers, knife edges, and as ornamental stones.
Synonyms and Related Terms
Achat (Deut.); agat (Dan., Pol.); ágata (Esp., Port.); agathe (Fr.); agaat (Ned.)
Examples include: onyx; sardonyx
Risks
May contain silica dust; chronic inhalation can cause silicosis.
Physical and Chemical Properties
- Fracture = conchoidal.
- Luster = vitreous to waxy.
- Streak = white to none
- Colors may include white, grey, light blue, orange, red, and black.
- Crystal system=hexagonal
- Mohs Hardness = 7.0
- Density = 2.65 g/ml
Comparisons
Properties of Common Gemstones
Additional Images
Resources and Citations
- Mineralogy Database: Quartz
- CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, Robert Weast (ed.), CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, v. 61, 1980 Comment: density = 2.5-2.7
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p.21
- Ralph Mayer, A Dictionary of Art Terms and Techniques, Harper and Row Publishers, New York, 1969 (also 1945 printing)
- Matt Roberts, Don Etherington, Bookbinding and the Conservation of Books: a Dictionary of Descriptive Terminology, U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington DC, 1982
- Robert Fournier, Illustrated Dictionary of Practical Pottery, Chilton Book Company, Radnor, PA, 1992
- C.W.Chesterman, K.E.Lowe, Audubon Society Field Guide to North American Rocks and Minerals, Alfred A. Knopf, New York, 1979
- Michael McCann, Artist Beware, Watson-Guptill Publications, New York City, 1979
- Sue Fuller, Rocks and Minerals, DK Publishing, Inc., New York City, 1995
- Jack Odgen, Jewellery of the Ancient World, Rizzoli International Publications Inc., New York City, 1982
- A.Lucas, J.R.Harris, Ancient Egyptian Materials and Industries, Edward Arnold Publishers Ltd., London, 4th edition, 1962