Difference between revisions of "Aluminum potassium sulfate"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| (7 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
| − | A white odorless powder with transparent crystals. Aluminum potassium sulfate occurs naturally in the minerals [[alunite|alunite]] and leucite. It has been used since ancient times as a [[mordant|mordant]] in dyeing textiles and for tawing skins. Aluminum potassium sulfate, or potash alum, is also used as a filler in [ | + | A white odorless powder with transparent crystals. Aluminum potassium sulfate occurs naturally in the minerals [[alunite|alunite]] and leucite. It has been used since ancient times as a [[mordant|mordant]] in dyeing textiles and for tawing skins. Aluminum potassium sulfate, or potash alum, is also used as a filler in [[paper|paper]], [[cement|cement]], and [[paint|paints]]. It is used to harden [[gelatin|gelatin]], [[plaster|plaster]], and cement. Potash alum has also been used as a substrate in the preparation of lake pigments. |
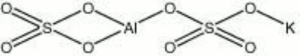
| − | + | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|aluminum potassium sulfate.jpg~Chemical structure]]] | |
| − | [[ | + | == Synonyms and Related Terms == |
| − | + | potassium aluminum sulfate; aluminum potassium sulphate (Br.); potash alum; alum NF; potassium alum; kalinite; alum flour; alum meal; cube alum; alumstone; common alum | |
| − | + | == Risks == | |
| − | [ | + | * Noncombustible. |
| + | * Harmful by ingestion and inhalation. | ||
| + | * Contact causes irritation. | ||
| + | * Fisher Scientific: [https://beta-static.fishersci.com/content/dam/fishersci/en_US/documents/programs/education/regulatory-documents/sds/chemicals/chemicals-a/S25152D.pdf SDS] | ||
| − | == | + | == Physical and Chemical Properties == |
Soluble in water. Insoluble in ethanol. | Soluble in water. Insoluble in ethanol. | ||
| Line 28: | Line 31: | ||
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Melting Point | ! scope="row"| Melting Point | ||
| − | | 92 | + | | 92 C |
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Density | ! scope="row"| Density | ||
| − | | 1.75 | + | | 1.75 g/ml |
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Molecular Weight | ! scope="row"| Molecular Weight | ||
| Line 37: | Line 40: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | == | + | ==Resources and Citations== |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | * Irene Bruckle, "The Role of Alum in Historical Papermaking", Abbey Newsletter, Volume 17(4), September 1993. [http://cool.conservation-us.org/byorg/abbey/an/an17/an17-4/an17-407.html Link] | |
* G.S.Brady, ''Materials Handbook'', McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 32, 33 | * G.S.Brady, ''Materials Handbook'', McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 32, 33 | ||
Latest revision as of 15:03, 2 July 2022
Description
A white odorless powder with transparent crystals. Aluminum potassium sulfate occurs naturally in the minerals Alunite and leucite. It has been used since ancient times as a Mordant in dyeing textiles and for tawing skins. Aluminum potassium sulfate, or potash alum, is also used as a filler in Paper, Cement, and paints. It is used to harden Gelatin, Plaster, and cement. Potash alum has also been used as a substrate in the preparation of lake pigments.
Synonyms and Related Terms
potassium aluminum sulfate; aluminum potassium sulphate (Br.); potash alum; alum NF; potassium alum; kalinite; alum flour; alum meal; cube alum; alumstone; common alum
Risks
- Noncombustible.
- Harmful by ingestion and inhalation.
- Contact causes irritation.
- Fisher Scientific: SDS
Physical and Chemical Properties
Soluble in water. Insoluble in ethanol.
| Composition | Al2(SO4)3-K2SO4-24H2O |
|---|---|
| CAS | 7784-24-9 |
| Mohs Hardness | 3.5 - 4.0 |
| Melting Point | 92 C |
| Density | 1.75 g/ml |
| Molecular Weight | mol. wt. = 474.38 |
Resources and Citations
- Irene Bruckle, "The Role of Alum in Historical Papermaking", Abbey Newsletter, Volume 17(4), September 1993. Link
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 32, 33
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- Hermann Kuhn, Conservation and Restoration of Works of Art and Antiquities, Butterworths, London, 1986
- Rosalie Rosso King, Textile Identification, Conservation, and Preservation, Noyes Publications, Park Ridge, NJ, 1985
- Palmy Weigle, Ancient Dyes for Modern Weavers, Watson-Guptill Publications, New York, 1974
- Susan E. Schur, Conservation Terminology: A review of Past & Current Nomenclature of Materials, Technology and Conservation, Spring (p.34-39); Summer (p.35-38); Fall (p.25-36), 1985
- Michael McCann, Artist Beware, Watson-Guptill Publications, New York City, 1979
- Book and Paper Group, Paper Conservation Catalog, AIC, 1984, 1989
- Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia, Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976
- The Merck Index, Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983
- A Glossary of Paper Conservation Terms, Margaret Ellis (ed.), Conservation Center of the Institute of Fine Arts, New York City, 1998