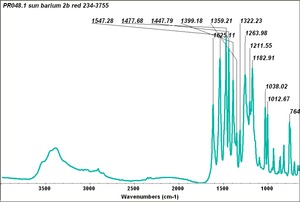
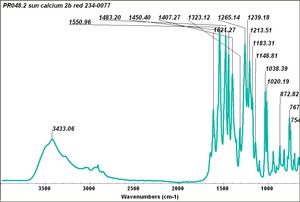
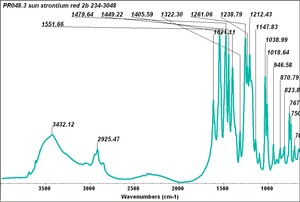
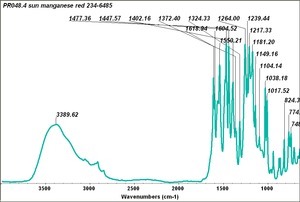
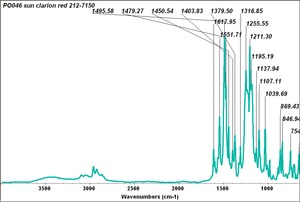
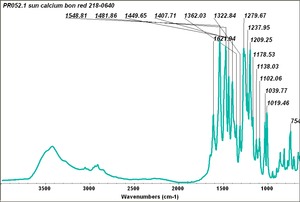
BON pigment
Description
A large class of azo-type pigments made by combining BON (3-hydroxy-2-naphthoic acid) with diazotized amines. BON pigments were first synthesized in 1887 and can be made in varying shades of red and violet. BON pigments have poor to good lightfastness and good bleed resistance. They are used in printing inks, plastics, exterior coatings and artists; watercolor paints.
See also Lithol Rubine, Red lake C, and Permanent Red 2B.
Synonyms and Related Terms
pigmento BON (It.);
Examples include: Lithol Rubine; Permanent Red 2B; BON Lake Red; Yellow BON Maroon; Red Lake C; Clarion red; Pigment Scarlet
Additional Information
° B.Berrie, S.Q.Lomax, "Azo Pigments: Their History, Synthesis, Properties and Use in Artists' Materials" in Studies in the History of Art, No.57, National Gallery of Art, Washington DC, 1997.
Sources Checked for Data in Record
- B. Berrie, S.Q. Lomax, 'Azo Pigments: Their History, Synthesis, Properties and Use in Artists' Materials', Studies in the History of Art , National Gallery of Art, Washington DC, No. 57, 1997