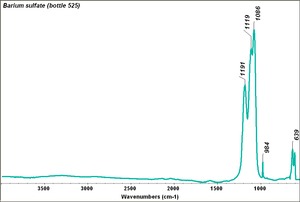
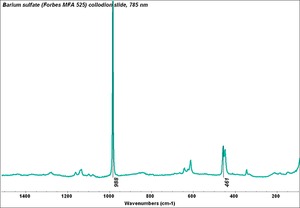
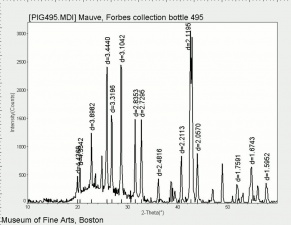
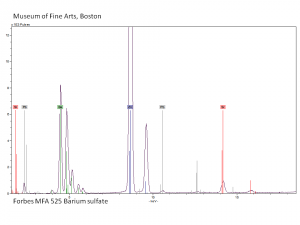
Barium sulfate
Description
A white pigment obtained naturally from the mineral Barite. Barium sulfate was developed as an artist pigment in the late 18th century as a nonpoisonous alternative to Lead white. Barium sulfate is an inert, transparent pigment that is often used as a filler or as a base for lake pigments. In recent years, it has also been used as a filler and extender in Paper, Wallpaper, Linoleum, Oilcloth, Rubber, plastics, Flannel, and Shoddy cloth. Barium sulfate can also be made artificially by a process discovered in late nineteenth century. Artificially prepared barium sulfate is called Blanc fixe. In order to increase its opacity, barium sulfate is mixed with Zinc sulfide, to form Lithopone. Permalba is an opaque version of barium sulfate which is sold as a permanent artist pigment.
Synonyms and Related Terms
baryte; Pigment White 22 (natural); Pigment White 21 (synthetic); CI 77120 (both); barium sulphate (Br.); blanc fixe (Fr.); basofor; Baryt (Deut.); Schwerspat (Deut.); Barytweiss (Deut.); solfato di bario (It.); bianco fisso (It.); blanco fijo (Esp.); sulfate de baryum (Fr.); baritis (Gr.); bariet (Ned.); sulfato de bário (Port.); artificial barite; baratine; baryta white; barium white; permanent white; Permalba; heavy spar; Bologna white; Bolognian spar; Tyrol white; cauk
Risks
Nonpoisonous. Used in medical radiography because of its density and its water insolubility. Noncombustible.
ThermoFisher: SDS
Physical and Chemical Properties
Chemically resistant to acids, alkalis and corrosive gases.
Particle size = 0.11-0.54 microns. Low birefringence.
Isotropic but under cross polars the particles may appear to twinkle.
| Composition | BaSO4 |
|---|---|
| CAS | 7727-43-7 |
| Melting Point | 1580 |
| Density | 4.25-4.5 |
| Molecular Weight | mol. wt. = 233.43 |
| Refractive Index | 1.636; 1.637; 1.648 |
Comparisons
Characteristics of Common White Pigments
Additional Images
Resources and Citations
- R. Feller, "Barium Sulfate", Artists Pigments, Volume 1, R. Feller (ed.), Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, 1986.
- R. J. Gettens, G.L. Stout, Painting Materials, A Short Encyclopaedia, Dover Publications, New York, 1966 Comment: density = 4.36 and ref. index = 1.62 - 1.64
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 83
- Ralph Mayer, A Dictionary of Art Terms and Techniques, Harper and Row Publishers, New York, 1969 (also 1945 printing)
- R. Newman, E. Farrell, 'House Paint Pigments', Paint in America , R. Moss ed., Preservation Press, New York City, 1994
- Michael McCann, Artist Beware, Watson-Guptill Publications, New York City, 1979
- Matt Roberts, Don Etherington, Bookbinding and the Conservation of Books: a Dictionary of Descriptive Terminology, U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington DC, 1982
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- Susan E. Schur, Conservation Terminology: A review of Past & Current Nomenclature of Materials, Technology and Conservation, Spring (p.34-39); Summer (p.35-38); Fall (p.25-36), 1985
- Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia, Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976
- Random House, Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language, Grammercy Book, New York, 1997
- The Merck Index, Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: Entry # 1023
- The American Heritage Dictionary or Encarta, via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998
- Art and Architecture Thesaurus Online, http://www.getty.edu/research/tools/vocabulary/aat/, J. Paul Getty Trust, Los Angeles, 2000