Difference between revisions of "Cedar wood"
| (14 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | [[File:03.1131-CR3654-d1.jpg|thumb|]] | + | [[File:03.1131-CR3654-d1.jpg|thumb|Egyptian throne portion<br>MFA 03.1131]] |
| + | [[File:1989.135-SC34195.jpg|thumb|Native American rattle<br>MFA 1989.135]] | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
A nonspecific term used for wood from several aromatic evergreen trees. The best known cedar is the [[cedar of Lebanon]] (''Cedrus libani'') which is native to Asia Minor. Cedars are characterized by having an strong smelling volatile oil whose odor persists after the wood is cut and dried. The wood has a fine grain, is a red and yellow in color and takes a beautiful polish. Cedar is durable and very resistant to insects and rotting. It is used for construction, cabinetry, interior trim, closets, and chest. Cedar shavings were once used as a repellent for ([[clothes moth|clothes moths]]) and ([[carpet beetle|carpet beetles]]), but were not very effective. Other true species of cedar are Atlas cedar (''C. atlantica''), Cyprus cedar (''C. brevifolia''), and deodar (''C. deodara''). | A nonspecific term used for wood from several aromatic evergreen trees. The best known cedar is the [[cedar of Lebanon]] (''Cedrus libani'') which is native to Asia Minor. Cedars are characterized by having an strong smelling volatile oil whose odor persists after the wood is cut and dried. The wood has a fine grain, is a red and yellow in color and takes a beautiful polish. Cedar is durable and very resistant to insects and rotting. It is used for construction, cabinetry, interior trim, closets, and chest. Cedar shavings were once used as a repellent for ([[clothes moth|clothes moths]]) and ([[carpet beetle|carpet beetles]]), but were not very effective. Other true species of cedar are Atlas cedar (''C. atlantica''), Cyprus cedar (''C. brevifolia''), and deodar (''C. deodara''). | ||
| + | [[File:image7_cedaroflebanon.jpg|thumb|Cedar of Lebanon]] | ||
| + | Other CAMEO entries include: | ||
| − | + | [[Alaska cedar]] (''Chamaecyparis nootkatensis'') | |
| + | |||
| + | [[Eastern red cedar]] (''Juniperus virginiana'') | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[giant arborvitae|Western red cedar]] (''Thuja plicata'') | ||
| − | [[ | + | [[Honduras cedar]] (''Cedrala mexicana'') |
| − | |||
| + | [[Incense cedar]] (''Librocedrus decurrens; Calocedrus decurrens'') | ||
| − | [[ | + | [[Port Orford cedar]] (''Chamaecyparis lawsoniana'') |
== Synonyms and Related Terms == | == Synonyms and Related Terms == | ||
| − | juniper; cedarwood; cedar chips; cedar shavings; Cedrus libani; cèdre (Fr.); Zedar (Deut.);cedro (It., Port., Esp.) | + | juniper; cedarwood; cedar chips; cedar shavings; ''Cedrus libani''; cèdre (Fr.); Zedar (Deut.);cedro (It., Port., Esp.) ; sedar |
| + | |||
| + | == Personal Risks == | ||
| + | |||
| + | Inhalation of dust may cause asthma. Skin contact may cause irritation. Toxic by ingestion. | ||
| − | + | == Collection Risks == | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | '''Links to Oddy Test results posted on AIC Wiki Materials Database Pages for individual materials below'''<br> | |
| − | + | ° [http://www.conservation-wiki.com/wiki/Oddy_Test_Results:_Case_Construction_Materials#cedar0001 Cedar], sample from old seasoned shelving plank Tested in 2016 | |
| + | |||
| + | ==Physical and Chemical Properties== | ||
| + | Wood density = 23-35 ppcf | ||
| − | |||
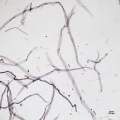
Paper fiber type: Softwood. Using transmitted light microscopy, fibers appear wide and thin-walled, with small taxodiod ray parenchyma pits. Appearance with [[Graff "C" stain]]: varies with pulping and bleaching. Average dimensions of fibers: length 3.5mm; width 30-40μm. Common pulping method: [[sulfite process|sulfite]] or [[kraft process|kraft]]. | Paper fiber type: Softwood. Using transmitted light microscopy, fibers appear wide and thin-walled, with small taxodiod ray parenchyma pits. Appearance with [[Graff "C" stain]]: varies with pulping and bleaching. Average dimensions of fibers: length 3.5mm; width 30-40μm. Common pulping method: [[sulfite process|sulfite]] or [[kraft process|kraft]]. | ||
| Line 32: | Line 41: | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
File:W red cedar 40x.jpg|Western red cedar paper pulp | File:W red cedar 40x.jpg|Western red cedar paper pulp | ||
File:W red cedar 10x.jpg|Western red cedar paper pulp | File:W red cedar 10x.jpg|Western red cedar paper pulp | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
| − | + | == Resources and Citations == | |
| − | == | + | * Alden Identification Services, Microscopic Wood Identification: [https://wood-identification.com/wood-types/ Link] |
* R. J. Gettens, G.L. Stout, ''Painting Materials, A Short Encyclopaedia'', Dover Publications, New York, 1966 | * R. J. Gettens, G.L. Stout, ''Painting Materials, A Short Encyclopaedia'', Dover Publications, New York, 1966 | ||
| Line 53: | Line 60: | ||
* ''Dictionary of Building Preservation'', Ward Bucher, ed., John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York City, 1996 | * ''Dictionary of Building Preservation'', Ward Bucher, ed., John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York City, 1996 | ||
| − | * Wikipedia | + | * Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cedrus_libani (Accessed Mar. 20, 2006) |
* ''CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics'', Robert Weast (ed.), CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, v. 61, 1980 Comment: density=30-35 ppcf (0.49-0.57 g/cm3) | * ''CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics'', Robert Weast (ed.), CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, v. 61, 1980 Comment: density=30-35 ppcf (0.49-0.57 g/cm3) | ||
| Line 65: | Line 72: | ||
| − | [[Category:Materials database]] | + | [[Category:Materials database]][[Category:MWG]] |
Latest revision as of 12:27, 16 June 2022
Description
A nonspecific term used for wood from several aromatic evergreen trees. The best known cedar is the Cedar of Lebanon (Cedrus libani) which is native to Asia Minor. Cedars are characterized by having an strong smelling volatile oil whose odor persists after the wood is cut and dried. The wood has a fine grain, is a red and yellow in color and takes a beautiful polish. Cedar is durable and very resistant to insects and rotting. It is used for construction, cabinetry, interior trim, closets, and chest. Cedar shavings were once used as a repellent for (clothes moths) and (carpet beetles), but were not very effective. Other true species of cedar are Atlas cedar (C. atlantica), Cyprus cedar (C. brevifolia), and deodar (C. deodara).
Other CAMEO entries include:
Alaska cedar (Chamaecyparis nootkatensis)
Eastern red cedar (Juniperus virginiana)
Western red cedar (Thuja plicata)
Honduras cedar (Cedrala mexicana)
Incense cedar (Librocedrus decurrens; Calocedrus decurrens)
Port Orford cedar (Chamaecyparis lawsoniana)
Synonyms and Related Terms
juniper; cedarwood; cedar chips; cedar shavings; Cedrus libani; cèdre (Fr.); Zedar (Deut.);cedro (It., Port., Esp.) ; sedar
Personal Risks
Inhalation of dust may cause asthma. Skin contact may cause irritation. Toxic by ingestion.
Collection Risks
Links to Oddy Test results posted on AIC Wiki Materials Database Pages for individual materials below
° Cedar, sample from old seasoned shelving plank Tested in 2016
Physical and Chemical Properties
Wood density = 23-35 ppcf
Paper fiber type: Softwood. Using transmitted light microscopy, fibers appear wide and thin-walled, with small taxodiod ray parenchyma pits. Appearance with Graff "C" stain: varies with pulping and bleaching. Average dimensions of fibers: length 3.5mm; width 30-40μm. Common pulping method: sulfite or kraft.
Additional Images
Resources and Citations
- Alden Identification Services, Microscopic Wood Identification: Link
- R. J. Gettens, G.L. Stout, Painting Materials, A Short Encyclopaedia, Dover Publications, New York, 1966
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 165
- Hermann Kuhn, Conservation and Restoration of Works of Art and Antiquities, Butterworths, London, 1986
- F. H. Titmuss, Commercial Timbers of the World, The Technical Press Ltd., London, 1965 Comment: 23-33 ppcf
- Michael McCann, Artist Beware, Watson-Guptill Publications, New York City, 1979
- Dictionary of Building Preservation, Ward Bucher, ed., John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York City, 1996
- Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cedrus_libani (Accessed Mar. 20, 2006)
- CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, Robert Weast (ed.), CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, v. 61, 1980 Comment: density=30-35 ppcf (0.49-0.57 g/cm3)
- Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia, Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976
- Random House, Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language, Grammercy Book, New York, 1997
- The American Heritage Dictionary or Encarta, via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998