Difference between revisions of "Corrosion"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| (16 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
| − | The electrochemical degradation of a material due to reactions with its environment or applied reagents. Corrosion may affect the color, texture, or form of the object. Corrosion is accelerated by the presence of acids, bases, | + | The electrochemical degradation of a material, usually a metal, due to reactions with its environment or applied reagents. Corrosion may affect the color, texture, or form of the object. Corrosion is accelerated by the presence of acids, bases, halogen salts, as well as oxygen and moisture. Contact of two metals of differing electrochemical potentials can result in [[galvanic corrosion]]. [[Copper]], [[nickel]], [[chromium]], and [[zinc]] are some of the more corrosion resistant metals and are often used as protective coatings for other metals. |
[[File:Azurite.corr.det1.jpg|thumb|Azurite and malachite on bronze]] | [[File:Azurite.corr.det1.jpg|thumb|Azurite and malachite on bronze]] | ||
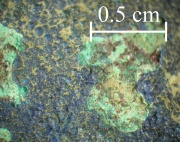
| + | [[File:Image3_802329.jpg|thumb|Blue-green corrosion]] | ||
Examples are corrosion are: | Examples are corrosion are: | ||
| − | + | * [[Iron]] reacts with water and oxygen to form rust. | |
| + | * [[Aluminum]] quickly oxidizes to form a protective oxide layer. | ||
| + | * [[Glass]] dissolves in alkaline solutions. | ||
| + | * [[Concrete]] is softened by sulfate solutions. | ||
| + | * [[Copper]] produces a stable patina in moist air. | ||
| − | + | Materials that minimize corrosion include: | |
| − | + | * [[Corrosion resistance|Corrosion inhibitor]]: a liquid or solid corrosion resistant layer coated onto the susceptible surface (painting, plating, anodizing, etc.) | |
| − | + | * [[Vapor phase corrosion inhibitor]]: a gas that provides a corrosion resistant layer on the susceptible surface | |
| − | + | * [[Scavenger]]: a sorbent that removes pollutants and/or moisture and oxygen from the air | |
| − | + | * [[Desiccant]]: a hygroscopic sorbent that removes moisture from the air | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
== Synonyms and Related Terms == | == Synonyms and Related Terms == | ||
| − | corrosive material | + | patina; oxidation; tarnish; rust; degradation; corrosive material; zinc pest; pitting; fouling; black spots |
== Additional Images == | == Additional Images == | ||
| Line 26: | Line 29: | ||
File:Bronze.Disease.Det.jpg|Bronze disease | File:Bronze.Disease.Det.jpg|Bronze disease | ||
File:Black.Spots.jpg|Corrosion | File:Black.Spots.jpg|Corrosion | ||
| − | |||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
==Resources and Citations== | ==Resources and Citations== | ||
* J.Waite, "Architectural Metals: Their Deterioration and Stabilization" in Preservation and Conservation: Principles and Practice, S.Timmons (ed.), Preservation Press, Washington DC, 1976, p. 213. | * J.Waite, "Architectural Metals: Their Deterioration and Stabilization" in Preservation and Conservation: Principles and Practice, S.Timmons (ed.), Preservation Press, Washington DC, 1976, p. 213. | ||
| − | + | * Wikipedia: [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/corrosion Corrosion] Accessed July 2023 | |
* Richard S. Lewis, ''Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary'', Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993 | * Richard S. Lewis, ''Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary'', Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993 | ||
| − | |||
* G.S.Brady, ''Materials Handbook'', McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 290 | * G.S.Brady, ''Materials Handbook'', McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 290 | ||
| − | |||
* Ralph Mayer, ''A Dictionary of Art Terms and Techniques'', Harper and Row Publishers, New York, 1969 (also 1945 printing) | * Ralph Mayer, ''A Dictionary of Art Terms and Techniques'', Harper and Row Publishers, New York, 1969 (also 1945 printing) | ||
| − | |||
* ''Dictionary of Building Preservation'', Ward Bucher, ed., John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York City, 1996 | * ''Dictionary of Building Preservation'', Ward Bucher, ed., John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York City, 1996 | ||
| − | |||
* Random House, ''Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language'', Grammercy Book, New York, 1997 | * Random House, ''Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language'', Grammercy Book, New York, 1997 | ||
| − | |||
* ''The American Heritage Dictionary'' or ''Encarta'', via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998 | * ''The American Heritage Dictionary'' or ''Encarta'', via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998 | ||
| − | + | * Art and Architecture Thesaurus Online, https://www.getty.edu/research/tools/vocabulary/aat/, J. Paul Getty Trust, Los Angeles, 2000 | |
| − | * Art and Architecture Thesaurus Online, | ||
[[Category:Materials database]] | [[Category:Materials database]] | ||
Latest revision as of 16:52, 13 July 2023
Description
The electrochemical degradation of a material, usually a metal, due to reactions with its environment or applied reagents. Corrosion may affect the color, texture, or form of the object. Corrosion is accelerated by the presence of acids, bases, halogen salts, as well as oxygen and moisture. Contact of two metals of differing electrochemical potentials can result in Galvanic corrosion. Copper, Nickel, Chromium, and Zinc are some of the more corrosion resistant metals and are often used as protective coatings for other metals.
Examples are corrosion are:
- Iron reacts with water and oxygen to form rust.
- Aluminum quickly oxidizes to form a protective oxide layer.
- Glass dissolves in alkaline solutions.
- Concrete is softened by sulfate solutions.
- Copper produces a stable patina in moist air.
Materials that minimize corrosion include:
- Corrosion inhibitor: a liquid or solid corrosion resistant layer coated onto the susceptible surface (painting, plating, anodizing, etc.)
- Vapor phase corrosion inhibitor: a gas that provides a corrosion resistant layer on the susceptible surface
- Scavenger: a sorbent that removes pollutants and/or moisture and oxygen from the air
- Desiccant: a hygroscopic sorbent that removes moisture from the air
Synonyms and Related Terms
patina; oxidation; tarnish; rust; degradation; corrosive material; zinc pest; pitting; fouling; black spots
Additional Images
Resources and Citations
- J.Waite, "Architectural Metals: Their Deterioration and Stabilization" in Preservation and Conservation: Principles and Practice, S.Timmons (ed.), Preservation Press, Washington DC, 1976, p. 213.
- Wikipedia: Corrosion Accessed July 2023
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 290
- Ralph Mayer, A Dictionary of Art Terms and Techniques, Harper and Row Publishers, New York, 1969 (also 1945 printing)
- Dictionary of Building Preservation, Ward Bucher, ed., John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York City, 1996
- Random House, Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language, Grammercy Book, New York, 1997
- The American Heritage Dictionary or Encarta, via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998
- Art and Architecture Thesaurus Online, https://www.getty.edu/research/tools/vocabulary/aat/, J. Paul Getty Trust, Los Angeles, 2000