Difference between revisions of "DDT"
| Line 45: | Line 45: | ||
LINK: [http://www.cdc.gov/niosh/ipcsneng/neng0034.html International Chemical Safety Card] | LINK: [http://www.cdc.gov/niosh/ipcsneng/neng0034.html International Chemical Safety Card] | ||
| − | == | + | ==For Additional Information== |
° L. Goldberg, A History Of Pest Control Measures In The Anthropology Collections, National Museum Of Natural History, Smithsonian Institution, ''JAIC'' (35):23-43, 1996 ([http://aic.stanford.edu/jaic/articles/jaic35-01-003_appx.html Link]) | ° L. Goldberg, A History Of Pest Control Measures In The Anthropology Collections, National Museum Of Natural History, Smithsonian Institution, ''JAIC'' (35):23-43, 1996 ([http://aic.stanford.edu/jaic/articles/jaic35-01-003_appx.html Link]) | ||
Revision as of 12:12, 17 August 2015
Description
Common abbreviation for the Insecticide dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane that was first synthesized in 1873. By 1939, Dr. Mueller discovered that the colorless, odorless crystals are toxic to insects, humans, and animals. Its successful use during World War II to combat insect carried diseases resulted in a Nobel Prize award to Dr. Mueller. In the United States, DDT was widely used as an insecticide in agriculture. Unfortunately, it was also used on many museum objects, such as plants and animals in ethnographic collections, as well as books and papers in libraries. Residues have also been found on wooden artifacts and musical instruments in museums. DDT is nonbiodegradable and its residues (DDE and DDD) may remain in or on objects for years. The breakdown of DDT may be catalyzed by some metals (Aluminum, Chromium, and Iron) and accelerated by light and heat. It was banned for use in the U.S. in 1972.
Synonyms and Related Terms
dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane; dicophane; chlorophenothane; D.D.T. [Geigy Co.]; Agritan; Azotox; Anofex; Ixodex; Gesapon; Gesarex; Gesarol [Ciba Geigy]; Guesapon; Neocid [Ciba Geigy];
Other Properties
Soluble in acetone, ether, benzene, carbon tetrachloride, kerosene, dioxane, and pyridine. Insoluble in water.
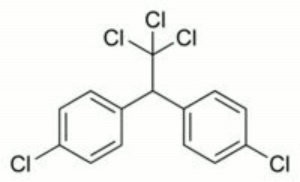
| Composition | (ClC6H4)2CHCCl3 |
|---|---|
| CAS | 50-29-3 |
| Melting Point | 109 |
| Density | 1.5 |
| Molecular Weight | mol. wt. = 354.5 |
| Boiling Point | 260 |
Hazards and Safety
Toxic by skin absorption, inhalation and ingestion. LD50 = 113-118 mg.kg
Degradation produces chlorine and hydrogen chloride. Combustible. Potential carcinogen and mutagen. Biohazard.
LINK: International Chemical Safety Card
For Additional Information
° L. Goldberg, A History Of Pest Control Measures In The Anthropology Collections, National Museum Of Natural History, Smithsonian Institution, JAIC (35):23-43, 1996 (Link)
Authority
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- Lynda A. Zycherman, J.Richard Schrock, A Guide to Museum Pest Control, FAIC and Association of Systematics Collections, Washington DC, 1988
- Website address 1 Comment: Olympus Microscopy resource Center at http://www.olympusmicro.com/galleries/abramowitz/pages/ddtsmall.html - description states banned in US in 1972.
- Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia, at http://www.wikipedia.com Comment: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/DDT (Accessed Jan. 25, 2006)
- Random House, Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language, Grammercy Book, New York, 1997