Difference between revisions of "Dichlorvos"
m (Text replace - "== Authority ==" to "== Sources Checked for Data in Record ==") |
|||
| Line 44: | Line 44: | ||
° L. Goldberg, A History Of Pest Control Measures In The Anthropology Collections, National Museum Of Natural History, Smithsonian Institution, ''JAIC'' (35):23-43, 1996 | ° L. Goldberg, A History Of Pest Control Measures In The Anthropology Collections, National Museum Of Natural History, Smithsonian Institution, ''JAIC'' (35):23-43, 1996 | ||
| − | == | + | == Sources Checked for Data in Record == |
* J. Dawson, ''CCI Technical Bulletin'', 'Solving Museum Insect Problems: Chemical Control' , Canadian Conservation Institute, Ottawa, No. 15 | * J. Dawson, ''CCI Technical Bulletin'', 'Solving Museum Insect Problems: Chemical Control' , Canadian Conservation Institute, Ottawa, No. 15 | ||
Revision as of 20:42, 30 April 2016
Description
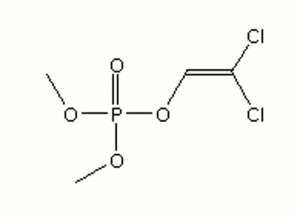
A colorless, toxic liquid Insecticide that has been commonly used in plastic insect strips. Dichlorvos has a high vapor pressures and when it is impregnated in the plastic strips, it will slowly evaporate over a three month period. It is most effective against flying insects and only effective for cockroaches in a sealed container (Zycherman and Shrock 1988). Dichlorvos functions as a cholinesterase inhibitor. In the presence of water, dichlorvos can decompose. Some metals (Iron, Steel, Copper, Brass, Tin, Zinc, Lead, and Silver) have tarnished when exposed to the vapors from dichlorvos strips (Zycherman and Shrock 1988). In 1995, the use of dichlorvos was restricted for all applications except for impregnated strips used in outdoor insect traps.
Synonyms and Related Terms
dimethyldichlorovinylphosphate; 2,2-dichlorodivinyldimethyl phosphate; DDVP; dichlorovos; Al-20; Vapona® strips [Shell]; Vaportale® [Shell]; No-Pest® strips [Spectrum]; Vaponite; Nuvan; Dichlorman; Estrosol; Herkol; Nogos; Sheltox
Other Properties
Miscible with ethanol and most nonpolar solvents. Slightly soluble in water. Decomposes in quickly in alkalis and slowly in water.
| Composition | C4H7Cl2O4P |
|---|---|
| CAS | 62-73-7 |
| Density | 1.415 |
| Molecular Weight | Mol. wt. = 220.98 |
| Boiling Point | 140 |
Hazards and Safety
Toxic by inhalation, skin absorption and ingestion causing headache, vomiting, convulsions and cardiac irregularities. Carcinogen and suspected teratogen by ingestion. Can corrode metals.
EXTOXNET: Dichlorvos
Additional Information
° L. Zycherman, J.R. Schrock, A Guide to Museum Pest Control, FAIC, Washington, DC, 1988.
° L. Goldberg, A History Of Pest Control Measures In The Anthropology Collections, National Museum Of Natural History, Smithsonian Institution, JAIC (35):23-43, 1996
Sources Checked for Data in Record
- J. Dawson, CCI Technical Bulletin, 'Solving Museum Insect Problems: Chemical Control' , Canadian Conservation Institute, Ottawa, No. 15
- Lynda A. Zycherman, J.Richard Schrock, A Guide to Museum Pest Control, FAIC and Association of Systematics Collections, Washington DC, 1988
- Pam Hatchfield, Pollutants in the Museum Environment, Archetype Press, London, 2002
- Website address 1 Comment: www.speclab.com/compound/c62737