Difference between revisions of "Goldthread (Coptis trifolia ) LC"
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
Goldthread, like all photoberberin dyes, is used as a direct dye, in a hot dye-bath, to obtain a bright golden yellow on silk or wool. The Micmac of the Gaspe peninsula and Acadia boiled the rhizomes to dye yellow [2]. The French settlers in Canada adopted this dye for their woolen cloth [3]. Japanese used ''Coptis japonica'' as a traditional dye. | Goldthread, like all photoberberin dyes, is used as a direct dye, in a hot dye-bath, to obtain a bright golden yellow on silk or wool. The Micmac of the Gaspe peninsula and Acadia boiled the rhizomes to dye yellow [2]. The French settlers in Canada adopted this dye for their woolen cloth [3]. Japanese used ''Coptis japonica'' as a traditional dye. | ||
| − | = Summary of results = | + | == Summary of results == |
| − | = Analytical instrumentation and procedures = | + | == Analytical instrumentation and procedures == |
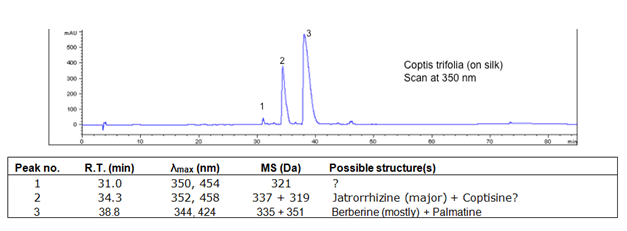
| − | = Chromatograms = | + | == Chromatograms == |
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
[[File:Goldthread info.PNG|center|frame|sample information, By R. A. Laursen, Boston University ]] | [[File:Goldthread info.PNG|center|frame|sample information, By R. A. Laursen, Boston University ]] | ||
| − | = Identified compounds = | + | == Identified compounds == |
[[[SliderGallery rightalign|~HPLC-DAD|.JPG~ UV-Vis|.jpg~ UV-Vis]]] | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|~HPLC-DAD|.JPG~ UV-Vis|.jpg~ UV-Vis]]] | ||
| Line 73: | Line 73: | ||
| − | [[Category:Analysis | + | [[Category:Dye Analysis]] |
Revision as of 10:17, 26 July 2017
Description
Goldthread is a perennial herb growing from slender bright yellow to orange rhizomes. Goldthread grows in wet coniferous and mixed forests, bogs, willow scrub and tundra, in areas include Japan, China, Korea, Eastern Siberia and North America [1].
Historical importance
Goldthread, like all photoberberin dyes, is used as a direct dye, in a hot dye-bath, to obtain a bright golden yellow on silk or wool. The Micmac of the Gaspe peninsula and Acadia boiled the rhizomes to dye yellow [2]. The French settlers in Canada adopted this dye for their woolen cloth [3]. Japanese used Coptis japonica as a traditional dye.
Summary of results
Analytical instrumentation and procedures
Chromatograms
Sample information
Identified compounds
| Compound | RT (min.) | MW | UV/vis | Other |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| xx | xx0 | xx | xx | Comments here |
| x | x | x | x | |
| x | x | x | x | |
| x | x | x | x |
References
[1] Cardon, Dominique. "Natural dyes, sources, Traditions, Technology and Science" 331 (2007).
[2] Whitehead, R. H. (1982) Micmac Quillwork; Micmac Indian Techniques of Porcupine Quill Decration, 1600-1950. Halifax: Nava Scotia Museum. p. 68;
[3] Yamazaki K. The illustrated book of dye plants, vol. 1 (1985/2002). pp. 46-7.