Difference between revisions of "Mica"
(username removed) |
|||
| (12 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | [[File:13.4284-E3977CR-d1.jpg|thumb|]] | + | [[File:13.4284-E3977CR-d1.jpg|thumb|Mica appliques<br>MFA# 13.4284]] |
== Description == | == Description == | ||
| + | [[File:41.262-C43305CR-d1.jpg|thumb|Japanese print<br>MFA# 41.262]] | ||
| + | A group of silicate minerals that cleave into thin, flexible sheets. Mica minerals range in color from colorless to black. They are composed of potassium aluminum silicates ([[muscovite|muscovite]]) and may also contain magnesium ([[phlogopite|phlogopite]]), chromium ([[fuchsite|fuchsite]]), iron ([[biotite|biotite]]), and lithium ([[lepidolite|lepidolite]]). Mica is mined commercially in India, Canada, Malagasy Republic, Brazil, and Argentina. Ground mica is used in paper, paints, and ceramic glazes to increase gloss and add sparkle. It has been used as a replacement for bronze powder in some metallic paints. Mica is also used as a filler in plastics, wallboard, mortar, and asphalt shingles. Sheets of mica were at one time used as small windows for houses ([[Muscovy%20glass|Muscovy glass]]); now thin sheets are used as windows in electrical equipment. It is also used as a fireproofing material, an agent in fire extinguishers, and as an electrical insulator. | ||
| − | + | [[File:Mica necklace.jpg|thumb|Mica chain<br>MFA# 2006.414]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
== Synonyms and Related Terms == | == Synonyms and Related Terms == | ||
Muscovy glass; isinglass stone; muscovite (colorless); phlogopite (brown); fuchsite (green); lepidolite (pink, lilac); biotite (black); glauconite (green); paragonite; apophyllite; Glimmer (Deut., Sven.); mika (Gr.); micare (Lat.); miki (Pol.); mica (Esp., Fr., It., Ned., Port.); | Muscovy glass; isinglass stone; muscovite (colorless); phlogopite (brown); fuchsite (green); lepidolite (pink, lilac); biotite (black); glauconite (green); paragonite; apophyllite; Glimmer (Deut., Sven.); mika (Gr.); micare (Lat.); miki (Pol.); mica (Esp., Fr., It., Ned., Port.); | ||
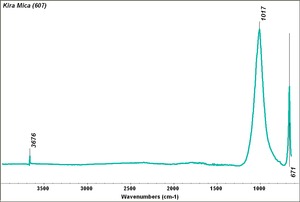
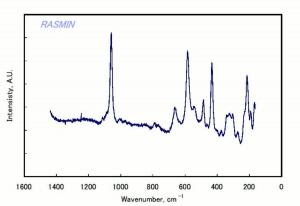
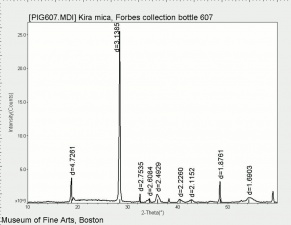
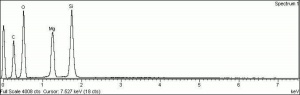
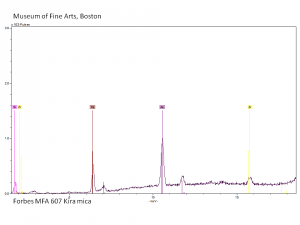
| − | [[[SliderGallery rightalign| | + | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|Kira Mica (607).TIF~FTIR (MFA)|apophyliteRS.jpg~Raman|PIG607.jpg~XRD|f607sem.jpg~SEM|f607edsbw.jpg~EDS|Slide26_F607.PNG~XRF]]] |
| + | == Risks == | ||
| − | + | * May contain silica which could produce silicosis by inhalation. | |
| + | * Crystex Composites: [https://crystexcompositesllc.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/01/MM-Synthetic-Mica-SDS-Rev-3_09242019.pdf SDS] | ||
| − | + | == Physical and Chemical Properties == | |
| − | Perfect cleavage in one direction. Fracture = uneven. Luster = pearly, iridescent. Streak = white to colorless | + | * Tetragonal system with tabular, cube-like or prismatic crystals. |
| + | * Perfect cleavage in one direction. | ||
| + | * Fracture = uneven. | ||
| + | * Luster = pearly, iridescent. | ||
| + | * Streak = white to colorless | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| Line 26: | Line 32: | ||
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Density | ! scope="row"| Density | ||
| − | | 2.7-3.2 | + | | 2.7-3.2 g/ml |
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Refractive Index | ! scope="row"| Refractive Index | ||
| 1.563; 1.604; 1.599 | | 1.563; 1.604; 1.599 | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
== Additional Images == | == Additional Images == | ||
| Line 43: | Line 43: | ||
File:Image3_802434.jpg|Mica | File:Image3_802434.jpg|Mica | ||
File:Muskovit-Pilsak.jpg|Mica (muscovite) | File:Muskovit-Pilsak.jpg|Mica (muscovite) | ||
| − | File:Kiramica C100x.jpg|Kira mica, powdered | + | File:Kiramica C100x.jpg|Kira mica, powdered at 100x (visible light left; UV light right) |
File:pa20607apophylite.jpg|Apophylite | File:pa20607apophylite.jpg|Apophylite | ||
File:fuchsiteF5.jpg|Fuchsite | File:fuchsiteF5.jpg|Fuchsite | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
| + | == Resources and Citations == | ||
| − | + | * ''Encyclopedia Britannica'', http://www.britannica.com Retrieved June 5, 2003. | |
| − | |||
| − | * ''Encyclopedia Britannica'', http://www.britannica.com | ||
* R. J. Gettens, G.L. Stout, ''Painting Materials, A Short Encyclopaedia'', Dover Publications, New York, 1966 | * R. J. Gettens, G.L. Stout, ''Painting Materials, A Short Encyclopaedia'', Dover Publications, New York, 1966 | ||
| Line 63: | Line 62: | ||
* Robert Fournier, ''Illustrated Dictionary of Practical Pottery'', Chilton Book Company, Radnor, PA, 1992 | * Robert Fournier, ''Illustrated Dictionary of Practical Pottery'', Chilton Book Company, Radnor, PA, 1992 | ||
| − | * Wikipedia | + | * Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mica (Accessed Sept. 10, 2005) |
* Michael McCann, ''Artist Beware'', Watson-Guptill Publications, New York City, 1979 | * Michael McCann, ''Artist Beware'', Watson-Guptill Publications, New York City, 1979 | ||
Latest revision as of 12:17, 21 September 2022
Description
A group of silicate minerals that cleave into thin, flexible sheets. Mica minerals range in color from colorless to black. They are composed of potassium aluminum silicates (Muscovite) and may also contain magnesium (Phlogopite), chromium (Fuchsite), iron (Biotite), and lithium (Lepidolite). Mica is mined commercially in India, Canada, Malagasy Republic, Brazil, and Argentina. Ground mica is used in paper, paints, and ceramic glazes to increase gloss and add sparkle. It has been used as a replacement for bronze powder in some metallic paints. Mica is also used as a filler in plastics, wallboard, mortar, and asphalt shingles. Sheets of mica were at one time used as small windows for houses (Muscovy glass); now thin sheets are used as windows in electrical equipment. It is also used as a fireproofing material, an agent in fire extinguishers, and as an electrical insulator.
Synonyms and Related Terms
Muscovy glass; isinglass stone; muscovite (colorless); phlogopite (brown); fuchsite (green); lepidolite (pink, lilac); biotite (black); glauconite (green); paragonite; apophyllite; Glimmer (Deut., Sven.); mika (Gr.); micare (Lat.); miki (Pol.); mica (Esp., Fr., It., Ned., Port.);
Risks
- May contain silica which could produce silicosis by inhalation.
- Crystex Composites: SDS
Physical and Chemical Properties
- Tetragonal system with tabular, cube-like or prismatic crystals.
- Perfect cleavage in one direction.
- Fracture = uneven.
- Luster = pearly, iridescent.
- Streak = white to colorless
| CAS | 12001-26-2 |
|---|---|
| Mohs Hardness | 2.0 - 5.0 |
| Density | 2.7-3.2 g/ml |
| Refractive Index | 1.563; 1.604; 1.599 |
Additional Images
Resources and Citations
- Encyclopedia Britannica, http://www.britannica.com Retrieved June 5, 2003.
- R. J. Gettens, G.L. Stout, Painting Materials, A Short Encyclopaedia, Dover Publications, New York, 1966
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 505
- Ralph Mayer, A Dictionary of Art Terms and Techniques, Harper and Row Publishers, New York, 1969 (also 1945 printing)
- Dictionary of Building Preservation, Ward Bucher, ed., John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York City, 1996
- Robert Fournier, Illustrated Dictionary of Practical Pottery, Chilton Book Company, Radnor, PA, 1992
- Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mica (Accessed Sept. 10, 2005)
- Michael McCann, Artist Beware, Watson-Guptill Publications, New York City, 1979
- Jack Odgen, Jewellery of the Ancient World, Rizzoli International Publications Inc., New York City, 1982
- The American Heritage Dictionary or Encarta, via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, Robert Weast (ed.), CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, v. 61, 1980 Comment: density=2.6-3.2
- Art and Architecture Thesaurus Online, http://www.getty.edu/research/tools/vocabulary/aat/, J. Paul Getty Trust, Los Angeles, 2000