Difference between revisions of "Pagoda tree (Styphnolobium japonicum) LC"
| (7 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
| − | The [[pagoda tree]] | + | The [[pagoda tree]], ''Styphnolobium japonicum''(=''Sophora japonica''), is medium sized tree native to Japan, China and India that has been used to produce a yellow dye. |
== Historical Importance == | == Historical Importance == | ||
| − | Pagoda tree buds have been recorded in ancient Chinese books as a dye source for yellow | + | Pagoda tree buds, which have to be roasted or steamed immediately after collection, have been recorded in ancient Chinese books as a dye source for yellow for thousands of years. The dyeing process, using pagoda tree buds has been recorded in several ancient Chinese books, including Tian Gong Kai Wu 《天工开物》(Chinese Technology in the Seventeenth Century), Duo Neng Bi Shi 《多能鄙事》(Many Abilities in Humble Activities), Bu Jing 《布經》 and Zhiranju buce 《織染局簿冊》. |
| − | Pagoda tree | + | Pagoda tree bud dyes have been reported to be the dyeing source of some historical textiles dated back to the Qing |
| − | Dynasty in China [2,3]. Pagoda tree buds | + | Dynasty in China [2,3]. Pagoda tree buds have also been identified in 19th century suzanis collected in |
Uzbekistan [4]. | Uzbekistan [4]. | ||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
[http://cameo.mfa.org/wiki/MAA_%D0%9A%D0%9F1276/3,_embroidered_suzani,_central_Asia_(19th_century) MAA КП1276/3] | [http://cameo.mfa.org/wiki/MAA_%D0%9A%D0%9F1276/3,_embroidered_suzani,_central_Asia_(19th_century) MAA КП1276/3] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [http://cameo.mfa.org/wiki/V%26A_T.43-1952,_Embroidered_robe,_China_(1770-1820) V&A T. 43-1952] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [http://cameo.mfa.org/wiki/PEM_E80968_Dragon_robe,_China_(19th_century) PEM E80968] | ||
== Synonyms and Related Terms == | == Synonyms and Related Terms == | ||
| − | Japanese pagoda tree (''Sophora japonica''; ''Styphnolobium japonicum''); Chinese scholar tree, waifa; enjo (Jap.) | + | Japanese pagoda tree (''Sophora japonica''; ''Styphnolobium japonicum''); Chinese scholar tree, waifa; enjo エンジュ(Jap.)槐(Chinese). |
[[File:Roasted pagoda tree buds.jpg |thumb|Roasted Pagoda tree buds. Photo by X. Zhang]] | [[File:Roasted pagoda tree buds.jpg |thumb|Roasted Pagoda tree buds. Photo by X. Zhang]] | ||
| Line 29: | Line 34: | ||
== Summary of results == | == Summary of results == | ||
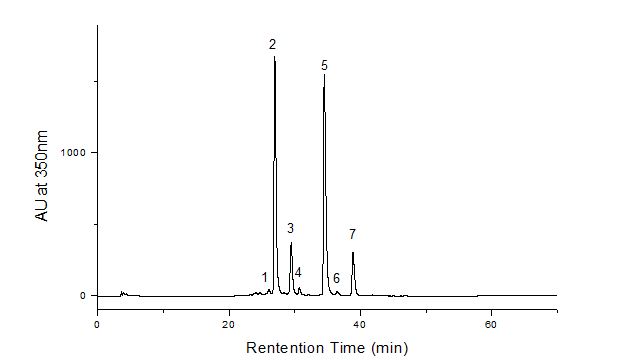
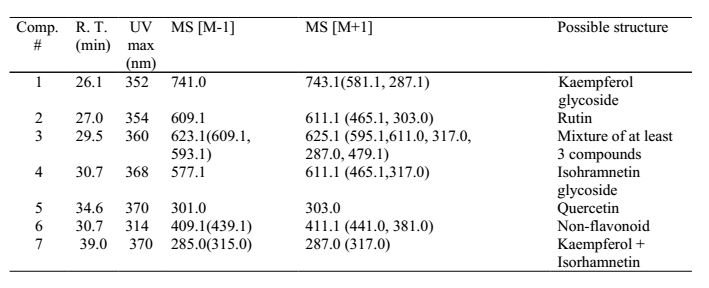
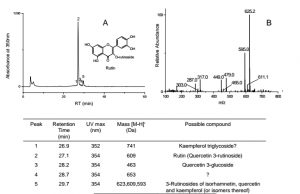
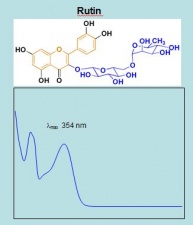
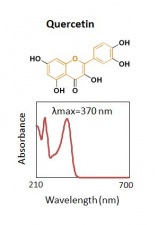
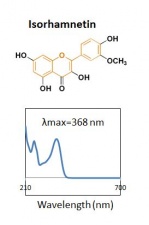
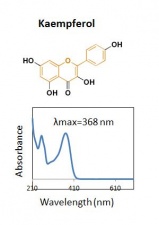
| − | The major components of | + | The major components of unheated pagoda tree buds are three flavonols and their glycosides, as shown in the chromatogram. The major glycoside is rutin. The buds contain an enzyme that converts rutin to its aglycone quercetin. Heating freshly harvested buds inactivates the enzyme, with the result that dyes prepared from such buds will mainly contain rutin, with very little quercetin. Historical textiles dyed with pagoda tree buds contain mainly rutin. |
| Line 40: | Line 45: | ||
== Chromatograms == | == Chromatograms == | ||
| − | HPLC-DAD | + | HPLC-DAD of pagoda tree bud extract. The sample (~0.1g), from Tanakanao, Japan, was extracted with 1 mL of methanol:H2O (v:v=1:1). Then the upper 30 μL of solution was removed for HPLC-DAD-MS analysis (20 μL was injected). |
[[File:Hplc-pagoda.JPG|center|frame|Absorbance at 350nm (mAU)]] | [[File:Hplc-pagoda.JPG|center|frame|Absorbance at 350nm (mAU)]] | ||
| Line 88: | Line 93: | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
| − | [1] | + | [1] X. Zhang, and , R. Laursen, Development of Mild Extraction Methods for the Analysis of Natural Dyes in Textiles of Historical Interest Using LC-Diode Array Detector-MS. Analytical Chemistry 77, 2022-2025 (2005). |
| − | [2] | + | [2] X. Zhang, Corrigan, K., MacLaren, B., , M., and , R. A. Laursen, Characterization of Yellow Dyes in Nineteenth Century Chinese Textiles. Studies in Conservation 52, 211-220 (2007). |
| − | [3] | + | [3] J. Han, The Historical and chemical investigation of dyes in high status Chinese costume and textiles of the Ming and Qing Dynasties (1368-1911), PhD thesis, University of Glasgow, February 2016. |
| − | [4] | + | [4] X. Zhang, R. Laursen, and S. Osipova, Analysis of dyes in some 19th-century Uzbek suzanis. Dyes in History and Archaeology (in press). |
[[Category:Dye Analysis]] | [[Category:Dye Analysis]] | ||
[[Category:Reference Materials]] | [[Category:Reference Materials]] | ||
[[Category:Natural Dyes]] | [[Category:Natural Dyes]] | ||
Latest revision as of 10:50, 21 December 2017
Description
The Pagoda tree, Styphnolobium japonicum(=Sophora japonica), is medium sized tree native to Japan, China and India that has been used to produce a yellow dye.
Historical Importance
Pagoda tree buds, which have to be roasted or steamed immediately after collection, have been recorded in ancient Chinese books as a dye source for yellow for thousands of years. The dyeing process, using pagoda tree buds has been recorded in several ancient Chinese books, including Tian Gong Kai Wu 《天工开物》(Chinese Technology in the Seventeenth Century), Duo Neng Bi Shi 《多能鄙事》(Many Abilities in Humble Activities), Bu Jing 《布經》 and Zhiranju buce 《織染局簿冊》.
Pagoda tree bud dyes have been reported to be the dyeing source of some historical textiles dated back to the Qing
Dynasty in China [2,3]. Pagoda tree buds have also been identified in 19th century suzanis collected in
Uzbekistan [4].
Examples:
Synonyms and Related Terms
Japanese pagoda tree (Sophora japonica; Styphnolobium japonicum); Chinese scholar tree, waifa; enjo エンジュ(Jap.)槐(Chinese).
Summary of results
The major components of unheated pagoda tree buds are three flavonols and their glycosides, as shown in the chromatogram. The major glycoside is rutin. The buds contain an enzyme that converts rutin to its aglycone quercetin. Heating freshly harvested buds inactivates the enzyme, with the result that dyes prepared from such buds will mainly contain rutin, with very little quercetin. Historical textiles dyed with pagoda tree buds contain mainly rutin.
Analytical instrumentation and procedures
HPLC-DAD-MS analysis was performed with an Agilent 1100 liquid chromatography system consisting of an automatic injector, a gradient pump, a HP series 1100 DAD, and an Agilent series 1100 VL on-line atmospheric pressure ionization electrospray ionization mass spectrometer. Separations were done on a Vydac 214TP52 analytical column (2.1 mm diameterX250 mm; 5-ím particle size). The column was eluted at a flow rate of 0.2 mL/min with a tertiary gradient of water (A),acetonitrile (B), and 1% (v/v) aqueous formic acid (C) with the following elution program: 0 min, 90% A, 5% B, 5% C; 0-55 min, a linear gradient to 35% A, 60% B, 5% C; 55-60 min, a linear gradient elution to 15% A, 80% B, 5% C; 60-62 min, isocratic elution at 15% A, 80% B, 5% C; 62-70 min gradient elution to 90% A, 5% B, 5% C; and reequilibration with the latter solvent for 15 min. The mass spectrometer was run both in the negative and positive ion mode.
Chromatograms
HPLC-DAD of pagoda tree bud extract. The sample (~0.1g), from Tanakanao, Japan, was extracted with 1 mL of methanol:H2O (v:v=1:1). Then the upper 30 μL of solution was removed for HPLC-DAD-MS analysis (20 μL was injected).
Results
Identified compounds
| Compound | RT (min.) | MW | UV/vis | Other |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| rutin | 27.0 | 610 | 278,352 | Comments here |
| quercetin | 34.6 | 302 | 280,395,370 | |
| kaempferol | 39.0 | 286 | 280,395,368 | |
| isorhamnetin | 39.0 | 316 | 280,395,368 |
References
[1] X. Zhang, and , R. Laursen, Development of Mild Extraction Methods for the Analysis of Natural Dyes in Textiles of Historical Interest Using LC-Diode Array Detector-MS. Analytical Chemistry 77, 2022-2025 (2005).
[2] X. Zhang, Corrigan, K., MacLaren, B., , M., and , R. A. Laursen, Characterization of Yellow Dyes in Nineteenth Century Chinese Textiles. Studies in Conservation 52, 211-220 (2007).
[3] J. Han, The Historical and chemical investigation of dyes in high status Chinese costume and textiles of the Ming and Qing Dynasties (1368-1911), PhD thesis, University of Glasgow, February 2016.
[4] X. Zhang, R. Laursen, and S. Osipova, Analysis of dyes in some 19th-century Uzbek suzanis. Dyes in History and Archaeology (in press).