Difference between revisions of "Polyolefin"
| (3 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
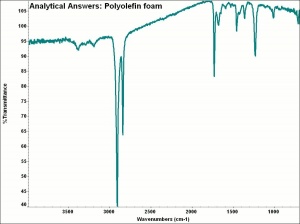
[[[SliderGallery rightalign|aaiPOLEFIN_FOAM.jpg~FTIR]]] | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|aaiPOLEFIN_FOAM.jpg~FTIR]]] | ||
| − | A general name for polymers or copolymers | + | A general name for polymers or copolymers derived from olefin hydrocarbons. Common polyolefins are [[polyethylene|polyethylene]], [[polypropylene|polypropylene]] and [[polystyrene]]. Isobutylene was the first olefin to be polymerized in 1873, but it was not made into a commercial product until I.G.Farbenindustrie of Germany developed it as a rubber substitute in the 1930s. Ethylene was first polymerized by ICI in England in the 1930s and it became an important plastic during W.W.II for fibers. Large scale applications for polyolefins were developed in the 1960s, when olefins were recognized as inexpensive raw materials. Currently, polyeolfins, also called polyalkenes, are the most common produced polymers. |
== Synonyms and Related Terms == | == Synonyms and Related Terms == | ||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
* Not susceptible to hydrolysis. | * Not susceptible to hydrolysis. | ||
| − | == | + | == Collection Risks == |
* Oxidative degradation is accelerated by UV and heat. | * Oxidative degradation is accelerated by UV and heat. | ||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
== Resources and Citations == | == Resources and Citations == | ||
| − | * Scott R. Williams. Plastic Storage Products. In ‘Preventive Conservation: Collection Storage’ Lisa Elkin and Christopher A. Norris (eds.), Society for the Preservation of Natural History Collections, New York. 2019. 774. | + | * Scott R. Williams. "Plastic Storage Products". In ‘Preventive Conservation: Collection Storage’ Lisa Elkin and Christopher A. Norris (eds.), Society for the Preservation of Natural History Collections, New York. 2019. 774. |
* Williams, S. R. (2002) “Polyolefin Foams,” AIC News, Volume 27, Number 1. | * Williams, S. R. (2002) “Polyolefin Foams,” AIC News, Volume 27, Number 1. | ||
* Contribution: Gina Watkinson, AIC Plastics Panel, 2020. | * Contribution: Gina Watkinson, AIC Plastics Panel, 2020. | ||
Latest revision as of 13:44, 22 October 2022
Description
A general name for polymers or copolymers derived from olefin hydrocarbons. Common polyolefins are Polyethylene, Polypropylene and Polystyrene. Isobutylene was the first olefin to be polymerized in 1873, but it was not made into a commercial product until I.G.Farbenindustrie of Germany developed it as a rubber substitute in the 1930s. Ethylene was first polymerized by ICI in England in the 1930s and it became an important plastic during W.W.II for fibers. Large scale applications for polyolefins were developed in the 1960s, when olefins were recognized as inexpensive raw materials. Currently, polyeolfins, also called polyalkenes, are the most common produced polymers.
Synonyms and Related Terms
polietileno (Esp.); poliolefina (Esp.); polyoléfine (Fr.); poliolefina (It.); poliolefina (Port.)
Applications
- Transparent sheets, films
- Foams
- Solid boards, Corrugated board
- Formed materials, pellets
- Non-woven fabics (Tyvek) fluff
Personal Risks
- Not susceptible to hydrolysis.
Collection Risks
- Oxidative degradation is accelerated by UV and heat.
Environmental Risks
- Films can be severely degraded by one year of outdoor exposure.
Resources and Citations
- Scott R. Williams. "Plastic Storage Products". In ‘Preventive Conservation: Collection Storage’ Lisa Elkin and Christopher A. Norris (eds.), Society for the Preservation of Natural History Collections, New York. 2019. 774.
- Williams, S. R. (2002) “Polyolefin Foams,” AIC News, Volume 27, Number 1.
- Contribution: Gina Watkinson, AIC Plastics Panel, 2020.
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: P. 636
- Hoechst Celanese Corporation, Dictionary of Fiber & Textile Technology (older version called Man-made Fiber and Textile Dictionary, 1965), Hoechst Celanese Corporation, Charlotte NC, 1990
- J.Gordon Cook, Handbook of Textile Fibres:II Man-made Fibres, Merrow Publishing Co. , Durham, England Comment: p. 536
- Theodore J. Reinhart, 'Glossary of Terms', Engineered Plastics, ASM International, 1988