Difference between revisions of "Prussian green"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m (Text replace - "== Authority ==" to "== Sources Checked for Data in Record ==") |
|||
| (2 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
| − | A green pigment originally prepared by the nearly the same process as [ | + | A green pigment originally prepared by the nearly the same process as [[Prussian%20blue|Prussian blue]]. Prussian green was produced by omitting the [[hydrochloric%20acid|hydrochloric acid]] step that converted the green to blue. However, by the mid 19th century, Prussian green sold commercially was prepared by mixing Prussian blue with a yellow pigment. Pink, a yellow dye, and gamboge were used occasionally and more often chrome yellow was used. The blue/yellow mixture has also been called [[Brunswick%20green|Brunswick green]], [[Hooker%27s%20green|Hooker's green]], and [[chrome%20green|chrome green]]. |
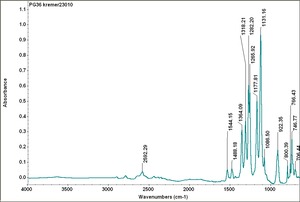
| − | [[[SliderGallery rightalign| | + | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|PG36 kremer23010.TIF~FTIR (MFA)]]] |
== Synonyms and Related Terms == | == Synonyms and Related Terms == | ||
| − | verde da Prússia (Port.) | + | verde da Prússia (Port.); original=Pigment green 36=CI 74160; |
| − | |||
| − | |||
M320-mixture: Brunswick green; chrome green; Hooker's green; malachite green; Pigment Green 15 | M320-mixture: Brunswick green; chrome green; Hooker's green; malachite green; Pigment Green 15 | ||
| − | == | + | ==Resources and Citations== |
* Ralph Mayer, ''A Dictionary of Art Terms and Techniques'', Harper and Row Publishers, New York, 1969 (also 1945 printing) | * Ralph Mayer, ''A Dictionary of Art Terms and Techniques'', Harper and Row Publishers, New York, 1969 (also 1945 printing) | ||
| Line 19: | Line 17: | ||
* R.D. Harley, ''Artists' Pigments c. 1600-1835'', Butterworth Scientific, London, 1982 | * R.D. Harley, ''Artists' Pigments c. 1600-1835'', Butterworth Scientific, London, 1982 | ||
| − | * Art and Architecture Thesaurus Online, | + | * Art and Architecture Thesaurus Online, https://www.getty.edu/research/tools/vocabulary/aat/, J. Paul Getty Trust, Los Angeles, 2000 |
[[Category:Materials database]] | [[Category:Materials database]] | ||
Latest revision as of 15:07, 22 October 2022
Description
A green pigment originally prepared by the nearly the same process as Prussian blue. Prussian green was produced by omitting the Hydrochloric acid step that converted the green to blue. However, by the mid 19th century, Prussian green sold commercially was prepared by mixing Prussian blue with a yellow pigment. Pink, a yellow dye, and gamboge were used occasionally and more often chrome yellow was used. The blue/yellow mixture has also been called Brunswick green, Hooker's green, and Chrome green.
Synonyms and Related Terms
verde da Prússia (Port.); original=Pigment green 36=CI 74160;
M320-mixture: Brunswick green; chrome green; Hooker's green; malachite green; Pigment Green 15
Resources and Citations
- Ralph Mayer, A Dictionary of Art Terms and Techniques, Harper and Row Publishers, New York, 1969 (also 1945 printing)
- R.D. Harley, Artists' Pigments c. 1600-1835, Butterworth Scientific, London, 1982
- Art and Architecture Thesaurus Online, https://www.getty.edu/research/tools/vocabulary/aat/, J. Paul Getty Trust, Los Angeles, 2000