Difference between revisions of "Sodium borate"
(username removed) |
|||
| (4 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
| − | A white, water soluble powder. Sodium borate is found in nature as [ | + | A white, water soluble powder. Sodium borate is found in nature as [[borax|borax]]. Borax is produced by the evaporation of water in shallow lakes. The white powder is mined from deposits in India, Russia, Iran, and and the U.S. (California). Sodium borate is used as a [[flux|flux]], [[cleanser|Cleansing agent]], tanning agent, fireproofing agent, and as an [[alkaline|alkaline]] ingredient in [[glass|glass]], [[ceramic|Ceramics]], and [[glaze|Glazes]]. It is also used in the developing bath for color photographs. Sodium borates are used to kill [[cockroach|Cockroaches]], and as an antifungal agent for wood. The slow acting material has also been used to clean and provide long-term inhibition of [[algae|algae]], [[lichen|lichen]], and moss on monuments (Richardson 1973). |
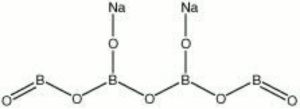
| − | + | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|sodium borate.jpg~Chemical structure]]] | |
== Synonyms and Related Terms == | == Synonyms and Related Terms == | ||
sodium pyroborate; borax; sodium tetraborate; disodium tetraborate; sodium biborate; tincar; tincal; Jaikin; Polybor | sodium pyroborate; borax; sodium tetraborate; disodium tetraborate; sodium biborate; tincar; tincal; Jaikin; Polybor | ||
| − | + | == Risks == | |
| − | == | + | * Noncombustible. |
| + | * Toxic by inhalation and ingestion. | ||
| + | * Hygroscopic. | ||
| + | * Skin contact causes irritation and burns. | ||
| + | * Science Company: [https://www.sciencecompany.com/msds/Sodium_Borate_MSDS.pdf MSDS] | ||
| + | == Physical and Chemical Properties == | ||
Soluble in water, glycerol. Insoluble in ethanol. | Soluble in water, glycerol. Insoluble in ethanol. | ||
| Line 22: | Line 27: | ||
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Melting Point | ! scope="row"| Melting Point | ||
| − | | 741 | + | | 741 C |
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Density | ! scope="row"| Density | ||
| − | | 2.367 | + | | 2.367 g/ml |
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Molecular Weight | ! scope="row"| Molecular Weight | ||
| Line 31: | Line 36: | ||
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Boiling Point | ! scope="row"| Boiling Point | ||
| − | | 1575 (dec) | + | | 1575 C (dec) |
|} | |} | ||
| − | == | + | == Resources and Citations == |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | * B.A.Richardson "Control of Biological Growths", ''Stone Industries'', 8(2):1-6, 1973. | |
* G.Caneva, M.P.Nugari, O.Salvadori, ''Biology in the Conservation of Works of Art'', ICCROM, Rome, 1991 | * G.Caneva, M.P.Nugari, O.Salvadori, ''Biology in the Conservation of Works of Art'', ICCROM, Rome, 1991 | ||
| Line 66: | Line 61: | ||
* ''The American Heritage Dictionary'' or ''Encarta'', via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998 | * ''The American Heritage Dictionary'' or ''Encarta'', via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998 | ||
| − | * | + | * Photographic chemicals at www.jetcity.com/~mrjones/chemdesc.htm |
[[Category:Materials database]] | [[Category:Materials database]] | ||
Latest revision as of 14:54, 1 June 2022
Description
A white, water soluble powder. Sodium borate is found in nature as Borax. Borax is produced by the evaporation of water in shallow lakes. The white powder is mined from deposits in India, Russia, Iran, and and the U.S. (California). Sodium borate is used as a Flux, Cleansing agent, tanning agent, fireproofing agent, and as an Alkaline ingredient in Glass, Ceramics, and Glazes. It is also used in the developing bath for color photographs. Sodium borates are used to kill Cockroaches, and as an antifungal agent for wood. The slow acting material has also been used to clean and provide long-term inhibition of Algae, Lichen, and moss on monuments (Richardson 1973).
Synonyms and Related Terms
sodium pyroborate; borax; sodium tetraborate; disodium tetraborate; sodium biborate; tincar; tincal; Jaikin; Polybor
Risks
- Noncombustible.
- Toxic by inhalation and ingestion.
- Hygroscopic.
- Skin contact causes irritation and burns.
- Science Company: MSDS
Physical and Chemical Properties
Soluble in water, glycerol. Insoluble in ethanol.
| Composition | Na2B4O7 |
|---|---|
| CAS | 1303-96-4 |
| Melting Point | 741 C |
| Density | 2.367 g/ml |
| Molecular Weight | mol. wt. = 201.22 |
| Boiling Point | 1575 C (dec) |
Resources and Citations
- B.A.Richardson "Control of Biological Growths", Stone Industries, 8(2):1-6, 1973.
- G.Caneva, M.P.Nugari, O.Salvadori, Biology in the Conservation of Works of Art, ICCROM, Rome, 1991
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 109
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia, Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976
- The Merck Index, Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: entry 8733
- Susan E. Schur, Conservation Terminology: A review of Past & Current Nomenclature of Materials, Technology and Conservation, Spring (p.34-39); Summer (p.35-38); Fall (p.25-36), 1985
- Michael McCann, Artist Beware, Watson-Guptill Publications, New York City, 1979
- Random House, Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language, Grammercy Book, New York, 1997
- The American Heritage Dictionary or Encarta, via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998
- Photographic chemicals at www.jetcity.com/~mrjones/chemdesc.htm