Difference between revisions of "Water"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:21.6765-SC152.jpg|thumb|Woodblock print<br>MFA# 21.6765]] | [[File:21.6765-SC152.jpg|thumb|Woodblock print<br>MFA# 21.6765]] | ||
| − | |||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
| Line 6: | Line 5: | ||
See also [[Distilled water]] and [[Deionized water]]. | See also [[Distilled water]] and [[Deionized water]]. | ||
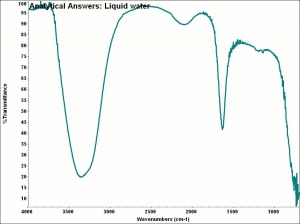
| − | + | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|aaiH2O-LIQUID.jpg~FTIR|water.jpg~Chemical structure]]] | |
== Synonyms and Related Terms == | == Synonyms and Related Terms == | ||
Latest revision as of 12:41, 27 June 2022
Description
A clear, colorless, odorless liquid that is essential for most plant and animal life. Pure water occurs in nature as rain, while water in lakes, streams, and oceans contains dissolved salts/minerals (Silica, Iron, Calcium, Magnesium, Potassium, Sodium, sulfates, chlorides, carbonates, nitrites/nitrates, etc.) and organic matter. Excessive amounts of dissolved solids constitute 'Hard water'. Dissolved solids are removed by distillation, filtration, reverse osmosis, or water softeners. Water is commonly used as a solvent and a diluent for aqueous paint media (Gouache, Tempera, Aquarelle, Fresco, etc.), for paper pulp, textile dyes, cement mixtures, photographic solutions, Detergent, and Adhesive. It is also used for cleaning, cooling, energy storage, and putting out fires.
See also Distilled water and Deionized water.
Synonyms and Related Terms
ice; steam; rain; moisture; dihydrogen oxide; oxygen hydride
Risks
- Chemical Book: SDS
Physical and Chemical Properties
- pH of pure water is 7.0.
- Standing water will absorb and dissolve carbon dioxide from the air to form carbonic acid, which can decrease the pH as low as 5.6.
- Precipitation may contain dissolved components that additionally decrease the pH (see Acid rain).
| Composition | H2O |
|---|---|
| CAS | 7732-18-5 |
| Density | 1.00 g/ml |
| Molecular Weight | mol. wt. = 18.02 |
| Refractive Index | 1.333 |
| Boiling Point | 100 C |
Comparisons
Resources and Citations
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 857
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- The Merck Index, Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: entry 10175
- Matt Roberts, Don Etherington, Bookbinding and the Conservation of Books: a Dictionary of Descriptive Terminology, U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington DC, 1982
- Reed Kay, The Painter's Guide To Studio Methods and Materials, Prentice-Hall, Inc., Englewood Cliffs, NJ, 1983
- Thomas B. Brill, Light Its Interaction with Art and Antiquities, Plenum Press, New York City, 1980
- Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia, Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976
- Random House, Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language, Grammercy Book, New York, 1997
- The American Heritage Dictionary or Encarta, via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998
- Website: www.hants.org.uk/museums/ofr/cmeth_t.html