Difference between revisions of "XIA 95BYYM15:3&4, Woolen robe and Embroidered trousers, China (Jin Dynasty, 265-430 CE)"
(Created page with "== Artifact Information == This object is a fragment of part of a samite with roundels of birds, which includes a bird with a ribbon in its beak in each roundel. The medallio...") |
|||
| (17 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Artifact Information == | == Artifact Information == | ||
| − | + | A male mummy (Yingpan man) (tomb No. 5) was discovered in Yingpan, Xinjiang by archaeologists of Xinjiang Institute of Archaeology [1]. The costume mainly includes a fine red woolen robe and an embroidered trousers. The robe was made of wool. The patterns of the robe shows the character and poses of nude putti. The robe patterns also have representations of goats and cattle with pomegranate trees standing between them [2].The colors on the two objects were well-preserved due to the special (very dry) climate in Xinjiang. | |
| + | Xinjiang Institute of Archaeology, 95BYYM15:3 Woolen robe with figures and animals. | ||
| − | + | Xinjiang Institute of Archaeology, 95BYYM15:4 Embroidered trousers with a cross pattern. | |
| − | [[File: | + | |
| + | [[File:XIA Yingpanman.png|center|frame|Image of the Yingpan man unearthed from tomb No.15 of Yingpan burial site in 1995. Copyright © Xinjiang Institute of Archaeology]] | ||
== Analytical instrumentation and procedures == | == Analytical instrumentation and procedures == | ||
| Line 17: | Line 19: | ||
== Summary of results == | == Summary of results == | ||
| − | |||
| − | '' | + | The results of dye analysis for woolen robe show that red dye was probably obtained from [http://cameo.mfa.org/wiki/Madder_(Rubia_tinctorum)_LC ''Rubia tinctorum''], whereas yellow dye was likely obtained from a luteolin-based dye source, for example, [http://cameo.mfa.org/wiki/Weld_(Reseda_luteola)_LC weld] or desert polar tree ( [http://cameo.mfa.org/wiki/Desert_Poplar_(Populus_euphratica)_LC ''Populus euphratica''] or [http://cameo.mfa.org/wiki/Desert_Poplar_(Populus_pruinosa)_LC "Populus_pruinosa"] ). |
| + | |||
| + | With regard to the embroidered trousers, brown and green threads were likely dyed with [http://cameo.mfa.org/wiki/Madder_(Rubia_tinctorum)_LC ''Rubia tinctorum''] and indigo-based dye sources, respectively. | ||
== HPLC profile == | == HPLC profile == | ||
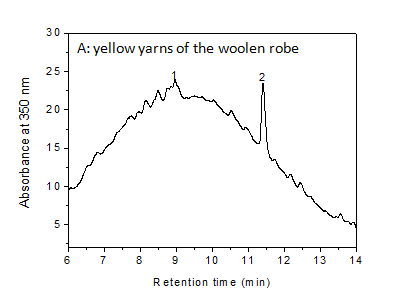
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:Yingpan A LC.PNG|center|frame| Extract from the yellow yarn of Yingpan man's woolen robe, Absorbance at 350nm (mAU) By Jian Liu, China National Silk Museum, Hangzhou]] |
| + | |||
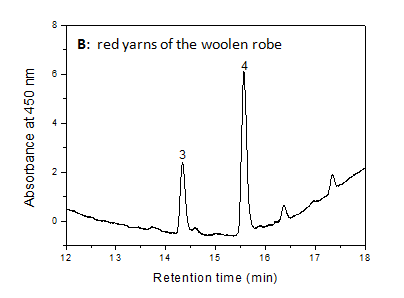
| + | [[File:Yingpan B LC.PNG|center|frame| Extract from the red yarn of Yingpan man's woolen robe, Absorbance at 450nm (mAU) By Jian Liu, China National Silk Museum, Hangzhou]] | ||
| + | |||
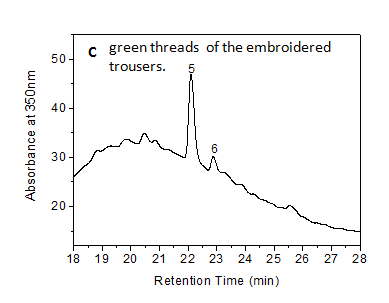
| + | [[File:Yingpan C LC.PNG|center|frame| Extract from the red yarn of Yingpan man's woolen robe, Absorbance at 350nm (mAU) By Jian Liu, China National Silk Museum, Hangzhou]] | ||
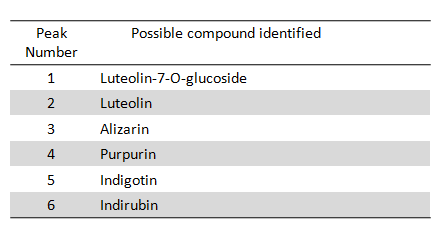
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:Yingpan peaks.PNG|center|frame| Possible compounds identified By Jian Liu, China National Silk Museum, Hangzhou]] |
== References == | == References == | ||
| − | [1] [ | + | [1] Li W and Zhou J. Archaeological finds at the burial site of Yingpan and some related questions. In: Ma C and Yue F (Eds.), Archaeological treasures of the Silk Road in Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region. Shanghai Translation Publishing House: Shanghai, pp 63-75. |
| + | |||
| + | [2] Jones R. Centaurs on the silk road: recent discoveries of Hellenistic textiles in western China. The Silk Road 2009; 16 (2): 23-32. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [3] Mouri C, Laursen R. Identification and partial characterization of C-glycosylfalvone markers in Asian plant dyes using liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Journal of Chromatography A 2011; 1218: 7325-30. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Acknowledge == | ||
| + | |||
| + | We would like to thank Prof. Li Wenying, Kang Xiaojing and Liu Yusheng of Xinjiang Institute of Archaeology for providing supporting materials and photographs. | ||
| − | |||
Latest revision as of 09:17, 18 September 2017
Artifact Information
A male mummy (Yingpan man) (tomb No. 5) was discovered in Yingpan, Xinjiang by archaeologists of Xinjiang Institute of Archaeology [1]. The costume mainly includes a fine red woolen robe and an embroidered trousers. The robe was made of wool. The patterns of the robe shows the character and poses of nude putti. The robe patterns also have representations of goats and cattle with pomegranate trees standing between them [2].The colors on the two objects were well-preserved due to the special (very dry) climate in Xinjiang.
Xinjiang Institute of Archaeology, 95BYYM15:3 Woolen robe with figures and animals.
Xinjiang Institute of Archaeology, 95BYYM15:4 Embroidered trousers with a cross pattern.
Analytical instrumentation and procedures
The dye was extracted from a thread (0.2-1mg) of the archaeological object in a solution of pyridine/water/1.0M oxalic acid as described by Mouri and Laursen [2]. The solution was evaporated to dryness under a nitrogen flow, and redissolved in 50 μL MeOH/H2O (1/1); subsequently, 20 μL of dye solution was injected onto HPLC column.
An extract was analyzed on an HPLC-PDA-MS system consisting of a Shimadzu LC-20A high performance liquid chromatography, a Shimadzu SPD-M20A photodiode array detector and a Thermo LTQ XL ion trap mass spectrometer. The separation was performed on a Shim-pack XR-ODS column (3.0 mm × 75 mm, 2.2-μm particle size) and a Phenomenex Luna C18 column (2.0 mm × 150 mm, 3-μm particle size). Columns were eluted with acetonitrile-water gradients containing 0.1% formic acid at a flow rate of 0.3 mL/min.
Summary of results
The results of dye analysis for woolen robe show that red dye was probably obtained from Rubia tinctorum, whereas yellow dye was likely obtained from a luteolin-based dye source, for example, weld or desert polar tree ( Populus euphratica or "Populus_pruinosa" ).
With regard to the embroidered trousers, brown and green threads were likely dyed with Rubia tinctorum and indigo-based dye sources, respectively.
HPLC profile
References
[1] Li W and Zhou J. Archaeological finds at the burial site of Yingpan and some related questions. In: Ma C and Yue F (Eds.), Archaeological treasures of the Silk Road in Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region. Shanghai Translation Publishing House: Shanghai, pp 63-75.
[2] Jones R. Centaurs on the silk road: recent discoveries of Hellenistic textiles in western China. The Silk Road 2009; 16 (2): 23-32.
[3] Mouri C, Laursen R. Identification and partial characterization of C-glycosylfalvone markers in Asian plant dyes using liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Journal of Chromatography A 2011; 1218: 7325-30.
Acknowledge
We would like to thank Prof. Li Wenying, Kang Xiaojing and Liu Yusheng of Xinjiang Institute of Archaeology for providing supporting materials and photographs.