Difference between pages "Thulium" and "Titanox"
(Difference between pages)
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | [[File:titanox C100x.jpg|thumb|Titanox at 100x (visible light left; UV light right)]] | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
| − | A | + | [Velsicol] A trademark name for a white pigment composed of [[titanium%20dioxide|titanium dioxide]]. Titanox is often extended with [[calcium%20sulfate|calcium sulfate]] and/or [[barium%20sulfate|barium sulfate]]. It is used industrially in paints, paper, rubber, plastics, leather, inks, ceramics, floor covering, and textile coatings. |
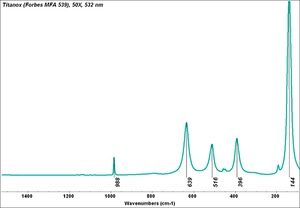
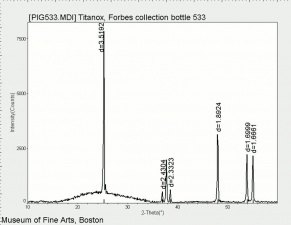
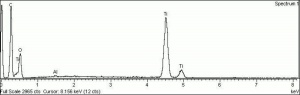
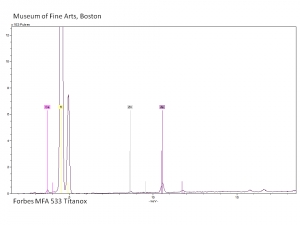
| + | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|Titanox (Forbes MFA 539), 50X, 532 nm copy.tif~Raman (MFA)|PIG533.jpg~XRD|f533sem.jpg~SEM|f533edsbw.jpg~EDS|Slide22_F533.PNG~XRF]]] | ||
| + | == Synonyms and Related Terms == | ||
| − | + | titanium dioxide | |
| − | |||
== Risks == | == Risks == | ||
| − | * | + | * Noncombustible |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | == | + | == Comparisons == |
| − | + | [[media:download_file_528.pdf|Characteristics of Common White Pigments]] | |
| − | + | ==Resources and Citations== | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | * R. Mayer, ''The Artist's Handbook of Materials and Techniques'', Viking Press, New York, 1981 | |
| − | * G.S.Brady, ''Materials Handbook'', McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. | + | * G.S.Brady, ''Materials Handbook'', McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 815 |
* Richard S. Lewis, ''Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary'', Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993 | * Richard S. Lewis, ''Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary'', Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993 | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
[[Category:Materials database]] | [[Category:Materials database]] | ||
Latest revision as of 15:38, 10 June 2022
Description
[Velsicol] A trademark name for a white pigment composed of Titanium dioxide. Titanox is often extended with Calcium sulfate and/or Barium sulfate. It is used industrially in paints, paper, rubber, plastics, leather, inks, ceramics, floor covering, and textile coatings.
Synonyms and Related Terms
titanium dioxide
Risks
- Noncombustible
Comparisons
Characteristics of Common White Pigments
Resources and Citations
- R. Mayer, The Artist's Handbook of Materials and Techniques, Viking Press, New York, 1981
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 815
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993