Difference between revisions of "Glossary of Ukiyo-e Colorants"
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
'''Yellow''' | '''Yellow''' | ||
| − | Orpiment, turmeric and flavonoid yellows (such as pagoda tree, rice plant) are the most commonly used yellow colorants that were easily detected. Gamboge is also likely to have been used but none of the MFA analysis techniques could detect gamboge. Additionally there is literature that points to the potential use of other organic yellows, such as yellowwood, but this has not been found in any of the prints so far. | + | Orpiment, turmeric and flavonoid yellows (such as pagoda tree, rice plant) are the most commonly used yellow colorants that were easily detected. Gamboge is also likely to have been used but none of the MFA analysis techniques could detect gamboge. Additionally there is literature that points to the potential use of other organic yellows, such as yellowwood, but this has not been found in any of the prints so far. |
| + | |||
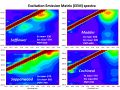
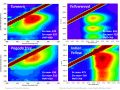
| + | Of the primary yellows, orpiment (arsenic sulfide) was detected by the X-ray fluorescence analysis. Turmeric and yellowwood both fluoresce very brightly in ultraviolet light and, luckily, give very distinctive EEM spectra (shown below). Some of the other organic yellows, like pagoda tree and rice plant, but fluoresce weakly in ultraviolet light. Chemically, these two compounds are both flavonoids and and only have slight differences in their EEM plots. Thus, the decision was made to call them by their chemical name, flavonoid, to minimize mistakes in identification. | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
| Line 48: | Line 50: | ||
'''Black/Gray''' | '''Black/Gray''' | ||
| − | Carbon black, sumi, or soot from oil lamps or pine soot mixed with animal glue is used to print the | + | Carbon black, sumi, or soot from oil lamps or pine soot mixed with animal glue is used to print the key block as well as any other black area. It can range from a deep black to a blue grey color (pine soot). |
'''Mica''' | '''Mica''' | ||
Revision as of 15:03, 28 April 2020
Glossary of Colorants
The ukiyo-e print or Japanese woodblock print colorant database is a…… This database currently focuses on prints from the MFA’s collection especially from 17XX-18XX. We hope to continue adding to the database but at this moment covers only the colorants found in the above mentioned time frame so does not yet cover the whole breadth of colorants used in Japanese woodblock prints.
Red
The primary organic red colorants used in the prints are: -Safflower -Madder -Sappanwood
Yellow
Orpiment, turmeric and flavonoid yellows (such as pagoda tree, rice plant) are the most commonly used yellow colorants that were easily detected. Gamboge is also likely to have been used but none of the MFA analysis techniques could detect gamboge. Additionally there is literature that points to the potential use of other organic yellows, such as yellowwood, but this has not been found in any of the prints so far.
Of the primary yellows, orpiment (arsenic sulfide) was detected by the X-ray fluorescence analysis. Turmeric and yellowwood both fluoresce very brightly in ultraviolet light and, luckily, give very distinctive EEM spectra (shown below). Some of the other organic yellows, like pagoda tree and rice plant, but fluoresce weakly in ultraviolet light. Chemically, these two compounds are both flavonoids and and only have slight differences in their EEM plots. Thus, the decision was made to call them by their chemical name, flavonoid, to minimize mistakes in identification.
Blue
Until the introduction of Prussian blue, indigo and dayflower were the only blues used. These blues can easily be identified using FORS. (I thought a little comment for each color and what is used to identify it would be nice but maybe it’s unnecessary since this will be explained in the color page) -Indigo -Dayflower -Prussian blue (Underline means link to another page)
Green
Green is created as a mixture or overprinting of a blue and yellow. -Indigo/orpiment -Other combinations (List maybe just the common ones and other could be Others)
Purple
Purple is created as a mixture or overprinting of a blue and red/pink. -Safflower/dayflower -Madder/dayflower -Other combinations
Brown
-hematite -red lead -mixtures --faded purple
White
White is often used in a mixture rather than on its own, allowing for the paper to be the “white” -calcium carbonate -white lead
Black/Gray
Carbon black, sumi, or soot from oil lamps or pine soot mixed with animal glue is used to print the key block as well as any other black area. It can range from a deep black to a blue grey color (pine soot).
Mica
description
Metallic
Description