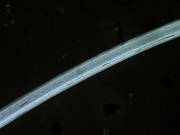
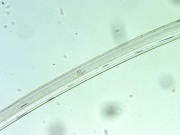
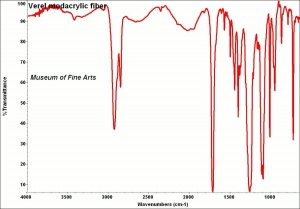
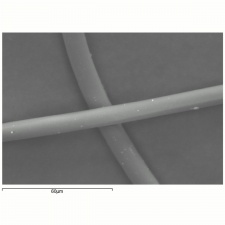
Modacrylic fiber
Description
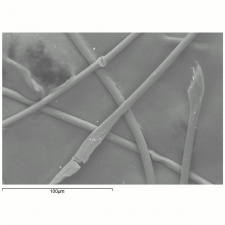
A manufactured fiber in which the fiber-forming substance is any long chain synthetic polymer composed of less than 85% but at least 35% by weight of acrylonitrile units (Federal Trade Commission definition). The first modacrylic (modified acrylic) fiber, Dynel® was introduced in 1949; many later followed but the only one still in production at the end of the twentieth century is SEF [Solutia]. The resilient modacrylic fibers have an irregular cross section and fair elastic recovery (79-99% at 2% elongation). SEF has a low moisture regain of 2.5%. It will maintain its properties to temperatures of 190C (375F). Modacrylic fibers are resistant to sunlight, bleaches and are considered non-allergenic. Because modacrylic fibers are fire resistant and self-extinguishing, they are commonly used in children's sleepwear. They are also used for wigs, stuffed toys and fake fur fabrics.
Synonyms and Related Terms
modacrylic fibre; polyacrylonitrile; Dynel® [Union Carbide]; Verel®[Tennessee Eastman]; SEF [Solutia]; Elura [Monsanto Fibers]; Teklan; Crylor; Kanecaron
Risks
- Fire resistant and self-extinguishing.
- Non-allergenic.
- Cellusuede: Modacrylic SDS
Physical and Chemical Properties
- Soluble in butyrolactone and warm acetone.
- Resistant to other organic solvents alkalis and acids.
- Tenacity = 1.8-2.5 g/denier (dry); 1.7-2.4 (wet);
- Elongation = 35-48%;
- Moisture regain = 0.4-4.0%.
- Melting Point = 120-125C (soften).
- Density = 1.35-1.37
Comparisons
Properties of Synthetic Fibers
Resources and Citations
- Hoechst Celanese Corporation, Dictionary of Fiber & Textile Technology (older version called Man-made Fiber and Textile Dictionary, 1965), Hoechst Celanese Corporation, Charlotte NC, 1990
- Marjory L. Joseph, Introductory Textile Science, Holt, Rinehart and Winston, Fort Worth, TX, 1986
- Identification of Textile Materials, The Textile Institute, Manchester, England, 1985
- Fairchild's Dictionary of Textiles, Phyllis G.Tortora, Robert S. Merkel (eds.), Fairchild Publications, New York City, 7th edition, 1996
- J.Gordon Cook, Handbook of Textile Fibres:II Man-made Fibres, Merrow Publishing Co. , Durham, England
- Website: www.fabrics.net
- Rosalie Rosso King, Textile Identification, Conservation, and Preservation, Noyes Publications, Park Ridge, NJ, 1985
- Random House, Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language, Grammercy Book, New York, 1997
- The American Heritage Dictionary or Encarta, via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998