Difference between revisions of "Alum"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
| − | A general name used for | + | A general name used for double sulfate salts of aluminum. The most common alums are double salts with potassium [KAl(SO<sub>4</sub>)<sub>2</sub>·12 H<sub>2</sub>O], sodium [NaAl(SO<sub>4</sub>)<sub>2</sub>·12 H<sub>2</sub>O] or ammonium [NH<sub>4</sub>Al(SO<sub>4</sub>)<sub>2</sub>·12 H<sub>2</sub>O]. All of these have some properties in common, such as they are water-soluble and have a sweet taste. Additionally they react as an acid by turning blue litmus paper to red. |
| + | Uses for the specific types of alum salts include: | ||
| + | * Potash alum, refers to [[aluminum potassium sulfate]]. It is a colorless, crystalline material used in the tawing of skins and as a mordant, or fixative, for many natural dyes. Potash alum is also used as the base for most [[Lake]] pigments. | ||
| + | * For papermakers, the term alum, refers to [[aluminum sulfate]] or the mixture of aluminum sulfates obtained by treating pulverized [[bauxite]] with [[sulfuric acid]]. | ||
| + | * In cooking, the term alum refers to [[aluminum ammonium sulfate]]. It is used in baking powder where it acts as a whitener and drying agent in wheat flour. It also acts as a flocculant to clarify cloudy liquids. | ||
| + | * Other materials referred to as alum are [[ferric ammonium sulfate]], chromium sodium sulfate, and chromium ammonium sulfate. | ||
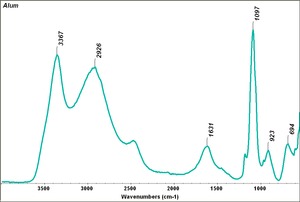
[[[SliderGallery rightalign|Alum.TIF~FTIR (MFA)]]] | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|Alum.TIF~FTIR (MFA)]]] | ||
| Line 8: | Line 13: | ||
aluminum potassium sulfate; aluminum ammonium sulfate; aluminum sulfate; alum cake; alunite | aluminum potassium sulfate; aluminum ammonium sulfate; aluminum sulfate; alum cake; alunite | ||
| + | |||
| + | =Risks= | ||
| + | * Alums will corrode metal | ||
== Resources and Citations == | == Resources and Citations == | ||
* Irene Bruckle, "The Role of Alum in Historical Papermaking", Abbey Newsletter, Volume 17(4), September 1993. [http://cool.conservation-us.org/byorg/abbey/an/an17/an17-4/an17-407.html Link] | * Irene Bruckle, "The Role of Alum in Historical Papermaking", Abbey Newsletter, Volume 17(4), September 1993. [http://cool.conservation-us.org/byorg/abbey/an/an17/an17-4/an17-407.html Link] | ||
| − | |||
* R. J. Gettens, G.L. Stout, ''Painting Materials, A Short Encyclopaedia'', Dover Publications, New York, 1966 Comment: aluminum hydrate: uses the term 'alum' | * R. J. Gettens, G.L. Stout, ''Painting Materials, A Short Encyclopaedia'', Dover Publications, New York, 1966 Comment: aluminum hydrate: uses the term 'alum' | ||
| − | |||
* G.S.Brady, ''Materials Handbook'', McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 32 | * G.S.Brady, ''Materials Handbook'', McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 32 | ||
| − | |||
* ''The Dictionary of Paper'', American Paper Institute, New York, Fourth Edition, 1980 | * ''The Dictionary of Paper'', American Paper Institute, New York, Fourth Edition, 1980 | ||
| − | |||
* E.J.LaBarre, ''Dictionary and Encyclopedia of Paper and Paper-making'', Swets & Zeitlinger, Amsterdam, 1969 | * E.J.LaBarre, ''Dictionary and Encyclopedia of Paper and Paper-making'', Swets & Zeitlinger, Amsterdam, 1969 | ||
| − | |||
* Matt Roberts, Don Etherington, ''Bookbinding and the Conservation of Books: a Dictionary of Descriptive Terminology'', U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington DC, 1982 | * Matt Roberts, Don Etherington, ''Bookbinding and the Conservation of Books: a Dictionary of Descriptive Terminology'', U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington DC, 1982 | ||
| − | |||
* Susan E. Schur, Conservation Terminology: A review of Past & Current Nomenclature of Materials, ''Technology and Conservation'', Spring (p.34-39); Summer (p.35-38); Fall (p.25-36), 1985 | * Susan E. Schur, Conservation Terminology: A review of Past & Current Nomenclature of Materials, ''Technology and Conservation'', Spring (p.34-39); Summer (p.35-38); Fall (p.25-36), 1985 | ||
| − | + | * Wikipedia: [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alum Alum] Accessed March 2025. | |
| − | + | * Bill Bryson, ‘At Home: A Short History of Private Life’ Doubleday Publishers, London 2010. | |
[[Category:Materials database]] | [[Category:Materials database]] | ||
Revision as of 09:25, 16 March 2025
Description
A general name used for double sulfate salts of aluminum. The most common alums are double salts with potassium [KAl(SO4)2·12 H2O], sodium [NaAl(SO4)2·12 H2O] or ammonium [NH4Al(SO4)2·12 H2O]. All of these have some properties in common, such as they are water-soluble and have a sweet taste. Additionally they react as an acid by turning blue litmus paper to red. Uses for the specific types of alum salts include:
- Potash alum, refers to Aluminum potassium sulfate. It is a colorless, crystalline material used in the tawing of skins and as a mordant, or fixative, for many natural dyes. Potash alum is also used as the base for most Lake pigments.
- For papermakers, the term alum, refers to Aluminum sulfate or the mixture of aluminum sulfates obtained by treating pulverized Bauxite with Sulfuric acid.
- In cooking, the term alum refers to Aluminum ammonium sulfate. It is used in baking powder where it acts as a whitener and drying agent in wheat flour. It also acts as a flocculant to clarify cloudy liquids.
- Other materials referred to as alum are Ferric ammonium sulfate, chromium sodium sulfate, and chromium ammonium sulfate.
Synonyms and Related Terms
aluminum potassium sulfate; aluminum ammonium sulfate; aluminum sulfate; alum cake; alunite
Risks
- Alums will corrode metal
Resources and Citations
- Irene Bruckle, "The Role of Alum in Historical Papermaking", Abbey Newsletter, Volume 17(4), September 1993. Link
- R. J. Gettens, G.L. Stout, Painting Materials, A Short Encyclopaedia, Dover Publications, New York, 1966 Comment: aluminum hydrate: uses the term 'alum'
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 32
- The Dictionary of Paper, American Paper Institute, New York, Fourth Edition, 1980
- E.J.LaBarre, Dictionary and Encyclopedia of Paper and Paper-making, Swets & Zeitlinger, Amsterdam, 1969
- Matt Roberts, Don Etherington, Bookbinding and the Conservation of Books: a Dictionary of Descriptive Terminology, U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington DC, 1982
- Susan E. Schur, Conservation Terminology: A review of Past & Current Nomenclature of Materials, Technology and Conservation, Spring (p.34-39); Summer (p.35-38); Fall (p.25-36), 1985
- Wikipedia: Alum Accessed March 2025.
- Bill Bryson, ‘At Home: A Short History of Private Life’ Doubleday Publishers, London 2010.