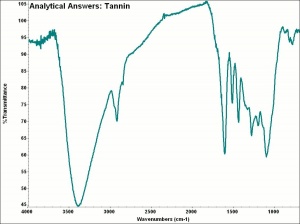
Difference between revisions of "Tannin"
(username removed) |
(username removed) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
| − | Any of several compounds used for dyeing cloth and tanning leather. Tannins are usually a catechol, pyrogallol, phenolic, or aldehyde type compounds. Natural tannins are found in many plants and are usually concentrated in bark and damaged tissues such as galls and wounds. Tannins reacts with proteins ([http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=animal | + | Any of several compounds used for dyeing cloth and tanning leather. Tannins are usually a catechol, pyrogallol, phenolic, or aldehyde type compounds. Natural tannins are found in many plants and are usually concentrated in bark and damaged tissues such as galls and wounds. Tannins reacts with proteins ([http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=animal%20skin skin], [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=albumin albumin], [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=gelatin gelatin], etc.) to form insoluble products that are resistant to degradation. Skin treated with tannins is called [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=leather leather]. Tannins have been used for several thousand years, especially in China. Examples of natural tannins are [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=tannic%20acid tannic acid], [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=myrobalan%20extract myrobalans], and [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=quebracho quebracho]. Examples of synthetic tannins are [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=formaldehyde formaldehyde], [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=glutaraldehyde glutaraldehyde], and [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=hydroxyacetic%20acid glycolic acid]. |
== Synonyms and Related Terms == | == Synonyms and Related Terms == | ||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
== Authority == | == Authority == | ||
| − | * | + | * G.S.Brady, ''Materials Handbook'', McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 796 |
| − | * | + | * Richard S. Lewis, ''Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary'', Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993 |
| − | * | + | * John and Margaret Cannon, ''Dye Plants and Dyeing'', Herbert Press, London, 1994 |
| − | * | + | * Random House, ''Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language'', Grammercy Book, New York, 1997 |
* ''The American Heritage Dictionary'' or ''Encarta'', via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998 | * ''The American Heritage Dictionary'' or ''Encarta'', via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998 | ||
| − | * ''Encyclopedia Britannica'', http://www.britannica.com Comment: "tannin" | + | * ''Encyclopedia Britannica'', http://www.britannica.com Comment: "tannin" Encyclopædia Britannica Premium Service. [Accessed 28 Sept. 2005]. |
* Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia, at http://www.wikipedia.com Comment: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tannin (Accessed Sept. 28, 2005) | * Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia, at http://www.wikipedia.com Comment: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tannin (Accessed Sept. 28, 2005) | ||
Revision as of 07:29, 24 July 2013
Description
Any of several compounds used for dyeing cloth and tanning leather. Tannins are usually a catechol, pyrogallol, phenolic, or aldehyde type compounds. Natural tannins are found in many plants and are usually concentrated in bark and damaged tissues such as galls and wounds. Tannins reacts with proteins (skin, albumin, gelatin, etc.) to form insoluble products that are resistant to degradation. Skin treated with tannins is called leather. Tannins have been used for several thousand years, especially in China. Examples of natural tannins are tannic acid, myrobalans, and quebracho. Examples of synthetic tannins are formaldehyde, glutaraldehyde, and glycolic acid.
Synonyms and Related Terms
Tannine (Deut., Ned.); tanin (Fr.); tannin (Sven.)
Other Properties
Soluble in water or ethanol. Insoluble in ether, chloroform, carbon disulfide, benzene. Precipitates gelatin.
Additional Information
Ann Hagerman, Tannin Handbook, at Website (provides extensive information on tannin chemistry and analysis)
Authority
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 796
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- John and Margaret Cannon, Dye Plants and Dyeing, Herbert Press, London, 1994
- Random House, Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language, Grammercy Book, New York, 1997
- The American Heritage Dictionary or Encarta, via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998
- Encyclopedia Britannica, http://www.britannica.com Comment: "tannin" Encyclopædia Britannica Premium Service. [Accessed 28 Sept. 2005].
- Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia, at http://www.wikipedia.com Comment: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tannin (Accessed Sept. 28, 2005)