Enstatite: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
bronzite; Enstatit (Deut.); enstatiet (Ned.) | bronzite; Enstatit (Deut.); enstatiet (Ned.) | ||
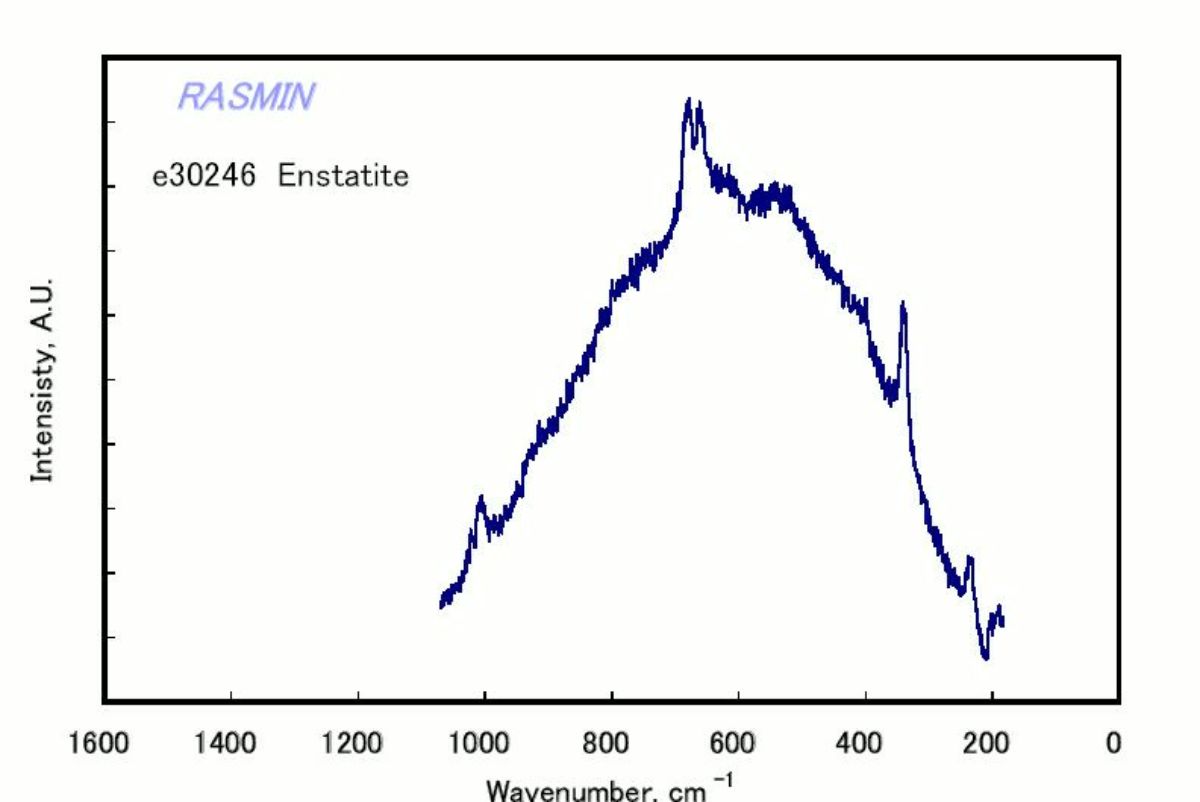
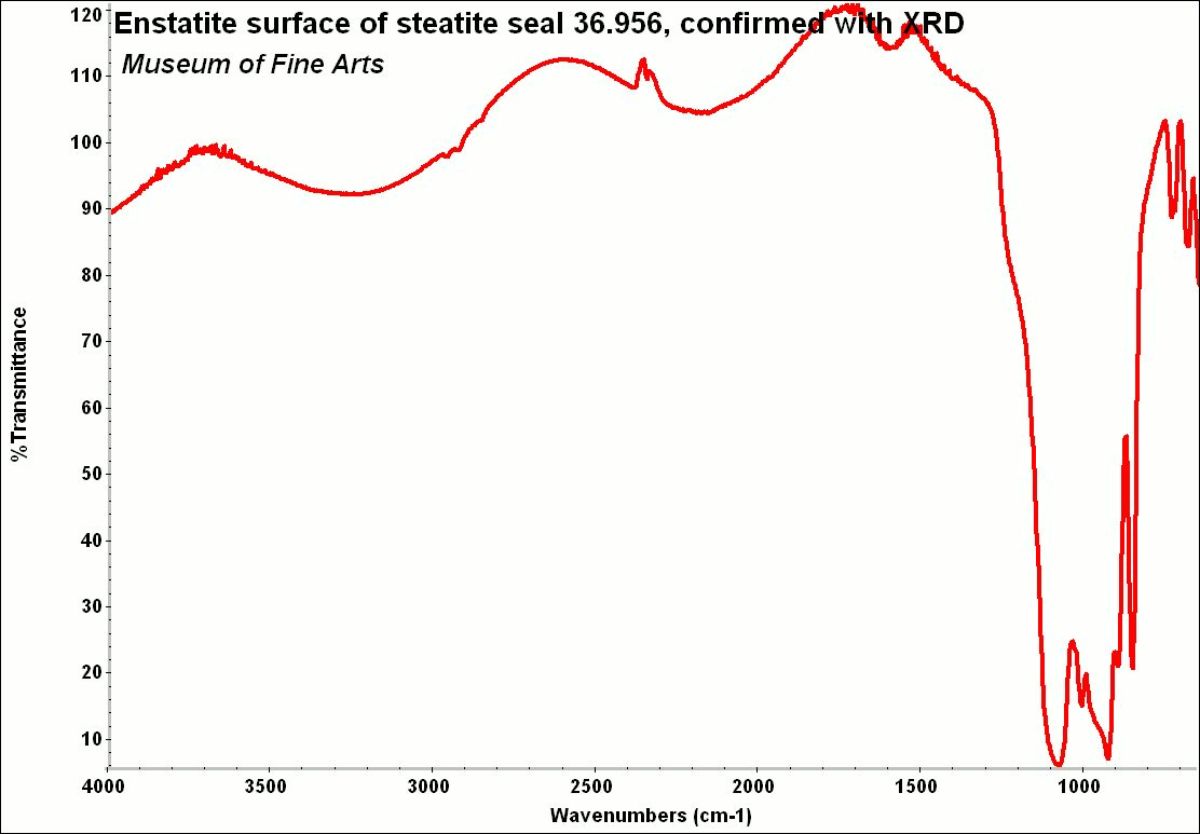
[[[SliderGallery rightalign|enstatiteRS.jpg~Raman]]] | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|enstatiteRS.jpg~Raman|Enstatite.jpg~FTIR]]] | ||
== Other Properties == | == Other Properties == | ||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
| 1.650-1.788 | | 1.650-1.788 | ||
|} | |} | ||
== Authority == | == Authority == | ||
Revision as of 07:29, 24 July 2013
Description
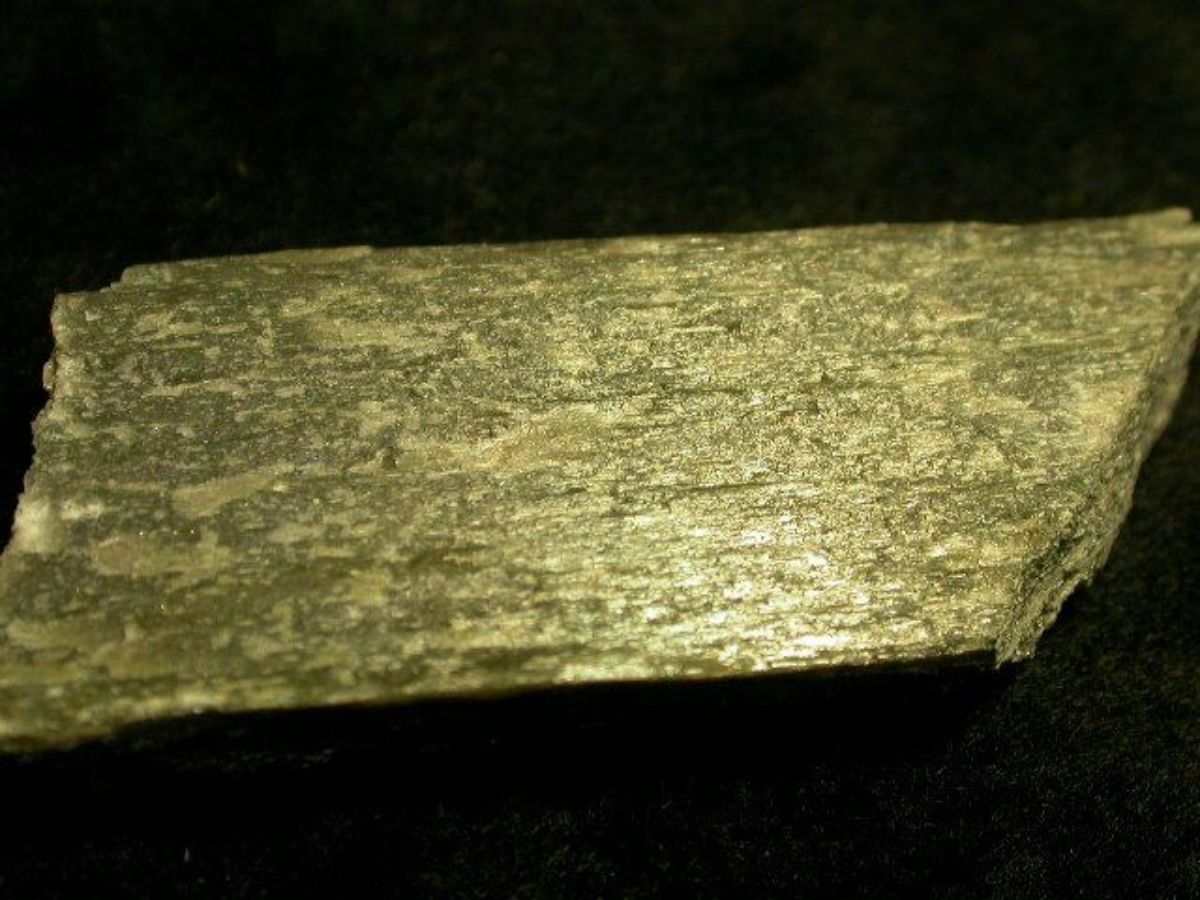
A pyroxene mineral composed of magnesium silicate. Enstatite was first described by G.A. Kenngott in 1855. It occurs naturally in metamorphic rocks and meterorites. The mineral is usually a gray, pale green, or brown in color although a gemstone quality emerald green variety occurs rarely. Weathered enstatite can have a metallic luster and is called bronzite. Enstatite can alter to form steatite. Steatite may also be heated to form enstatite.
Synonyms and Related Terms
bronzite; Enstatit (Deut.); enstatiet (Ned.)
Other Properties
Orthorhombic crystal system .
| Composition | MgSiO3 |
|---|---|
| Mohs Hardness | 5-6 |
| Density | 3.21-3.96 |
| Refractive Index | 1.650-1.788 |
Authority
- Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia, at http://www.wikipedia.com Comment: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Enstatite (Accessed Nov. 2, 2005)