Difference between revisions of "Casein fiber"
(username removed) |
(username removed) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:Lanital 200X BF.jpg|thumb|Lanital fibers]] |
== Description == | == Description == | ||
| − | Regenerated [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=protein | + | Regenerated [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=protein%20fiber protein fibers] made from polymerized [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=casein casein]. In the early 1930s, an Italian chemist, Antonio Ferretti developed a successful method to make casein into fibers (see [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=Lanital Lanital]). Casein is processed with [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=formaldehyde formaldehyde] or [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=benzaldehyde benzaldehyde] and metal salts then pressed through spinnerets to form long, silklike fibers. Casein fibers are softer and smoother than [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=wool wool] and contain less [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=sulfur sulfur]. They are not susceptible to moths but can be degraded by some bacteria. Casein fibers are usually cream colored. They accept dyes well but have poor washfastness. Most often casein fibers are blended with wool in fabrics, carpets and hat felts. Lanital, along with other regenerated protein fibers, have been replaced by other synthetic fibers, because casein fibers were weak when wet and susceptible to microbiological growths. |
| − | |||
== Synonyms and Related Terms == | == Synonyms and Related Terms == | ||
| − | casein fibre (Br.); fibras de casina (Esp.); | + | casein fibre (Br.); fibras de casina (Esp.); caseïnevezel (Ned); casein wool; caslen; Aralac; Lanital [Snia Viscosa, Italy]; Lactofil; Casolana; Tiolan; Polana; Cargan; Merinova; Fibrolan [Courtaulds, England] |
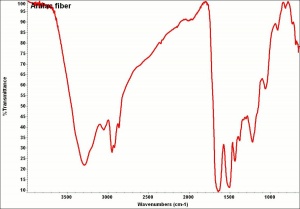
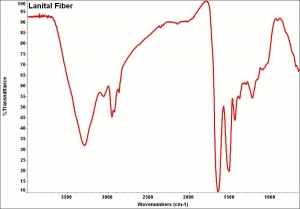
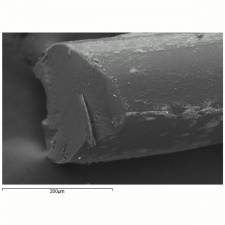
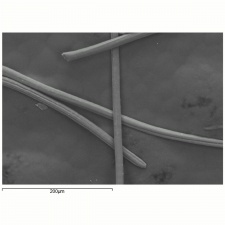
| − | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|aralac300m.jpg~SEM|lanital250m.jpg~SEM]]] | + | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|Aralacfiberkj1.jpg~FTIR|LanitaFiberkj1.jpg~FTIR|Aralacfiberkj1.jpg~FTIR|LanitaFiberkj1.jpg~FTIR|aralac300m.jpg~SEM|lanital250m.jpg~SEM]]] |
== Other Properties == | == Other Properties == | ||
| Line 33: | Line 32: | ||
G.Cook, ''Handbook of Textile Fibres:II. Man-made Fibres'', 5th edition, Merrow Publishing Co., Durham, England, 1984. | G.Cook, ''Handbook of Textile Fibres:II. Man-made Fibres'', 5th edition, Merrow Publishing Co., Durham, England, 1984. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
== Authority == | == Authority == | ||
| Line 47: | Line 37: | ||
* ''Identification of Textile Materials'', The Textile Institute, Manchester, England, 1985 | * ''Identification of Textile Materials'', The Textile Institute, Manchester, England, 1985 | ||
| − | * | + | * J.Gordon Cook, ''Handbook of Textile Fibres:II Man-made Fibres'', Merrow Publishing Co. , Durham, England |
| − | * | + | * F. Kidd, ''Brushmaking Materials'', Bristish Brush Manufacturers, London, 1957 Comment: p. 58 |
| − | * | + | * Thomas Gregory, ''The Condensed Chemical Dictionary'', Reinhold Publishing, New York, 3rd ed., 1942 |
| − | * | + | * G.S.Brady, ''Materials Handbook'', McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 153 |
[[Category:Materials database]] | [[Category:Materials database]] | ||
Revision as of 06:36, 24 July 2013
Description
Regenerated protein fibers made from polymerized casein. In the early 1930s, an Italian chemist, Antonio Ferretti developed a successful method to make casein into fibers (see Lanital). Casein is processed with formaldehyde or benzaldehyde and metal salts then pressed through spinnerets to form long, silklike fibers. Casein fibers are softer and smoother than wool and contain less sulfur. They are not susceptible to moths but can be degraded by some bacteria. Casein fibers are usually cream colored. They accept dyes well but have poor washfastness. Most often casein fibers are blended with wool in fabrics, carpets and hat felts. Lanital, along with other regenerated protein fibers, have been replaced by other synthetic fibers, because casein fibers were weak when wet and susceptible to microbiological growths.
Synonyms and Related Terms
casein fibre (Br.); fibras de casina (Esp.); caseïnevezel (Ned); casein wool; caslen; Aralac; Lanital [Snia Viscosa, Italy]; Lactofil; Casolana; Tiolan; Polana; Cargan; Merinova; Fibrolan [Courtaulds, England]
Other Properties
Insoluble in dilute acids, hydrogen peroxide and most organic solvents. Affected by alkalis. Burns with odor of burning hair.
Filaments are smooth. Cross sections = circular, bean-shaped. Diameter=20-30 micrometers. Tenacity = 0.9-1.1 g/denier (dry); 0.3-0.6 (wet); Elongation =60-70%; Moisture regain = 14%
| Melting Point | 150 (dec) |
|---|---|
| Density | 1.30 |
Hazards and Safety
Burns slowly and brightly in air, but extinguishes with removal of flame source.
Additional Information
G.Cook, Handbook of Textile Fibres:II. Man-made Fibres, 5th edition, Merrow Publishing Co., Durham, England, 1984.
Authority
- Identification of Textile Materials, The Textile Institute, Manchester, England, 1985
- J.Gordon Cook, Handbook of Textile Fibres:II Man-made Fibres, Merrow Publishing Co. , Durham, England
- F. Kidd, Brushmaking Materials, Bristish Brush Manufacturers, London, 1957 Comment: p. 58
- Thomas Gregory, The Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Reinhold Publishing, New York, 3rd ed., 1942
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 153