Difference between revisions of "Obsidian"
(username removed) |
(username removed) |
||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
== Synonyms and Related Terms == | == Synonyms and Related Terms == | ||
| − | volcanic glass; basalt glass; tachylite; perlite; calite; mountain mahogany (deep red obsidian); Apache tears (pebble-like nodules); | + | volcanic glass; basalt glass; tachylite; perlite; calite; mountain mahogany (deep red obsidian); Apache tears (pebble-like nodules); obsidian snowflake (black with white inclusions); obsidiana (Esp., Port.); obsidienne (Fr.); Obsidian (Deut.); obsidiaan (Ned.) |
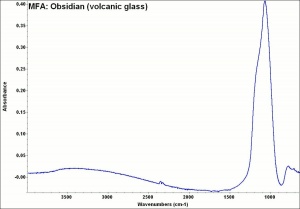
[[[SliderGallery rightalign|MFA- Obsidian (volcanic glass).jpg~FTIR]]] | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|MFA- Obsidian (volcanic glass).jpg~FTIR]]] | ||
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
== Authority == | == Authority == | ||
| − | * | + | * G.S.Brady, ''Materials Handbook'', McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 641 |
| − | * | + | * Jack Odgen, ''Jewellery of the Ancient World'', Rizzoli International Publications Inc., New York City, 1982 |
* ''Encyclopedia of Archaeology'', Glyn E. Daniel, ed., Thomas Y. Crowell Co., New York, 1977 | * ''Encyclopedia of Archaeology'', Glyn E. Daniel, ed., Thomas Y. Crowell Co., New York, 1977 | ||
| − | * | + | * A.Lucas, J.R.Harris, ''Ancient Egyptian Materials and Industries'', Edward Arnold Publishers Ltd., London, 4th edition, 1962 |
| − | * | + | * C.W.Chesterman, K.E.Lowe, ''Audubon Society Field Guide to North American Rocks and Minerals'', Alfred A. Knopf, New York, 1979 Comment: Mohs hardness = 6-7 |
* Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia, at http://www.wikipedia.com Comment: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Obsidian (Accessed Nov. 9, 2005) - Mohs hardness = 5.0-5.5 | * Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia, at http://www.wikipedia.com Comment: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Obsidian (Accessed Nov. 9, 2005) - Mohs hardness = 5.0-5.5 | ||
| − | * | + | * George Savage, ''Art and Antique Restorer's Handbook'', Rockliff Publishing Corp, London, 1954 |
* ''Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia'', Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976 | * ''Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia'', Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976 | ||
| − | * | + | * Random House, ''Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language'', Grammercy Book, New York, 1997 |
* ''The American Heritage Dictionary'' or ''Encarta'', via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998 | * ''The American Heritage Dictionary'' or ''Encarta'', via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998 | ||
Revision as of 07:41, 24 July 2013
Description
A dark, shiny glass formed in nature by the rapid cooling of lava. Obsidian is widely distributed and has been used since Paleolithic (before 3500 BCE) times for mirrors, weapons, tools, and jewelry. Sources of obsidian include Anatolia, Armenia, Ethiopia, Greece (Milos), Italy (Lipari, Eolie), Iceland, the U.S. (Wyoming), Mexico (Teotihuacan), Guatemala (Tikal), and Peru. Obsidian is often black in color but may also be red, brown or green. It produces conchoidal fractures when cleaved. Analysis of trace elements in obsidian pieces can be traced back to their original deposits. This has been used to evaluate early trading patterns.
Synonyms and Related Terms
volcanic glass; basalt glass; tachylite; perlite; calite; mountain mahogany (deep red obsidian); Apache tears (pebble-like nodules); obsidian snowflake (black with white inclusions); obsidiana (Esp., Port.); obsidienne (Fr.); Obsidian (Deut.); obsidiaan (Ned.)
Other Properties
Luster = vitreous Transparent to translucent
| Mohs Hardness | 5 - 7 |
|---|---|
| Density | 2.6 |
| Refractive Index | 1.482-1.496 |
Additional Images
Authority
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 641
- Jack Odgen, Jewellery of the Ancient World, Rizzoli International Publications Inc., New York City, 1982
- Encyclopedia of Archaeology, Glyn E. Daniel, ed., Thomas Y. Crowell Co., New York, 1977
- A.Lucas, J.R.Harris, Ancient Egyptian Materials and Industries, Edward Arnold Publishers Ltd., London, 4th edition, 1962
- C.W.Chesterman, K.E.Lowe, Audubon Society Field Guide to North American Rocks and Minerals, Alfred A. Knopf, New York, 1979 Comment: Mohs hardness = 6-7
- Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia, at http://www.wikipedia.com Comment: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Obsidian (Accessed Nov. 9, 2005) - Mohs hardness = 5.0-5.5
- George Savage, Art and Antique Restorer's Handbook, Rockliff Publishing Corp, London, 1954
- Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia, Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976
- Random House, Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language, Grammercy Book, New York, 1997
- The American Heritage Dictionary or Encarta, via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998
- CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, Robert Weast (ed.), CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, v. 61, 1980 Comment: ref. index=1.482-1.496