Difference between revisions of "Zeolite"
(username removed) |
(username removed) |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
| − | A group of naturally occurring minerals composed of alkali-hydrated aluminum silicates. Examples are analcite, chabazite, heulandite, [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=natrolite natrolite], phillipsite, scolecite, stilbite, and thomosonite. Zeolites are soft, fibril minerals with numerous interconnecting voids that can absorb water as well as other liquids and gases. Additionally, zeolites have an ion-exchange capability since its alkaline cations, such as calcium, are mobile and capable of switching with other cations that pass through the cavities. By varying pressure and heat, synthetic zeolite matrices can be prepared from [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=silica silicon dioxide] and [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=aluminum | + | A group of naturally occurring minerals composed of alkali-hydrated aluminum silicates. Examples are analcite, chabazite, heulandite, [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=natrolite natrolite], phillipsite, scolecite, stilbite, and thomosonite. Zeolites are soft, fibril minerals with numerous interconnecting voids that can absorb water as well as other liquids and gases. Additionally, zeolites have an ion-exchange capability since its alkaline cations, such as calcium, are mobile and capable of switching with other cations that pass through the cavities. By varying pressure and heat, synthetic zeolite matrices can be prepared from [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=silica silicon dioxide] and [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=aluminum%20oxide aluminum oxide] with selected pore sizes and textures ranging from gelatinous to sand-like. Zeolites are used as [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=absorbent absorbents], [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=catalyst catalysts], [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=desiccant desiccants], filters, [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=ion%20exchange%20resin ion exchange resins], and [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=molecular%20sieve molecular sieves]. |
[[File:ps20510stilbite.jpg|thumb|stilbite]] | [[File:ps20510stilbite.jpg|thumb|stilbite]] | ||
== Synonyms and Related Terms == | == Synonyms and Related Terms == | ||
| − | molecular sieve; Kaken gel; Nikka pellets; Arten gel; MicroChamber; chabazite; analcite; heulandite; natrolite; phillipsite; scolecite; stilbite; thomosonite; seolit (Dan.); Zeolith (Deut.); zeolita (Esp.); | + | molecular sieve; Kaken gel; Nikka pellets; Arten gel; MicroChamber; chabazite; analcite; heulandite; natrolite; phillipsite; scolecite; stilbite; thomosonite; seolit (Dan.); Zeolith (Deut.); zeolita (Esp.); zéolithe (Fr.); zeoliet (Ned.); zeólito (Port.) |
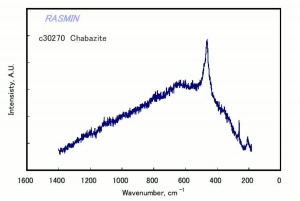
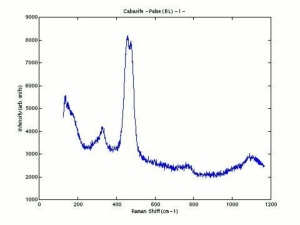
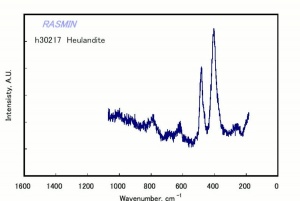
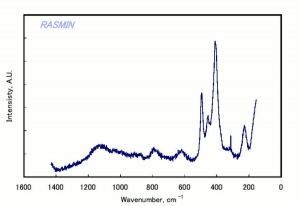
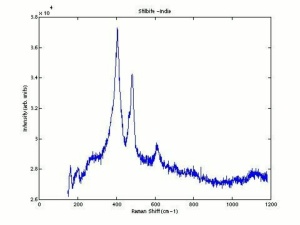
[[[SliderGallery rightalign|chabaziteRS.jpg~Raman|Chabasiteitaly1.jpg~Raman|heulanditeRS.jpg~Raman|stilbiteRS.jpg~Raman|Stilbiteitaly1.jpg~Raman]]] | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|chabaziteRS.jpg~Raman|Chabasiteitaly1.jpg~Raman|heulanditeRS.jpg~Raman|stilbiteRS.jpg~Raman|Stilbiteitaly1.jpg~Raman]]] | ||
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
== Additional Information == | == Additional Information == | ||
| − | A. Dyer, "An Introduction to Zeolite Molecular Sieves', J. Wiley & Sons, London, 1988. S. Rempel "Zeolite Molecular Traps and their use in Preventive Conservation ", WAAC Newsletter, Vol.18 No. 1 1996 | + | ° A. Dyer, "An Introduction to Zeolite Molecular Sieves', J. Wiley & Sons, London, 1988.° S. Rempel "Zeolite Molecular Traps and their use in Preventive Conservation ", WAAC Newsletter, Vol.18 No. 1 1996 |
== Additional Images == | == Additional Images == | ||
| Line 43: | Line 43: | ||
== Authority == | == Authority == | ||
| − | * | + | * G.S.Brady, ''Materials Handbook'', McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 328 |
| − | * | + | * Walter C. McCrone, John Gustave Delly, ''The Particle Atlas'', W. McCrone Associates, Chicago, IV, 1972 |
| − | * ''Encyclopedia Britannica'', http://www.britannica.com Comment: "Zeolite." | + | * ''Encyclopedia Britannica'', http://www.britannica.com Comment: "Zeolite." Encyclopædia Britannica. 2004. Encyclopædia Britannica Premium Service. 19 May 2004 . |
| − | * | + | * C.W.Chesterman, K.E.Lowe, ''Audubon Society Field Guide to North American Rocks and Minerals'', Alfred A. Knopf, New York, 1979 |
* Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia, at http://www.wikipedia.com Comment: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Zeolite (Accessed Sept. 20, 2005) | * Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia, at http://www.wikipedia.com Comment: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Zeolite (Accessed Sept. 20, 2005) | ||
Revision as of 06:42, 24 July 2013
Description
A group of naturally occurring minerals composed of alkali-hydrated aluminum silicates. Examples are analcite, chabazite, heulandite, natrolite, phillipsite, scolecite, stilbite, and thomosonite. Zeolites are soft, fibril minerals with numerous interconnecting voids that can absorb water as well as other liquids and gases. Additionally, zeolites have an ion-exchange capability since its alkaline cations, such as calcium, are mobile and capable of switching with other cations that pass through the cavities. By varying pressure and heat, synthetic zeolite matrices can be prepared from silicon dioxide and aluminum oxide with selected pore sizes and textures ranging from gelatinous to sand-like. Zeolites are used as absorbents, catalysts, desiccants, filters, ion exchange resins, and molecular sieves.
Synonyms and Related Terms
molecular sieve; Kaken gel; Nikka pellets; Arten gel; MicroChamber; chabazite; analcite; heulandite; natrolite; phillipsite; scolecite; stilbite; thomosonite; seolit (Dan.); Zeolith (Deut.); zeolita (Esp.); zéolithe (Fr.); zeoliet (Ned.); zeólito (Port.)
Other Properties
Hexagonal crystal system forming cube-like rhombohedrons. Luster = vitreous. Fracture = uneven. Streak = white.
| Composition | Na2O.Al2O3.xSiO2.xH2O |
|---|---|
| Mohs Hardness | 4.0 -5.0 |
| Density | 2.0-2.1 |
| Refractive Index | 1.470-1.494 |
Additional Information
° A. Dyer, "An Introduction to Zeolite Molecular Sieves', J. Wiley & Sons, London, 1988.° S. Rempel "Zeolite Molecular Traps and their use in Preventive Conservation ", WAAC Newsletter, Vol.18 No. 1 1996
Additional Images
Authority
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 328
- Walter C. McCrone, John Gustave Delly, The Particle Atlas, W. McCrone Associates, Chicago, IV, 1972
- Encyclopedia Britannica, http://www.britannica.com Comment: "Zeolite." Encyclopædia Britannica. 2004. Encyclopædia Britannica Premium Service. 19 May 2004 .
- C.W.Chesterman, K.E.Lowe, Audubon Society Field Guide to North American Rocks and Minerals, Alfred A. Knopf, New York, 1979
- Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia, at http://www.wikipedia.com Comment: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Zeolite (Accessed Sept. 20, 2005)