Difference between revisions of "Aluminum sulfate"
(username removed) |
|||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
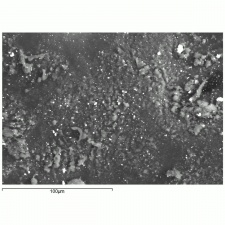
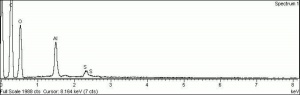
| − | A white crystalline compound that has historically been called papermakers' alum. Aluminum sulfate occurs in nature as the mineral alunogenite. It is prepared synthetically by treating [ | + | A white crystalline compound that has historically been called papermakers' alum. Aluminum sulfate occurs in nature as the mineral alunogenite. It is prepared synthetically by treating [[bauxite|bauxite]] with [[sulfuric%20acid|sulfuric acid]]. Starting in the 1820s, aluminum sulfate began to be used for sizing paper. It reacts with [[rosin|rosin]] causing it to flocculate to the cellulosic fibers in the pulp solution. However, residual alum in the paper produces an acidic environment that will accelerated degradation of paper. Aluminum sulfate has also been used to taw leather, as a dye mordant, as a substrate for lake pigments, for waterproofing concrete, and for fireproofing textiles. It is also used as a flocculant in water purification systems. |
== Synonyms and Related Terms == | == Synonyms and Related Terms == | ||
Revision as of 11:45, 7 January 2014
Description
A white crystalline compound that has historically been called papermakers' alum. Aluminum sulfate occurs in nature as the mineral alunogenite. It is prepared synthetically by treating Bauxite with Sulfuric acid. Starting in the 1820s, aluminum sulfate began to be used for sizing paper. It reacts with Rosin causing it to flocculate to the cellulosic fibers in the pulp solution. However, residual alum in the paper produces an acidic environment that will accelerated degradation of paper. Aluminum sulfate has also been used to taw leather, as a dye mordant, as a substrate for lake pigments, for waterproofing concrete, and for fireproofing textiles. It is also used as a flocculant in water purification systems.
Synonyms and Related Terms
aluminium sulfate (IUPAC): aluminium sulphate (Br.); Aluminiumsulfat (Deut.); sulfate d'aluminium (Fr.); aluminum trisulfate; alum; pearl alum; pickle alum; cake alum; filter alum; papermakers alum; patent alum
Other Properties
Soluble in water. Insoluble in ethanol.
| Composition | Al2(SO4)3. 16H20 |
|---|---|
| CAS | 10043-01-3 (anh.) 16828-11-8 (hyd.) |
| Melting Point | 770 (dec.) |
| Density | 2.71 (hydrate) |
| Molecular Weight | mol. wt. = 630.40 |
Hazards and Safety
Noncombustible.
International Chemical Safety Card
Authority
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 33
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- Matt Roberts, Don Etherington, Bookbinding and the Conservation of Books: a Dictionary of Descriptive Terminology, U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington DC, 1982
- E.J.LaBarre, Dictionary and Encyclopedia of Paper and Paper-making, Swets & Zeitlinger, Amsterdam, 1969
- The Merck Index, Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: entry 381
- Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia, at http://www.wikipedia.com Comment: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Aluminum_sulfate (Accessed Mar. 15, 2006)
- Random House, Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language, Grammercy Book, New York, 1997
- The American Heritage Dictionary or Encarta, via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998
- Rosalie Rosso King, Textile Identification, Conservation, and Preservation, Noyes Publications, Park Ridge, NJ, 1985
- Boise Cascade Paper Group, The Paper Handbook, Boise Cascade, Portland OR, 1989
- Susan E. Schur, Conservation Terminology: A review of Past & Current Nomenclature of Materials, Technology and Conservation, Spring (p.34-39); Summer (p.35-38); Fall (p.25-36), 1985
- Hermann Kuhn, Conservation and Restoration of Works of Art and Antiquities, Butterworths, London, 1986