Difference between revisions of "Paper pulp"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
JMcGlinchey (talk | contribs) |
JMcGlinchey (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
==Additional Images== | ==Additional Images== | ||
| + | <gallery> | ||
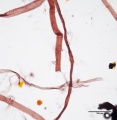
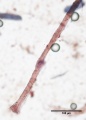
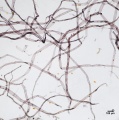
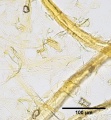
Cotton rag 40x endslabel.jpg|Cotton rag paper pulp stained with Graff "C" stain | Cotton rag 40x endslabel.jpg|Cotton rag paper pulp stained with Graff "C" stain | ||
Hemp 40x2.jpg|Hemp paper pulp stained with Graff "C" stain | Hemp 40x2.jpg|Hemp paper pulp stained with Graff "C" stain | ||
| Line 17: | Line 18: | ||
File:Rice 40x.jpg|Rice paper pulp stained with Graff "C" stain | File:Rice 40x.jpg|Rice paper pulp stained with Graff "C" stain | ||
File:Rice 40x smallvessels.jpg|Rice paper pulp stained with Graff "C" stain | File:Rice 40x smallvessels.jpg|Rice paper pulp stained with Graff "C" stain | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | |||
== Authority == | == Authority == | ||
Revision as of 12:13, 17 July 2015
Description
A dispersion of Cellulose fibers in water. Paper manufactured in the west before the 1850s was made primarily from Cotton and Bast fiber (usually Linen textile made from Flax). Most raw materials for paper production in the western world came from rags or other textile waste. Due to shortages of these materials, experiments with other raw materials for paper pulp were common, but not as successful. In 1854, a process was patented for the production of paper pulp from Wood. Wood pulp can be created from wood mechanically (see Mechanical wood pulp) or chemically (see Chemical wood pulp).
Additional Images
Authority
- The Dictionary of Paper, American Paper Institute, New York, Fourth Edition, 1980
- E.J.LaBarre, Dictionary and Encyclopedia of Paper and Paper-making, Swets & Zeitlinger, Amsterdam, 1969
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 578