Difference between revisions of "Graff "C" stain"
JMcGlinchey (talk | contribs) |
m (Text replace - "== Authority ==" to "== Sources Checked for Data in Record ==") |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
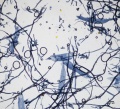
Euc vessel 40x.jpg|Eucalyptus paper pulp stained with Graff "C" Stain | Euc vessel 40x.jpg|Eucalyptus paper pulp stained with Graff "C" Stain | ||
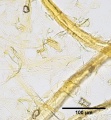
Flax 40x nodes bastshive.jpg|Flax paper pulp stained with Graff "C" Stain | Flax 40x nodes bastshive.jpg|Flax paper pulp stained with Graff "C" Stain | ||
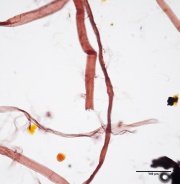
| − | Cotton | + | Cotton linter 40x taperlabel.jpg|Cotton paper pulp stained with Graff "C" Stain |
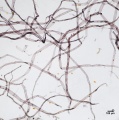
| + | Esparto 40x se commas.jpg|Esparto paper pulp stained with Graff "C" Stain | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
| − | == | + | == Sources Checked for Data in Record == |
* J. H. Graff "Color Atlas for Fiber Identification" The Institute of Paper Chemistry, Appleton, WI, 1940. | * J. H. Graff "Color Atlas for Fiber Identification" The Institute of Paper Chemistry, Appleton, WI, 1940. | ||
Latest revision as of 21:14, 30 April 2016
Description
A chemical stain used for general analysis of paper fibers using optical microscopy. The stain can help distinguish common pulping methods and fibers due to the range of colors presented. Stain color can range from vivid yellow with high Lignin pulps such as Mechanical wood pulp, to red with high Alpha cellulose pulps such as Cotton. "C" stain is a solution prepared from aluminum chloride, Calcium chloride, Zinc chloride, and Potassium iodide. "C" stain can be used as a spot test for the presence of lignin.
Synonyms and Related Terms
"C" Stain
Other Properties
When used for fiber analysis, "C" stain will create a vivid yellow color when used on pulps that are high in lignin. With decreasing amounts of lignin (increased cooking of pulp), the degree of yellow will decrease to greenish yellow or brown/yellow. Bleaching will result in a reddish tint that becomes more pronounced with increased bleaching. Pulps that are high in alpha cellulose and free from lignin will stain bright red. The red tones can be difficult to see in hardwood pulps. Some specific fibers can produce additional colors. "C" stain will permanently discolor fibers, but diagnostic colors are temporary and will darken with oxidation.
Additional Images
Sources Checked for Data in Record
- J. H. Graff "Color Atlas for Fiber Identification" The Institute of Paper Chemistry, Appleton, WI, 1940.
- Walter Rantanen. 'Fiber ID Course.' Integrated Paper Services. June 2013. Lecture.
- TAPPI Official Standard T401 om-08. Fiber analysis of paper and paperboard. 2008. http://www.tappi.org/Downloads/Test-Methods/UNTITLED-0104T401pdf.aspx